(Press-News.org) About The Study: The results of this neuroimaging study of 8,900 children ages 9 to 11 suggest that the observed sex differences in cognitive performance and brain connectivity likely reflect faster brain maturation in girls than boys. The findings are relevant to the future creation of brain developmental trajectory charts to monitor for deviations associated with impairments in cognition or behavior, including those due to psychiatric or neurological disorders.
Authors: Dardo Tomasi, Ph.D., of the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism in Bethesda, Maryland, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.0157)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.0157?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=022123
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Measures of brain connectivity, cognition by sex in children
JAMA Network Open
2023-02-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A sight for sore eyes: Anti-VEGF treatment in an ocular model of viral infection
2023-02-21
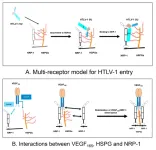
Tokyo, Japan – A retrovirus known as human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) is known to cause a number of diseases, including inflammatory diseases of the eye. Recently, researchers in Japan have investigated an antibody treatment for inflammatory eye disease in ocular cells infected with HTLV-1.
In a new study published in Frontiers in Immunology, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) evaluated the safety of an anti-VEGF drug, Aflibercept, in a cell culture model exposed to HTLV-1. HTLV-1 infection can cause such diseases as adult T-cell leukemia and HTLV-1 uveitis, an inflammatory eye condition.
Vascular ...
Physicists create new model of ringing black holes
2023-02-21
When two black holes collide into each other to form a new bigger black hole, they violently roil spacetime around them, sending ripples called gravitational waves outward in all directions. Previous studies of black hole collisions modeled the behavior of the gravitational waves using what is known as linear math, which means that the gravitational waves rippling outward did not influence, or interact, with each other. Now, a new analysis has modeled the same collisions in more detail and revealed so-called nonlinear ...
Bouncing seismic waves reveal distinct layer in Earth's inner core
2023-02-21
Data captured from seismic waves caused by earthquakes has shed new light on the deepest parts of Earth’s inner core, according to seismologists from The Australian National University (ANU).
By measuring the different speeds at which these waves penetrate and pass through the Earth’s inner core, the researchers believe they’ve documented evidence of a distinct layer inside Earth known as the innermost inner core -- a solid “metallic ball” that sits within the centre of the inner core.
Not long ago it was thought Earth’s structure was comprised of four distinct layers: the crust, the mantle, the outer core and the inner core. The ...
Researchers map mosquito cells that may help the insects choose tastiest humans
2023-02-21
In a bid to understand why mosquitoes may be more attracted to one human than another, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers say they have mapped specialized receptors on the insects’ nerve cells that are able to fine-tune their ability to detect particularly “welcoming” odors in human skin.
Receptors on mosquito neurons have an important role in the insects’ ability to identify people who present an attractive source of a blood meal, according to Christopher Potter, Ph.D., associate professor of neuroscience at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. “Understanding ...
US Census data vulnerable to attack without enhanced privacy measures
2023-02-21
Computer scientists at the University of Pennsylvania School of Engineering and Applied Science have designed a “reconstruction attack” that proves U.S. Census data is vulnerable to exposure and theft.
Aaron Roth, Henry Salvatori Professor of Computer & Cognitive Science in Computer and Information Science (CIS), and Michael Kearns, National Center Professor of Management & Technology in CIS, led a recent PNAS study demonstrating that statistics released by the U.S. Census Bureau can be reverse engineered to reveal ...
Excess nutrients lead to dramatic ecosystem changes in Cape Cod’s Waquoit Bay; the bay is a harbinger for estuaries worldwide, say researchers
2023-02-21
Woods Hole, Mass. (Feb. 21, 2023) -- When the Covid-19 pandemic hit in 2020 with associated travel restrictions, Matthew Long thought his students could shift their overseas research projects to instead study the seagrass meadow ecosystem in Waquoit Bay. It’s a shallow, micro-tidal estuary on the south side of Cape Cod in Massachusetts, near the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) where Long is an associate scientist in the Marine Chemistry and Geochemistry Department.
However, when Long and his students looked for seagrass meadows where he had seen them in previous years, there were only a few shoots of dying Zostera marina eelgrass, ...
New AGA guideline recommends blood and stool tests for monitoring ulcerative colitis
2023-02-21
Bethesda, MD (Feb. 21, 2023) — In new evidence-based guidelines, the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) recommends non-invasive biomarkers as a first-line strategy for monitoring many patients with ulcerative colitis (UC). These guidelines were published today in Gastroenterology.
The AGA guidelines outline use cases for three biomarkers that provide accurate insights into ulcerative colitis disease activity: serum C-reactive protein (CRP) (blood), fecal calprotectin (stool) and fecal lactoferrin (stool).
“For decades we have regarded endoscopy as the gold ...
RIT researcher awarded NSF CAREER funding to develop advanced computer memory and devices
2023-02-21
Kai Ni was awarded a National Science Foundation CAREER Award to improve computing memory through the use of ferroelectric materials and capacity.
The assistant professor of electrical and microelectronic engineering in RIT’s Kate Gleason College of Engineering, Ni has been at the forefront of advancing ferroelectric memory, a familiar but never widely adopted technology that has the potential to meet the growing demand for more energy-efficient computing performance.
“The appetite for semiconductors just keeps growing. With the data we are generating every day, we need ways to process ...
CHOP researchers develop first effective preclinical models for most common genetic cause of Leigh Syndrome
2023-02-21
Philadelphia, February 21, 2023 – Researchers from Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) developed two new zebrafish models for studying a specific genetic form of mitochondrial disease that represents the most common cause of Leigh syndrome. Using these models, the team identified two drugs already approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for other conditions that could be repurposed to treat this specific cause of Leigh syndrome. The findings were recently published in the journal Human Molecular Genetics.
SURF1 deficiency ...
Public lecture: how can we have a good future with artificial intelligence?
2023-02-21
Public lecture: how can we have a good future with artificial intelligence?AI expert and educator Professor Anikó Ekárt to discuss one of today’s most provocative topics
Lecture will take place on 28 February at Aston University
Talk to explore artificial intelligence’s capabilities, benefits and pitfalls.
The potential impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on our daily lives will be explored in a public lecture at Aston University.
The University is inviting the public onto its campus on Tuesday 28 February to hear Professor ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
[Press-News.org] Measures of brain connectivity, cognition by sex in childrenJAMA Network Open