New in the Hastings Center Report, July-August 2021
Should ethicists be activists? Four calls to action, and more
2021-07-21
(Press-News.org) Activism and the Clinical Ethicist
Christopher Meyers
Although clinical ethics scholarship and practice have largely avoided assuming an activist stance, the many health care crises of the last 18 months motivated a distinct change: activist language has permeated conversations over such issues as the impact of triage policies on persons with disabilities and of color, and how the health care system has historically failed African Americans. "This activism is, to my mind, an overdue and welcome turn, and my goal here is to defend it--generally and with particular emphasis on institutional activism," writes Meyers, a professor emeritus of philosophy and a director emeritus of the Kegley Institute of Ethics at California State University, Bakersfield.
Other Voices:
Activism and Bioethics: Taking a Stand on Things That Matter
Wendy A. Rogers and Jackie Leach Scully take a broader view than Meyers, looking beyond activism within individual institutions and arguing that some issues are so morally egregious that bioethicists have a duty to take a stand against them, even if the prospects of success are dim.
Antiracism Activism in Clinical Ethics: What's Stopping Us?
Holly Vo and Georgina D. Campelia write that clinical ethicists should recognize barriers imbedded in the field of clinical ethics itself and support antiracism work by altering their institutional structures to be more inclusive.
Why Clinical Ethicists Are Not Activists
Carl Elliott notes that activism is rare among clinical ethicists because they have little formal power and few job protections. "Asking the clinical ethicist to fix the problems of an academic health center is like asking the butler to fix the problems of the British monarchy. He is not there to rule, but to serve."
INFORMATION:
Table of contents of the July-August 2021 Hastings Center Report: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/toc/1552146x/2021/51/4
For more information, contact
Susan Gilbert
Director of Communications
The Hastings Center
845-424-4040 x244
gilberts@thehastingscenter.org
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-21
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. -- Researchers at Sandia National Laboratories have designed a new class of molten sodium batteries for grid-scale energy storage. The new battery design was shared in a paper published today in the scientific journal Cell Reports Physical Science.
Molten sodium batteries have been used for many years to store energy from renewable sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines. However, commercially available molten sodium batteries, called sodium-sulfur batteries, typically operate at 520-660 degrees Fahrenheit. Sandia's new molten sodium-iodide battery operates at a much cooler 230 degrees Fahrenheit instead.
"We've been working to bring the operating temperature of molten sodium batteries down as low as physically possible," ...
2021-07-21
Scientists have developed a new way to model and map the health of coral reef ecosystems using data collected on the Khaled bin Sultan Living Oceans Foundation's Global Reef Expedition. This innovative method, presented today at the International Coral Reef Symposium (ICRS), can determine which natural and anthropogenic factors are most likely to lead to persistently vibrant coral and fish communities. Their findings can help scientists identify the reefs most likely to survive in a changing world.
The new models are a first step in being able to produce maps of global coral reef resilience.
To create these models, scientist Anna Bakker needed a lot of data on coral reefs from ...
2021-07-21
Drugs must be safe not just for the patients; in the case of pregnant patients, drugs must also be safe for the unborn children still in the womb. Therefore, at an early stage in the development of new medicines, candidate substances are tested in the Petri dish on embryonic stem cells from mouse cell lines. This is to avoid that an embryo-damaging effect would only be noticed at a later stage during tests with pregnant mice.
However, these cell culture tests are a highly simplified version of what takes place in the uterus. Researchers just add the test material to a culture of embryonic stem cells in a Petri dish, and can identify substances that have a direct adverse effect on embryonic cells. By contrast, in the body of a pregnant woman, active pharmaceutical ...
2021-07-21
New Rochelle, NY, July 21, 2021-- Evaluating the efficacy of novel therapies requires the ability to monitor wound progression accurately and reproducibly over time. Researchers have proposed a new scoring system for wound healing in mice based on parameters in each phase of healing, as described in an article in the peer-reviewed journal Stem Cells and Development. Click here to read the article for free through August 21, 2021.
The parameters include re-epithelization, epithelial thickness index, keratinization, granulation tissue thickness, remodeling, and the scar elevation index. The parameters can be assessed using either Hematoxylin & Eosin or ...
2021-07-21
By José Tadeu Arantes | Agência FAPESP – Gluten is a protein complex found in cereals such as wheat, rye and barley. It is responsible for the elastic texture of dough so that loaves and rolls can be baked into different shapes while remaining flexible and crusty. It also lengthens the shelf life of bread at room temperature, when associated with preservatives.
Gluten intolerance, however, has become a global epidemic, and gluten-free products are increasingly popular. The problem is that most of those available on the market are far from corresponding to consumers’ expectations in terms of appearance, aroma, flavor and durability. A research line focusing on ways to enhance gluten-free products is being pursued ...
2021-07-21
No one wants bad breath -- not when visiting friends and family, at a job interview, and especially not on a first date. Smelly breath can make things awkward, but it also is a natural warning sign, indicating that serious dental issues are occurring. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Nano have constructed a portable, thumb-sized device that diagnoses bad breath by quickly "sniffing" exhalations for the gas that makes it stinky -- hydrogen sulfide.
Because most people can't smell their own breath, they need to ask someone else, which can be embarrassing and awkward. Some devices measure small amounts of stinky hydrogen sulfide, but they require exhaled air to be collected and tested on expensive instruments in a lab, which is not feasible ...
2021-07-21
Safe and effective vaccines offer hope for an end to the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the possible emergence of vaccine-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants, as well as novel coronaviruses, make finding treatments that work against all coronaviruses as important as ever. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Journal of Proteome Research have analyzed viral proteins across 27 coronavirus species and thousands of samples from COVID-19 patients, identifying highly conserved sequences that could make the best drug targets.
Drugs often bind inside "pockets" on proteins that hold the drug snugly, causing it to interfere with the protein's function. Scientists can identify potential drug-binding pockets from the 3D structures of viral proteins. ...
2021-07-21
WASHINGTON, July 21, 2021 -- As the Summer Olympics draw near, the world will shift its focus to photo finishes and races determined by mere fractions of a second. Obtaining such split-second measurements relies on faultlessly rounding a raw time recorded by a stopwatch or electronic timing system to a submitted time.
Researchers at the University of Surrey found certain stopwatches commit rounding errors when converting raw times to final submitted times. In American Journal of Physics, by AIP Publishing, David Faux and Janet Godolphin outline a series of computer simulations based on procedures for converting raw race times for display.
Faux was inspired when he encountered ...
2021-07-21
ITHACA, N.Y. - Cornell researchers have developed nanostructures that enable record-breaking conversion of laser pulses into high-harmonic generation, paving the way for new scientific tools for high-resolution imaging and studying physical processes that occur at the scale of an attosecond - one quintillionth of a second.
High-harmonic generation has long been used to merge photons from a pulsing laser into one, ultrashort photon with much higher energy, producing extreme ultraviolet light and X-rays used for a variety of scientific purposes. Traditionally, gases have been used as sources of harmonics, but a research team led by Gennady Shvets, professor of applied and engineering physics ...
2021-07-21
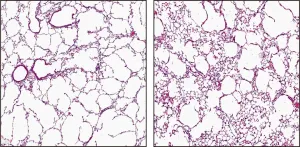
Researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian in New York have discovered that injecting mice with pulmonary endothelial cells--the cells that line the walls of blood vessels in the lung--can reverse the symptoms of emphysema. The study, which will be published July 21 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM), may lead to new treatments for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), an inflammatory lung disease associated with smoking that is thought to be the third leading cause of death worldwide.
Emphysema is one of the characteristic features ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New in the Hastings Center Report, July-August 2021
Should ethicists be activists? Four calls to action, and more