Toward one drug to treat all coronaviruses
2021-07-21
(Press-News.org) Safe and effective vaccines offer hope for an end to the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the possible emergence of vaccine-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants, as well as novel coronaviruses, make finding treatments that work against all coronaviruses as important as ever. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Journal of Proteome Research have analyzed viral proteins across 27 coronavirus species and thousands of samples from COVID-19 patients, identifying highly conserved sequences that could make the best drug targets.
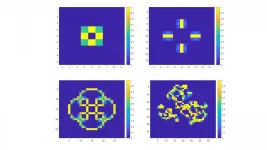
Drugs often bind inside "pockets" on proteins that hold the drug snugly, causing it to interfere with the protein's function. Scientists can identify potential drug-binding pockets from the 3D structures of viral proteins. Over time, however, viruses can mutate their protein pockets so that drugs no longer fit. But some drug-binding pockets are so essential to the protein's function that they can't be mutated, and these sequences are generally conserved over time in the same and related viruses. Matthieu Schapira and colleagues wanted to find the most highly conserved drug-binding pockets in viral proteins from COVID-19 patient samples and from other coronaviruses, revealing the most promising targets for pan-coronavirus drugs.
The team used a computer algorithm to identify drug-binding pockets in the 3D structures of 15 SARS-CoV-2 proteins. The researchers then found corresponding proteins in 27 coronavirus species and compared their sequences in the drug-binding pockets. The two most conserved druggable sites were a pocket overlapping the RNA binding site of the helicase nsp13, and a binding pocket containing the catalytic site of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase nsp12. Both of these proteins are involved in viral RNA replication and transcription. The drug-binding pocket on nsp13 was also the most highly conserved across thousands of SARS-CoV-2 samples taken from COVID-19 patients, with not a single mutation. The researchers say that novel antiviral drugs targeting the catalytic site of nsp12 are currently in phase II and III clinical trials for COVID-19, and that the RNA binding site of nsp13 is a previously underexplored target that should be a high priority for drug development.
INFORMATION:
The authors acknowledge funding from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the European Molecular Biology Laboratory and the Structural Genomics Consortium.
The abstract that accompanies this paper is available here.
For more of the latest research news, register for our upcoming meeting, ACS Fall 2021. Journalists and public information officers are encouraged to apply for complimentary press registration by emailing us at newsroom@acs.org.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS' mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world's scientific knowledge. ACS' main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-21
WASHINGTON, July 21, 2021 -- As the Summer Olympics draw near, the world will shift its focus to photo finishes and races determined by mere fractions of a second. Obtaining such split-second measurements relies on faultlessly rounding a raw time recorded by a stopwatch or electronic timing system to a submitted time.
Researchers at the University of Surrey found certain stopwatches commit rounding errors when converting raw times to final submitted times. In American Journal of Physics, by AIP Publishing, David Faux and Janet Godolphin outline a series of computer simulations based on procedures for converting raw race times for display.
Faux was inspired when he encountered ...
2021-07-21
ITHACA, N.Y. - Cornell researchers have developed nanostructures that enable record-breaking conversion of laser pulses into high-harmonic generation, paving the way for new scientific tools for high-resolution imaging and studying physical processes that occur at the scale of an attosecond - one quintillionth of a second.
High-harmonic generation has long been used to merge photons from a pulsing laser into one, ultrashort photon with much higher energy, producing extreme ultraviolet light and X-rays used for a variety of scientific purposes. Traditionally, gases have been used as sources of harmonics, but a research team led by Gennady Shvets, professor of applied and engineering physics ...
2021-07-21
Researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian in New York have discovered that injecting mice with pulmonary endothelial cells--the cells that line the walls of blood vessels in the lung--can reverse the symptoms of emphysema. The study, which will be published July 21 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM), may lead to new treatments for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), an inflammatory lung disease associated with smoking that is thought to be the third leading cause of death worldwide.
Emphysema is one of the characteristic features ...
2021-07-21
Wearable devices can detect people's stress, according to new Washington State University research, opening potential new interventions for people with addictions.
In a paper published today, July 21, in the END ...
2021-07-21
A landmark scientific study involving marine biologists from Greece, Turkey, Cyprus, Libya, Italy, Tunisia, the UK, the US and even Malta, documenting instances where native Mediterranean species have preyed upon two highly invasive marine fish - the Pacific red lionfish and the silver-cheeked toadfish - has just been published. Prof. Alan Deidun, coordinator of the Spot the Alien Fish citizen science campaign and resident academic within the Department of Geosciences of the Faculty of Science, is a co-author of such an extensive study.
The Pacific red lionfish (Pterois miles) and the silver-cheeked toadfish (Lagocephalus sceleratus) are amongst the most invasive of non-indigenous fish species to enter the Mediterranean in recent years, posing both ecological and socio-economic hazards. ...
2021-07-21
SARS-CoV-2 still poses major challenges to mankind. The frequent emergence of mutant forms makes the threat posed by the virus difficult to predict. The SARS-CoV-2 variant B.1.617 circulated in India and gave rise to the Delta variant, B.1.617.2, which is now becoming dominant in many countries. Infection researchers from the German Primate Center (DPZ) - Leibniz Institute for Primate Research in Göttingen have investigated the B.1.617 variant in detail. In cell culture studies, they found that this variant can infect certain lung and intestinal cell lines more efficiently than the original ...
2021-07-21
A high proportion of staff working in intensive care units during the COVID-19 pandemic have experienced mental health conditions, according to a new study.
In a study of 515 healthcare staff working in intensive care units (ICUs) across seven countries, the researchers found that on average 48 percent of participants showed signs of mental health conditions - depression, insomnia and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Their mental health was assessed using a detailed questionnaire and a clinical scoring system.
The team also found a 40 per cent increase in the conditions for those who spent more than six hours in personal protective equipment (PPE) over ...
2021-07-21
At low temperatures, certain materials lose their electrical resistance and conduct electricity without any loss - this phenomenon of superconductivity has been known since 1911, but it is still not fully understood. And that is a pity, because finding a material that would still have superconducting properties even at high temperatures would probably trigger a technological revolution.
A discovery made at TU Wien (Vienna) could be an important step in this direction: A team of solid-state physicists studied an unusual material - a so-called "strange metal" made of ytterbium, rhodium and silicon. Strange metals show an unusual relationship between electrical resistance and temperature. ...
2021-07-21
A protein involved in making cells move offers a clue to how certain types of cancer metastasize and develop into secondary tumours, according to new research from the University of Warwick.
Scientists from Warwick Medical School have demonstrated for the first time that levels of this protein can increase and decrease the movement of a cell, including cancer cells - suggesting that they could play a role in the spread of tumours.
The study is published today (21 July) in the Journal of Cell Biology and was funded by the Medical Research Council, part of UK Research and Innovation.
The researchers are investigating a tiny cell component called an Intracellular nanovesicle (INV) which acts like a courier within a cell by transporting cargo to where it ...
2021-07-21
Classical molecular sieve membranes, with 3D microparticles and 2D nanosheets as primary building blocks, are promising in chemical separation.
Separation within such membranes relies on molecular movement and transport though their intrinsic or artificial nanopores. Since the weak connections by nature between the neighboring "bricks" usually result in intercrystalline gaps in membranes, the prevailing selectivity for classical molecular sieve membranes is moderate.
Recently, a research group led by Prof. YANG Weishen and Dr. BAN Yujie from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) proposed ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Toward one drug to treat all coronaviruses