Generation and application of the high-Q resonance in all-dielectric metasurfaces
2021-07-22
(Press-News.org) In a new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2021.200030 , Researchers led by Professor Liu Yan from Xidian University, China and Professor Gan Xuetao from Northwestern Polytechnical University, China consider generation and application of the high-Q resonance in all-dielectric metasurfaces.
Metamaterials are artificial composite electromagnetic structures consisting of subwavelength units, which can realize efficient and flexible control of the electromagnetic waves. Metamaterials are an emerging research area for optoelectronics, physics, chemistry and materials, due to their novel physical properties and potential applications.
With the development in the fabrication of nanostructures, all-dielectric metasurfaces have attracted much research attention because of their high efficiency and low loss. However, metasurfaces based on traditional optical materials (such as silicon) can only support relatively low Q resonances, limiting their applications in lasing action, sensing, and nonlinear optics. A recently emerged concept of bound states in the continuum (BICs) provides a new solution to overcome this problem. The concept of BICs was first introduced in quantum mechanics. It represents a wave phenomenon of modes, which have the energy lying in the delocalized states inside the continuum. The BIC-supporting metasurfaces can achieve controllable high-Q resonance, which can extend their applicability to the devices requiring sharp spectral features.
The authors of this article propose a Si metasurface based on symmetry-broken blocks, which can achieve the high-Q resonance. Nanoparticles made of conventional materials can only support a relatively low quality factor. The concept of BIC provides a new solution to overcome this problem. This concept firstly appears in quantum mechanics, where a true BIC is a mathematical abstraction with infinite Q factor. In this work, symmetry breaking is introduced into the symmetric periodic structure and the ideal BICs turn into the leaky mode with a high Q factor. At the same time, the Q factor of the resonance can be controlled by varying the size of the introduced defects. In addition, by changing the design proposal, the relationship between the Q factor and defect size can also be adjusted. A high-Q resonance can be easily realized in this way and the nonlinear optical effect of the structure can be obviously enhanced at the resonance.
The research reported in this article paves a way to manipulate BICs and realize high-Q dynamic resonances, which constitutes a significant step towards the development of high-Q resonant photonic applications. innovative and advanced optical technologies.
INFORMATION:
Article reference: Fang CZ, Yang QY, Yuan QC, Gan XT, Zhao JL et al. High-Q resonances governed by the quasi-bound states in the continuum in all-dielectric metasurfaces. Opto-Electron Adv 4, 200030 (2021). doi: 10.29026/oea.2021.200030
Keywords: all-dielectric metasurface, bound states in the continuum, optical nonlinearity, topological configuration
Author Biographies
Professor Liu Yan, Xidian University, China, mainly focuses on ferroelectric nanodevices and novel nanophotonic devices. Engaged in the research of semiconductor materials and devices, Professor Yan has made much pioneering research in high mobility channel CMOS and steep subthreshold swing devices and is now, undertaking the Major research plan of the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Key Research and Development Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology. Recent activities over the last five years include the publication of more than 50 papers in mainstream journals and applications for more than 20 patents in related fields.
Professor Hao Yue, Chinese Academy of Sciences, is a senior member of the IEEE and executive director of the Chinese Association of Electronics. Professor Yue leads the expert group for the implementation of the major sci-tech items of "core electronic devices, high-end universal chips, and basic software products" and the microelectronic technology experts group of the General Armament Department of the People's Liberation Army of China. Professor Yue has published more than 150 papers to date during his academic career.
Professor Han Genquan, Xidian University, China is a member of the "Hundred Talent Program" supported by Shaanxi Province, China. Professor Genquan has made many breakthroughs in high mobility channel CMOS and Beyond CMOS devices, including the implementation of high-performance strain germanium-tin, strain germanium, and InGaAs MOSFET devices, germanium-tin tunneling field-effect transistor, and the negative capacitance of the transistor. Professor Genquan has published more than 150 papers, submitted applications for more than 30 patents and has been a frequent invited speaker at international conferences.
Professor Gan Xuetao, Northwestern Polytechnical University, China, is mainly engaged in the research of micro nanophotonics, including two-dimensional layered material optoelectronics and spectroscopy among other areas and is committed to providing new theories and technologies for new optical information processing, optical interconnection on-chip, and optoelectronic devices. Professor Xuetao has previously hosted National Science and Technology Fund "Excellent Youth Projects", "Surface Projects" and "Youth Projects". Professor Xuetao has been a frequent invited speaker at international and domestic academic conferences and has published more than 50 papers in international journals such as Nature Photonics, Light Science & Applications and Opto-Electronic Advances.
Opto-Electronic Advances (OEA) is a high-impact, open access, peer reviewed monthly SCI journal with an impact factor of 9.636 (Journals Citation Reports for IF 2020). Since its launch in March 2018, OEA has been indexed in SCI, EI, Scopus, CA and ICI databases over the time and expanded its Editorial Board to 33 members from 17 countries and regions (average h-index 46).
The journal is published by The Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, aiming at providing a platform for researchers, academicians, professionals, practitioners, and students to impart and share knowledge in the form of high quality empirical and theoretical research papers covering the topics of optics, photonics and optoelectronics.
More information: http://www.oejournal.org/oea
Editorial Board: http://www.oejournal.org/oea/editorialboard/list
All issues available in the online archive (http://www.oejournal.org/oea/archive).
Submissions to OEA may be made using ScholarOne (https://mc03.manuscriptcentral.com/oea).
ISSN: 2096-4579
CN: 51-1781/TN
Contact Us: oea@ioe.ac.cn
Twitter: @OptoElectronAdv (https://twitter.com/OptoElectronAdv?lang=en)
WeChat: OE_Journal
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-22
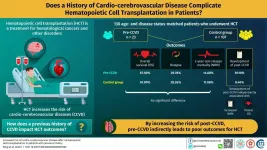
Hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) is a recognized treatment option for certain blood and bone marrow cancers as well as some autoimmune and hereditary disorders. Performed to replace or modulate the body's malfunctioning hematopoietic system (which produces blood cells) or a compromised immune system following a medical condition or treatment, HCT can be autologous or allogenic. In autologous HCT, a patient's own stem cells are injected into the bloodstream, while in allogenic HCT donor stem cells are used.
Although a difficult procedure, over the years, the safety of HCT has been improved ...
2021-07-22
Irvine, Calif., July 21, 2021 -- It's not exactly X-ray vision, but it's close. In research published in the journal Optica, University of California, Irvine researchers describe a new type of camera technology that, when aimed at an object, can rapidly retrieve 3D images, displaying its chemical content down to the micrometer scale. The new tech promises to help companies inspect things like the insides of computer chips without having to pry them open -- an advancement the researchers say could accelerate the production time of such goods by more than a hundred times.
"This is a paper about a way to visualize things in 3D very fast, even at video rate," said Dmitry Fishman - director of laser spectroscopy labs in the UCI Department of ...
2021-07-22
New University of Otago research has been examining how alpine-based hedgehogs hibernate from a different perspective - their backs.
Dr Nick Foster from the Department of Zoology has been involved with the Te Manahuna Aoraki project and has been attaching small transmitting 'backpacks' onto hedgehogs in the Mackenzie Basin's alpine zones. The mammals are considered pests in New Zealand for the damage they cause to native insects and wildlife throughout the country.
The goal of this study, which has just been published in the New Zealand Journal of Ecology, was to find out whether hedgehogs, which can be found up to 2000 metres in summer, travel ...
2021-07-22
FINDINGS
Scientists from the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center have identified a key protein, transcription factor TAF12, that plays a critical role in the formation of a preinitiation complex, which consists of over one hundred proteins that are necessary for the transcription of protein-coding genes. The team found by eliminating TAF12, the entire preinitiation complex is destroyed and the genome-wide transcription is downregulated drastically.
The findings could help pave the way for cancer therapies that target TAF12, potentially stopping transcription in cancer cells and helping decrease the growth of cancerous tumors. TAF12 had previously been shown by ...
2021-07-22
The future of Samoa's electricity system could go green, a University of Otago study has shown.
Pacific Island nations are particularly susceptible to climate change and face high costs and energy security issues from imported fossil fuels.
For these reasons many Pacific Island nations have developed ambitious 100 per cent renewable energy targets. However, they have not been subject to rigorous peer-reviewed studies to help develop these targets and pathways for achieving them in the same way as more developed countries.
To meet this need, Otago Energy Science and Technology Masters student Tupuivao Vaiaso mapped future scenarios for Samoa's electricity system by carefully balancing renewable supply and electricity demand.
The study, published in Renewable ...
2021-07-22
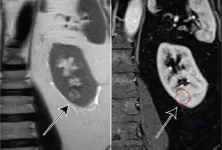
Leesburg, VA, July 22, 2021--According to ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), the standardized non-invasive clear cell likelihood score (ccLS)--derived from MRI--correlates with the growth rate of small renal masses (cT1a, END ...
2021-07-22
Scientists have completed the largest and most diverse genetic study of type 1 diabetes ever undertaken, identifying new drug targets to treat a condition that affects 1.3 million American adults.
Several potential drugs are already in the pipeline. Drugs targeting 12 genes identified in the diabetes study have been tested or are being tested in clinical trials for autoimmune diseases. That could accelerate the drugs' repurposing for treating or preventing type 1 diabetes, the researchers say.
"This work represents the largest, most ancesty-diverse study of type 1 diabetes ...
2021-07-22
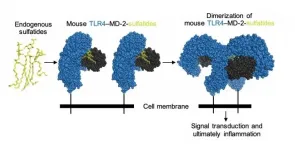
DALLAS - July 20, 2021 - UT Southwestern researchers report the first structural confirmation that endogenous - or self-made - molecules can set off innate immunity in mammals via a pair of immune cell proteins called the TLR4?MD-2 receptor complex. The work has wide-ranging implications for finding ways to treat and possibly prevent autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis and antiphospholipid syndrome.
The TLR4?MD-2 receptor complex is well known for its role in the body's response to infection by gram-negative bacteria. Its role in autoimmunity had been long suspected, although direct proof was lacking. The team, led by Nobel Laureate Bruce Beutler, M.D., director of the Center for the Genetics of Host Defense (CGHD), identified lipids called sulfatides ...
2021-07-22
In one out of every six local authorities, rates of hunger are more than 150 per cent (one and a half times) the national average. Shockingly, in one in 10 local authorities, the rate is almost double, according to new research by the University of Sheffield.
Researchers at the University of Sheffield Institute for Sustainable Food modelled data from the Food Foundation, who surveyed people across the UK, and for the first time were able to identify food insecurity at a local authority scale. Local authority percentages show the marked variation in levels of food insecurity between local areas and, whereas national ...
2021-07-22
Persistence may be the key when quitting smoking using an electronic nicotine delivery system (ENDS), commonly known as vaping, a University of Otago study found.
Researchers found people attempting to switch from cigarettes to ENDS reported highly varied smoking and ENDS use. They recommend people persist in their attempts to transition away from smoking, even if their progress feels slow and uncertain.
Lead author Associate Professor Tamlin Conner, of the Department of Psychology, says, although people may plan to use ENDS exclusively instead of cigarettes, making the switch is not always straightforward.
"We found that dual use of ENDS and cigarettes was very common, suggesting that people ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Generation and application of the high-Q resonance in all-dielectric metasurfaces