(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, Feb. 21, 2023 – It is a cruel paradox that on a planet with a surface mostly covered by water, hundreds of millions of people don’t have access to clean drinking water. As for the pollution of potable and natural water sources, one of the main culprits is arsenic, an abundant and toxic element in the earth’s crust. Arsenic is currently known as the cause of groundwater contamination in more than 100 countries – and can produce life-threatening diseases, especially for populations in developing countries. Such circumstances necessitate efficient and reliable arsenic detection methods for water, food, and soil.
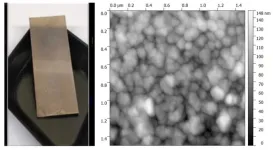
In Journal of Applied Physics, from AIP Publishing, a team of French scientists fabricated sensitive nanostructured silver surfaces to detect arsenic, even at very low concentrations.
The sensors make use of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS). As a molecule containing arsenic adheres to the surface, it is also hit with a laser. The arsenic compound scatters the laser light, creating an identifiable signature that indicates its presence.
“Arsenic exists in water in different forms, so it is important to be able to quantify the species, in addition to the global content,” said author Dominique Vouagner. “By using SERS, we can detect and speciate pollutants even at the lowest concentration. This includes arsenic, which should not exceed 10 ppb, as per the World Health Organization’s recommendations.”
The team compared the detection and speciation performances of two SERS substrates. One was prepared by conventional thermal evaporation, where material is heated until it vaporizes. The other was created with an electroless process, in which a coating is deposited on a material by submerging it in a liquid and instigating a chemical reaction. The latter was revealed to be much more sensitive and is relatively easy and safe to produce, according to Vouagner.
“Our technique for developing this SERS substrate makes it simple to manufacture because the electroless films can be easily deposited on various substrates,” she said. “Plus, the starting compounds have low environmental toxicity, which is a benefit for detection measurements in natural as well as potable water.”
The technique is a departure from existing reference methods for trace arsenic speciation, which are time-consuming and expensive. Conventional methods also require sample pre-treatment in a lab, so they are not ideally suited to on-site field assays.
Additionally, the new method employs the use of a solid substrate, which enables optical interrogation.
“Because they’re less ‘noisy,’ optical detection systems are much more sensitive than electronic systems,” said author Bernard Dussardier. “At the same time, they’re less sensitive to parasitic electromagnetic fields. Also, the SERS technique allows direct physical-chemical property measurements, whereas electronic systems, and some other optical systems, are indirect.”
###
The article “Towards surface-enhanced Raman scattering using electroless substrate for trace arsenic detection and speciation” is authored by Marie Adier, Anne‐Marie Jurdyc, Charlotte Hurel, François Goutaland, Jean‐Yves Michalon, Alexandre Merlen, Bernard Dussardier, and Dominique Vouagner. It will appear in Journal of Applied Physics on Feb. 21, 2023 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0126372). After that date, it can be accessed at http://aip.scitation.org/doi/full/10.1063/5.0126372.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Journal of Applied Physics is an influential international journal publishing significant new experimental and theoretical results in all areas of applied physics. See https://aip.scitation.org/journal/jap.
###
END
Enhanced arsenic detection in water, food, soil
Sensor can identify the global content and form of arsenic-containing molecules at very low concentrations
2023-02-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A new model to better understand what’s inside colliding black holes
2023-02-21
In 2015, scientists for the first time detected gravitational waves, ripples in space-time that occur when major cosmic events—like the collision and merging of two black holes—disrupt the cosmos. The observation of these waves confirmed Einstein’s theory of general relativity, which predicted such waves would occur if space-time worked as he believed it did. In the seven years since, nearly 100 merging black holes have been detected by observing the gravitational waves that these extraterrestrial events emit.
Now, thanks to new research from a team of 14 led by Caltech ...
History of low hourly wage and all-cause mortality among middle-age workers
2023-02-21
About The Study: Sustained low-wage earning in midlife may be associated with elevated mortality risk and excess deaths, especially when experienced alongside unstable employment, according to the results of this study including 4,000 workers. If causal, the findings suggest that social and economic policies that improve the financial standing of low-wage workers (e.g., minimum wage laws) could improve mortality outcomes.
Authors: Katrina L. Kezios, Ph.D., of Columbia University in New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.0367)
Editor’s ...
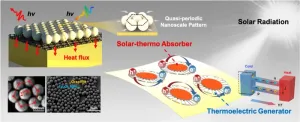
Nanoparticles self-assemble to harvest solar energy
2023-02-21
WASHINGTON, Feb. 21, 2023 – Solar-thermal technology is a promising environmentally friendly energy harvesting method with a potential role to play in solving the fossil fuel energy crisis.
The technology transforms sunlight into thermal energy, but it’s challenging to suppress energy dissipation while maintaining high absorption. Existing solar energy harvesters that rely on micro- or nanoengineering don’t have sufficient scalability and flexibility, and will require a novel strategy for high-performance ...
Accessibility of public health websites for information on COVID-19 outpatient treatments
2023-02-21
About The Study: This study found that COVID-19 treatment information on U.S. public health websites was poorly accessible, particularly for people with low literacy or limited English language proficiency, with worse accessibility for states and territories with Republican governors. The results suggest the need for national guidelines on accessibility and readability for public health websites.
Authors: Kevin A. Fiscella, M.D., M.P.H., of the University of Rochester Medical Center in Rochester, New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media ...
Measures of brain connectivity, cognition by sex in children
2023-02-21
About The Study: The results of this neuroimaging study of 8,900 children ages 9 to 11 suggest that the observed sex differences in cognitive performance and brain connectivity likely reflect faster brain maturation in girls than boys. The findings are relevant to the future creation of brain developmental trajectory charts to monitor for deviations associated with impairments in cognition or behavior, including those due to psychiatric or neurological disorders.
Authors: Dardo Tomasi, Ph.D., of the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism ...
A sight for sore eyes: Anti-VEGF treatment in an ocular model of viral infection
2023-02-21
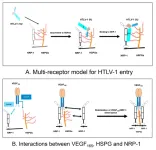
Tokyo, Japan – A retrovirus known as human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) is known to cause a number of diseases, including inflammatory diseases of the eye. Recently, researchers in Japan have investigated an antibody treatment for inflammatory eye disease in ocular cells infected with HTLV-1.
In a new study published in Frontiers in Immunology, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) evaluated the safety of an anti-VEGF drug, Aflibercept, in a cell culture model exposed to HTLV-1. HTLV-1 infection can cause such diseases as adult T-cell leukemia and HTLV-1 uveitis, an inflammatory eye condition.
Vascular ...
Physicists create new model of ringing black holes
2023-02-21
When two black holes collide into each other to form a new bigger black hole, they violently roil spacetime around them, sending ripples called gravitational waves outward in all directions. Previous studies of black hole collisions modeled the behavior of the gravitational waves using what is known as linear math, which means that the gravitational waves rippling outward did not influence, or interact, with each other. Now, a new analysis has modeled the same collisions in more detail and revealed so-called nonlinear ...
Bouncing seismic waves reveal distinct layer in Earth's inner core
2023-02-21
Data captured from seismic waves caused by earthquakes has shed new light on the deepest parts of Earth’s inner core, according to seismologists from The Australian National University (ANU).
By measuring the different speeds at which these waves penetrate and pass through the Earth’s inner core, the researchers believe they’ve documented evidence of a distinct layer inside Earth known as the innermost inner core -- a solid “metallic ball” that sits within the centre of the inner core.
Not long ago it was thought Earth’s structure was comprised of four distinct layers: the crust, the mantle, the outer core and the inner core. The ...
Researchers map mosquito cells that may help the insects choose tastiest humans
2023-02-21
In a bid to understand why mosquitoes may be more attracted to one human than another, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers say they have mapped specialized receptors on the insects’ nerve cells that are able to fine-tune their ability to detect particularly “welcoming” odors in human skin.
Receptors on mosquito neurons have an important role in the insects’ ability to identify people who present an attractive source of a blood meal, according to Christopher Potter, Ph.D., associate professor of neuroscience at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. “Understanding ...
US Census data vulnerable to attack without enhanced privacy measures
2023-02-21
Computer scientists at the University of Pennsylvania School of Engineering and Applied Science have designed a “reconstruction attack” that proves U.S. Census data is vulnerable to exposure and theft.
Aaron Roth, Henry Salvatori Professor of Computer & Cognitive Science in Computer and Information Science (CIS), and Michael Kearns, National Center Professor of Management & Technology in CIS, led a recent PNAS study demonstrating that statistics released by the U.S. Census Bureau can be reverse engineered to reveal ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
[Press-News.org] Enhanced arsenic detection in water, food, soilSensor can identify the global content and form of arsenic-containing molecules at very low concentrations