Nanofluidic devices offer solutions for studying single molecule chemical reactions
2023-02-22
(Press-News.org)
In a chemical reaction, molecules in different substances meet one another to form new molecules causing changes in the bonds of their atoms. The molecules collide at an extremely close distance—a nanometer or less—in an extremely short amount of time. This makes investigating the details of chemical reactions at the molecular scale difficult. Most experimental knowledge, used to explain single-molecule reaction dynamics, was obtained by studying reactions in gases. However, the overwhelming majority of chemical reactions take place in liquids, so elucidating single-molecule reaction dynamics in solution is an important challenge, with very few experimental tools.
A nanofluidic device—a few square centimeters of glass plate with nanometer-sized nanofluidic channels carved into it—provides a test tube-like environment to confine individual molecules. But nanofluidic devices have the potential to be used in combination with various existing analytical instruments with high temporal resolution, to investigate extremely fast single molecule reactions.
The authors of the review, Associate Professor Yan Xu and Dr. Nattapong Chantipmanee of the Osaka Metropolitan University Graduate School of Engineering, have engineered principles and technologies to freely manipulate nanomaterials, biomaterials, and molecules at the single-molecule level. The methodologies covered by their review use fundamental technologies such as nanofluidic processing, functional integration, and fluidic control and measurement, pioneering the way to integrate various fields by using nanofluidics. In addition, to elucidate the single molecule dynamics of reactions in solution using their unique nanofluidic devices, they are working to solve problems such as how to precisely manipulate small molecules in solution and how to measure their extremely quick—nano- to picosecond—reactions.
The researchers published their review article on single-molecule reaction dynamics in solution pioneered by nanofluidic devices, in the January 2023 issue of TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry. As pioneers in this new field, the review provides a bird's eye view, including the forefront of research and development, future challenges, and where new these discoveries may lead.
“Nanofluidic devices have the potential to become a fantastic experimental tool to elucidate the dynamics of solution reactions. I hope this paper will encourage more researchers to join this budding field of research,” said Professor Xu.
###
About OMU
Osaka Metropolitan University is a new public university established in April 2022, formed by merger between Osaka City University and Osaka Prefecture University. For more research news visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ or follow @OsakaMetUniv_en and #OMUScience.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-02-22
A team of researchers from the Keck School of Medicine of USC found that exposure to a mixture of synthetic chemicals found widely in the environment alters several critical biological processes, including the metabolism of fats and amino acids, in both children and young adults. The disruption of these biological processes is connected to an increased risk of a very broad range of diseases, including developmental disorders, cardiovascular disease, metabolic disease and many types of cancer.
Known as per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, or PFAS, these man-made chemicals are used in a wide range of consumer and industrial products. PFAS are sometimes ...
2023-02-21
Eighteen cartoons have been selected as finalists in the 2023 Ethics Cartooning Competition, an annual contest sponsored by the Morgridge Institute for Research.
Participants from the University of Wisconsin-Madison and affiliated biomedical centers or institutes submitted their work, then a panel of judges selected the final cartoons for display to the public, who is invited to vote and help determine the 2023 winners.
This year’s cartoons depict a variety of research ethics topics, such as the ethics of scientific publishing, research funding and environments, questionable research practices, ...
2023-02-21
The Boyce Thompson Institute (BTI) is delighted to announce that faculty member Fay-Wei Li has been promoted to Associate Professor on January 13. Li was evaluated on his achievements to date and likelihood of continued success in the future.
Since joining BTI in 2017, Li has developed an internationally-recognized program on seed-free plants, both in terms of genome sequencing and in making biological discoveries. He also is an excellent science communicator, with a knack for explaining the importance of scientific discoveries to a wide range of audiences.
The ...
2023-02-21
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. – So much of modern life is spent on screens: Zoom meetings and websites, smartphones and videogames, televisions and social media. How are all those pixels and rectangles affecting how we see?
Binghamton University, State University of New York Professor of Psychology Peter Gerhardstein and doctoral candidate Nicholas Duggan explore the phenomenon in “Levels of Orientation Bias Differ Across Digital Content Categories: Implications for Visual Perception,” recently published in the journal Perception. Their paper covers the extent to which online content ...
2023-02-21
CLEVELAND: Supported by a new $3.14 million grant from the National Institutes of Health to Cleveland Clinic, researchers are using an emerging technology known as “digital twins” to better understand healthcare disparities based on where someone lives. Researchers from Cleveland Clinic and MetroHealth aim to use this information to develop strategies designed to reduce these disparities in health outcomes.
The research team, led by Jarrod Dalton, Ph.D., of Cleveland Clinic, and Adam Perzynski, Ph.D., of MetroHealth, ...
2023-02-21
(MIAMI, FL, FEB. 21, 2023) – To create the most effective, personalized treatment plans for patients with Hodgkin lymphoma or other cancers, scientists and clinicians need the clearest picture of the genetic changes leading to the cancer’s development. That picture, say scientists at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center in the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, comes into much better focus when whole genome sequencing – rather than the current standard, exome sequencing – is used to identify changes driving the cancer.
Exome sequencing, which reads only protein-coding genes, can detect some specific mutations and other variants that propel cancers, ...
2023-02-21
Written by Kay Ledbetter, 806-547-0002, skledbetter@ag.tamu.edu
Imagine your favorite cured meat like beef jerky, pepperoni or bacon without any added sodium nitrite from any source currently necessary for color and shelf life. Wes Osburn, Ph.D., is doing exactly that.
At center, Wes Osburn, Ph.D., Texas A&M University meat scientist, is working in his lab with students Tanner Wright and Arlie Reeves on a new no nitrite-added cured meat system. (Texas A&M AgriLife photo ...
2023-02-21
Eurasian spruce bark beetles (Ips typographus) burrow into the bark of Norway spruce (Picea abies) trees where they mate and lay their eggs. Major outbreaks in Europe have decimated millions of hectares of conifer forests. The beetles preferentially attack trees that are already infected with symbiotic fungi (such as Grosmannia penicillata), which is thought to weaken host trees and break down their chemical defenses, allowing the beetles to successfully develop in the bark.
To investigate the chemical signals ...
2023-02-21
The mass outbreaks of bark beetles observed in recent years have caused shocking amounts of forest damage throughout Germany. As reported by the Federal Statistical Office in July 2022, more than 80% of the trees that had to be felled in the previous year were damaged by insects. The damaged timber felled due to insect damage amounted to more than 40 million cubic meters. One of the main pests is the European spruce beetle Ips typographus. In the Thuringian Forest and the Harz Mountains, for example, the beetle, which is only a few millimeters long, encountered spruce monocultures that had already been weakened by high temperatures and extended ...
2023-02-21
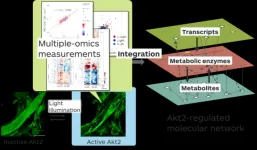
Takeaki Ozawa and his team from the University of Tokyo reveal the metabolic reactions upon activating an enzyme called Akt2. In doing so, they reveal the inner workings of insulin-regulated metabolism. The findings lead the way for Akt2-targeting therapeutics for diabetes and metabolic disorders.
It takes energy to do anything—even to exist. You can metabolize food to convert glucose into energy: thanks to many cascades of molecular reactions within your cells. As soon as you eat, your pancreas secretes insulin hormone, which starts ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Nanofluidic devices offer solutions for studying single molecule chemical reactions