(Press-News.org) URBANA, Ill. - When kids sit down to eat lunch at school, fruits and vegetables may not be their first choice. But with more time at the lunch table, they are more likely to pick up those healthy foods. If we want to improve children's nutrition and health, ensuring longer school lunch breaks can help achieve those goals, according to research from the University of Illinois.
"Ten minutes of seated lunch time or less is quite common. Scheduled lunch time may be longer, but students have to wait in line to get their food. And sometimes lunch periods are shared with recess. This means the amount of time children actually have to eat their meals is much less than the scheduled time," says Melissa Pflugh Prescott, assistant professor in the Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition at U of I.
Prescott and study co-authors Xanna Burg, Jessica Metcalfe, and Brenna Ellison compared fruit and vegetable consumption during 10 and 20 minutes of seated lunch time, and the results were clear.
"During shorter lunch periods, children ate significantly less of the fruit and vegetable parts of their meal, while there was no significant difference in the amount of beverages or entrees they consumed. It makes sense that you might eat the part of the meal you look forward to first, and if there's enough time left you might go towards the other parts. But if there's not enough time those items suffer, and they tend to be fruits and vegetables," Prescott explains.
This particularly impacts children from low-income families who participate in the National School Lunch Program and who may not have resources to bring their own lunch from home to avoid lunch line wait times, she adds.
Prescott and her colleagues conducted the study with elementary- and middle school-aged children enrolled in a summer camp on the University of Illinois campus. The researchers set up the lunch area as a school cafeteria where students would go through the lunch line and select their food. They prepared the meals according to National School Lunch Program guidelines.
"We tried to make this as comparable to everyday school as possible. We worked with the local school district and used the same food distributors as they did, and we selected the menu items based on the local public school menu," Prescott explains.
Each day was randomly assigned to be either a short or a long lunch day. Each short lunch day was paired with a long lunch day featuring an identical menu. The researchers wanted to rule out that food types served would create any differences in what the children ate.
Research assistants took a picture of each tray as the children exited the lunch line. They monitored the time from the children sat down until they were done eating, and observed behavior throughout the meal, including any food sharing, interaction with peers, and phone use.
After the lunch period was over, the children placed their tray with any leftovers on a rack and filled out a two-question survey about the taste and appearance of their meal. The researchers measured all servings before and after the meal to obtain an estimate of how much each child ate.
While fruits were consumed at an overall higher rate than vegetables, consumption of both food types was significantly higher for longer seated lunch times, Prescott says.
She notes the study has implications for the effectiveness of the Healthy Hunger-Free Kids Act, which the U.S. government implemented in 2010 to improve nutrition standards for school meals.
"In my opinion, one of the best things about the new nutrition standards is that they require a variety of vegetables be served each week, to ensure children from all income and resource levels get exposed to different healthy foods they might not have access to at home. But if we have lunch periods that are too short to allow children the opportunity to get used to those foods, then we're almost setting the policies up to fail," Prescott says.
"A main takeaway from our study is that children need protected time to eat their fruits and vegetables. Our findings support policies that require at least 20 minutes of seated lunch time at school," she states.
School lunch time policies can be decided at the district level, with some room for individual schools to set their own standards; for example, schools can institute a longer lunch time than the district mandates.
Prescott notes that longer lunch times can also have beneficial effects for children beyond healthy eating.
"The amount of seated time children have is also a really valuable time for them to connect with their peers; they might have limited opportunities to do so throughout the school day. We found significantly fewer social interactions during the 10-minute lunch times. That indicates other positive outcomes may come from longer lunch breaks as well," she concludes.
INFORMATION:
The Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition is in the College of Agricultural, Consumer and Environmental Sciences, University of Illinois.
The paper, "Effects of Longer Seated Lunch Time on Food Consumption and Waste in Elementary and Middle School-age Children: A Randomized Clinical Trial," is published in JAMA Network Open. [DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.14148]. Authors are Xanna Burg, Jessica Jarick Metcalfe, Brenna Ellison, and Melissa Pflugh Prescott.
COLUMBUS, Ohio - The oral targeted therapy drug ibrutinib is an effective treatment option for high-risk hairy cell leukemia, according to a new study conducted by researchers at The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center - Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute (OSUCCC - James).
Hairy cell leukemia is a rare form of B-cell blood cancer that is diagnosed in 600 to 800 people annually in the United States. Researchers note that while the disease generally has a good prognosis for the majority of people affected, ...
Domesticated rabbits come in all sizes and colors, including tiny Netherland Dwarfs, floppy-eared French lops, Flemish Giants, and fluffy Angoras.
These breeds belong to Europe's only rabbit species, originally limited to the Iberian Peninsula and Southern France and used for meat and fur since the last Ice Age, culminating in domestication about 1,500 years ago.
The Americas, on the other hand, have many rabbit species with ranges throughout both continents. The archaeological record shows rabbits were used as extensively in the Americas as they were on the Iberian Peninsula, with clear archaeological evidence that rabbits were being deliberately raised. Why, then, were rabbits domesticated in Europe and not the Americas?
Recent work ...
A new University of Chicago study has found that the drug masitinib may be effective in treating COVID-19.
The drug, which has undergone several clinical trials for human conditions but has not yet received approval to treat humans, inhibited the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in human cell cultures and in a mouse model, leading to much lower viral loads.
Researchers at UChicago's Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (PME), working with collaborators at Argonne National Laboratory and around the world, also found that the drug could be effective against many types of coronaviruses and picornaviruses. Because of the way it inhibits replication, it ...
Older people appear to have fewer antibodies against the novel coronavirus, a new laboratory study from Oregon Health & Science University suggests.
Antibodies are blood proteins that are made by the immune system to protect against infection. They are known to be key players in protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The study published today in the Journal of the American Medical Association.
"Our older populations are potentially more susceptible to the variants even if they are vaccinated," said senior author Fikadu Tafesse, Ph.D., assistant professor of molecular microbiology and immunology in the OHSU School of Medicine.
Tafesse and colleagues emphasized that even though they measured diminished antibody ...
The average American spends 5 days each year in line by some estimates. Many of these lines are for things like a cup of coffee, movie theater tickets or a ride on the newest roller coaster, but for some the wait is for something far more pressing -- a new kidney.
In South Carolina, the average time spent on a waitlist for a kidney transplant is 42 months, but according to a recent paper in JAMA Surgery, changes to the U.S. kidney allocation system could result in reduced access to kidney transplants and longer times spent in line.
"At face value, the changes in the allocation system seem quite appropriate," said Derek DuBay, M.D., director of ...
Common yeast are able to adapt and thrive in response to a long-term rise in temperature by changing the shape, location and function of some of their proteins. The surprising findings demonstrate the unappreciated plasticity in the molecular and conformational level of proteins and bring the power of molecular biology to the organismal response to climate change. Results from the Zhou lab at the Buck Institute in collaboration with the Si lab from the Stowers Institute are published in Molecular Cell.
Temperature is an unstable parameter in the wild, affecting almost ...
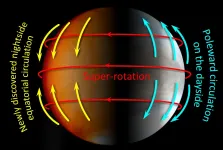
Little is known about the weather at night on Venus as the absence of sunlight makes imaging difficult. Now, researchers have devised a way to use infrared sensors on board the Venus orbiter Akatsuki to reveal the first details of the nighttime weather of our nearest neighbor. Their analytical methods could be used to study other planets including Mars and gas giants as well. Furthermore, the study of Venusian weather granted by their methods could allow researchers to learn more about the mechanisms underpinning Earth's weather systems.
Earth and Venus ...
Researchers at the RIKEN Center for Biosystems Dynamics Research (BDR) have succeeded in creating the first genetically engineered marsupial. This study, published in the scientific journal Current Biology, will contribute to deciphering the genetic background of unique characteristics observed only in marsupials.
Genetically modified animals, particularly mice and rats, are extremely important tools for researching biological processes. For example, researchers often silence genes to find out what their normal functions are. Since marsupials have unique characteristics, studying them requires developing ...
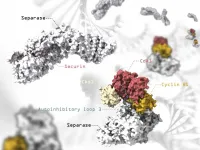
During cell division, chromosomes are duplicated and separated so that one copy of each chromosome is inherited by each of the two emerging daughter cells. Correct distribution of chromosomes requires high accuracy and defects in this process can cause aberrant distribution of chromosomes and facilitate cancer development. By analyzing the structure of the protein responsible for chromosome separation, an international team, led by scientists from the University of Geneva (UNIGE), has shed light on the mechanisms controlling this essential player in cell division. This work is published in the journal ...
MIT physicists have observed signs of a rare type of superconductivity in a material called magic-angle twisted trilayer graphene. In a study appearing in Nature, the researchers report that the material exhibits superconductivity at surprisingly high magnetic fields of up to 10 Tesla, which is three times higher than what the material is predicted to endure if it were a conventional superconductor.
The results strongly imply that magic-angle trilayer graphene, which was initially discovered by the same group, is a very rare type of superconductor, known as a "spin-triplet," that is impervious to high ...