(Press-News.org) St. Jude Children's Research Hospital investigators have demonstrated that comprehensive genomic sequencing of all pediatric cancer patients is feasible and essential to capitalize on the lifesaving potential of precision medicine. Results from the St. Jude Genomes for Kids study appear online today in the journal Cancer Discovery.
Whole genome and whole exome sequencing of germline DNA was offered to all 309 patients who enrolled in the study. Whole genome, whole exome and RNA sequencing of tumor DNA was carried out for the 253 patients for whom adequate tumor samples were available.
Overall, 86% of patients had at least one clinically significant variation in tumor or germline DNA. Those included variants related to diagnosis, prognosis, therapy or cancer predisposition. Researchers estimated that 1 in 5 patients had clinically relevant mutations that would have gone undetected using standard sequencing methods.
"Some of the most clinically relevant findings were only possible because the study combined whole genome sequencing with whole exome and RNA sequencing," said Jinghui Zhang, Ph.D., St. Jude Department of Computational Biology chair and co-corresponding author of the study.
Every tumor is unique. Every patient is unique.
Comprehensive clinical sequencing that includes whole genome, whole exome and RNA sequencing is not widely available. But as the technology becomes less expensive and accessible to more patients, researchers said comprehensive sequencing will become an important addition to pediatric cancer care.
"We want to change the thinking in the field," said David Wheeler, Ph.D., St. Jude Precision Genomics team director and a co-author of the study. "We showed the potential to use genomic data at the patient level. Even in common pediatric cancers, every tumor is unique, every patient is unique.
"This study showed the feasibility of identifying tumor vulnerabilities and learning to exploit them to improve patient care," he said.
Tumor sequencing guided the change in treatment for 12 of the 78 study patients for whom standard of care was unsuccessful. In four of the 12 patients, the changes stabilized disease and extended patient lives. Another patient, one with acute myeloid leukemia, went into remission and was cured by blood stem cell transplantation.
"Through the comprehensive genomic testing in this study, we were able to clearly identify tumor variations that could be treated with targeted agents, opening doors for how oncologists manage their patients," said co-corresponding author Kim Nichols, M.D., St. Jude Cancer Predisposition Division director.
Additional findings and details
Genomes for Kids enrolled patients between August 2015 and March 2017.
Eighteen percent of patients carried germline variations in one of 156 known, cancer-predisposition genes.
Almost two-thirds of the germline variations identified would not have been detected based on current screening guidelines.
Next steps
Genomes for Kids helped launch the hospital's clinical genomics program, which has enrolled about 2,700 cancer patients to date.
Meanwhile, data generated through the Genomes for Kids study are available at no cost to the international research community. By sharing the data, St. Jude aims to speed advances in understanding and treatment of pediatric cancer. The data are available in St. Jude Cloud.
"Even the most treatable cancers are not curable in all patients. For example, relapse remains the leading cause of death for the most common childhood cancer, acute lymphoblastic leukemia," Nichols said. "Being able to understand and predict which patients will respond to treatment and which won't requires collecting comprehensive genomic data on all patients."
INFORMATION:
Authors and funding
2Co-first authors are Wheeler, Scott Newman, Joy Nakitandwe, Chimene Kesserwan and Elizabeth Azzato, all formerly of St. Jude. James R. Downing and David Ellison of St. Jude are co-senior authors. The other authors are Michael Rusch, Sheila Shurtleff, Dale Hedges, Kayla Hamilton, Scott Foy, Michael Edmonson, Andrew Thrasher, Armita Bahrami, Brent Orr, Jeffery Klco, Jiali Gu, Lynn Harrison, Lu Wang, Michael Clay, Annastasia Ouma, Antonina Silkov, Yanling Liu, Zhaojie Zhang, Yu Liu, Samuel Brady, Xin Zhou, Ti-Cheng Chang, Manjusha Pande, Eric Davis, Jared Becksfort, Aman Patel, Mark Wilkinson, Delaram Rahbarinia, Manish Kubal, Jamie Maciaszek, Victor Pastor, Jay Knight, Alexander Gout, Jian Wang, Zhaohui Gu, Charles Mullighan, Rose McGee, Emily Quinn, Regina Nuccio, Roya Mostafavi, Elise Gerhardt, Leslie Taylor, Jessica Valdez, Stacy Hines-Dowell, Alberto Pappo, Giles Robinson, Liza-Marie Johnson and Ching-Hon Pui, all of St. Jude.
The research was funded in part by National Cancer Institute grants (CA216354, CA216391) and ALSAC, the St. Jude fundraising and awareness organization.
MEADVILLE, PA - July 22, 2021 - Shark Week is many things. First and foremost, it's a week of shark-themed documentary programming on the Discovery Channel. Now in its 33rd year, it's the longest-running cable event in history. It's the biggest audience that marine biologists and ocean conservationists get, attracting millions of viewers who might otherwise not ever think about sharks at all. It's a stage that has launched careers of shark scientists and inspired many others to pursue jobs as ocean scientists.
However, a new analysis shows that Shark Week is also deeply flawed in ways that undermine its goals, potentially harming both sharks and shark scientists. To document just how pervasive ...
Toronto -- People post 500 million tweets and 4 billion pieces of content on Facebook a day. What makes them do it?
An urge to share and connect with others seems obvious. But, despite how toxic the social media sandbox can get, people more often share attitudes that are framed in terms of support instead of opposition, according to new research. That happens regardless of whether the opinion itself is positive or negative.
Take gun control. The research found that people were likelier to express themselves on that issue in terms of, "I support allowing guns," or, "I support banning guns," versus, "I oppose banning guns," or, "I oppose allowing guns."
"There are a lot of controversial issues where both sides talk about what they support - pro-life and pro-choice on abortion, for example," ...
Recently, a research group led by Prof. YUAN Kaijun and Prof. YANG Xueming from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences revealed strong isotope effects in photodissociation of the water isotopologue (HOD) using the Dalian Coherent Light Source.
Their findings were published in Science Advances on July 23.
"Our experimental results illustrate dramatically different quantum state population distributions of OH and OD fragments from HOD photodissociation. The branching ratios of the H+OD and D+OH channels display large wavelength-dependent isotopic fractionation," said Prof. YUAN.
Because ...
Research in mice, published today in Science Immunology by researchers at the Babraham Institute, UK and VIB-KU Leuven, Belgium, provides two solutions with potential to overcome a key clinical limitation of immune cell therapies. Regulatory T cells have potential in treating autoimmunity and inflammatory diseases yet they can switch from a protective to damaging function. By identifying the unstable regulatory T cells, and understanding how they can be purged from a cell population, the authors highlight a path forward for regulatory T cell transfer therapy.
Cell therapy is based on purifying cells from a patient, growing them up in cell culture to improve their properties, and then reinfusing them into the patient. Professor Adrian ...
In the evolving field of cancer biology and treatment, innovations in organ-on-a-chip microdevices allow researchers to discover more about the disease outside the human body. These organs-on-chips serve as a model of the state an actual cancer patient is in, thus allowing an opportunity to finding the correct treatment before administering it to the patient. At Texas A&M University, researchers are pushing these devices to new levels that could change the way clinicians approach cancer treatment, particularly ovarian cancer.
The team has recently submitted a patent disclosure with the Texas A&M Engineering Experiment Station.
"We claim several novelties in technological ...
A study by researchers at the Texas A&M University School of Public Health shows that inexpensive and convenient devices such as silicone wristbands can be used to yield quantitative air quality data, which is particularly appealing for periods of susceptibility such as pregnancy.
The research team found that the wristbands, when used as passive samplers, have the ability to bind smaller molecular weight semi-volatile polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) -- a class of chemicals that occur naturally in coal, crude oil and gasoline and are produced when coal, oil, gas, wood, garbage and tobacco are burned -- in a similar pattern as active sampling.
Published recently in Nature's ...
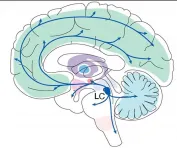
Small and seemingly specialized, the brain's locus coeruleus (LC) region has been stereotyped for its outsized export of the arousal-stimulating neuromodulator norepinephrine. In a new paper and with a new grant from the National Institutes of Health, an MIT neuroscience lab is making the case that the LC is not just an alarm button but has a more nuanced and multifaceted impact on learning, behavior and mental health than it has been given credit for.
With inputs from more than 100 other brain regions and sophisticated control of where and when it sends out norepinephrine (NE), the LC's tiny population of surprisingly diverse cells may represent an important regulator of learning from ...
Alexandria, Va., USA - Hiba Nasir, Wayzata High School, Plymouth, Minn., presented the poster "Oral-Health Impact Profile 5: Analyzing A Private Practice Adult Population's Distribution" at the virtual 99th General Session & Exhibition of the International Association for Dental Research (IADR), held in conjunction with the 50th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Dental Research (AADR) and the 45th Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for Dental Research (CADR), on July 21-24, 2021.
Nasir, a high school student, along with Sheila Riggs, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, USA, performed an observational study to understand the ...
Alexandria, Va., USA - Ruth Lipman, American Dental Association (ADA) Science and Research Institute, Chicago, Ill., U.S., presented the poster "Strategies for Disseminating Guidance to Dentists during the COVID-19 Pandemic" at the virtual 99th General Session & Exhibition of the International Association for Dental Research (IADR), held in conjunction with the 50th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Dental Research (AADR) and the 45th Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for Dental Research (CADR), on July 21-24, 2021.
Rapidly formulated, actionable infection risk mitigation strategies for dental care professionals were needed during the initial acceleration phase of the COVID-19 ...
Coffee shops and casual restaurants are an important part of American life. Even beyond the food and drinks they sell, they offer us a place to use the restroom or rest our feet while we're out and about, and they provide internet access to those on the go, those in need of a temporary office, or those who don't have an internet connection at home. Many of us take for granted that a nearby Starbucks or McDonald's can offer us a little respite, even if we don't always make a purchase.
But access to these sorts of quasi-public spaces isn't always equal in America, particularly for Black people and other people of color. One such example of this is the infamous 2018 incident in Philadelphia when two Black men waiting at Starbucks for an acquaintance were ...