(Press-News.org)
After more than two years since its discovery, six million deaths, and half a billion reported cases, there is still no effective cure for COVID-19. Even though vaccines have lowered the impact of outbreaks, patients that contract the disease can only receive supportive care while they wait for their own body to clear the infection.
A promising COVID-19 treatment strategy that has been gaining traction lately is targeting angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). This is a receptor found on the cell membrane that allows entry of the virus into the cell due to its high affinity for SARS-CoV-2’s spike protein. The idea is that reducing the levels of ACE2 on the membrane of cells could be a way to prevent the virus from entering them and replicating, thereby lowering its infectious capabilities.
In a recent study published in PLOS ONE, a team of scientists including Associate Professor Shun-Ichiro Ogura from Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan, analyzed the potential of a natural amino acid called 5-Aminolevulinic acid (ALA) to reduce the expression of ACE2. This research was performed in collaboration with SBI Pharmaceuticals Co. Ltd.
As the researchers explain in their paper, ALA had been identified in 2021 as a compound that seemed to reduce the infectivity of SARS-CoV-2. However, the underlying mechanisms that led to this phenomenon remained unknown, until now.
The team hypothesized that the results of the 2021 study could be explained by an effect of ALA on the expression of ACE2. To test their hypothesis, they prepared human cell cultures, administered ACE2 on some of them, and compared the levels of ACE2 in treated cells versus control cells. As expected, the amount of available ACE2 in treated cells was significantly lower than in control cells.
But the story doesn’t end there. Upon uptake, cells transform ALA into a molecule called protoporphyrin IX (PpIX) and subsequently into heme—a precursor of hemoglobin and other useful proteins. This hinted that the expression of ACE2 could be linked to the production of either of these compounds. Thus, the team checked the levels of PpIX and heme in cells treated with ALA. “We observed significant increases in the concentration of intracellular PpIX, suggesting that ALA was uptaken into the cell and converted into PpIX,” remarks Ogura, “However, only a slight increase in heme concentration was observed, which might be due to the lack of an iron source to convert PpIX into heme.”
After introducing an iron source in the form of sodium ferrous citrate, the intracellular levels of heme increased significantly and the expression of ACE2 became even lower. These results suggest ACE2 expression is kept in check by heme production, the latter of which can be boosted by the co-administration of ALA and an iron source.
Overall, this study sheds light on how ALA and the heme production pathway could form the basis of a cure for COVID-19. “We believe ALA could be developed into a potential anti-viral agent for SARS-CoV-2, which may play an important role in the eradication of the disease in a global scale in the near future,” concludes Dr. Ogura.
Let us hope further studies can help us put an end to COVID-19 soon!
END
Quantum entanglement refers to a phenomenon in quantum mechanics in which two or more particles become linked such that the state of each particle cannot be described independently of the others, even when they are separated by a large distance. The principle, referred to by Albert Einstein as "spooky action at a distance", is now utilized in quantum networks to transfer information. The building blocks of these networks—quantum nodes—can generate and measure quantum states.
Among the candidates that can function as ...
February 24, 2023 – Demographic factors including low income and living in a rural area are linked to low telemedicine literacy – which may limit access to plastic surgeons and other healthcare providers at a time of expanding use of telehealth and video visits, according to a report in the March issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Our ...
Although genetic mutations in BRCA1 or BRCA2 are associated with a younger onset of breast and ovarian cancer, women with these genetic mutations continue to face a high risk of cancer incidence after age 50, even if they have not been previously diagnosed with cancer. This is according to a new study led by Kelly Metcalfe, a professor at the Lawrence S. Bloomberg Faculty of Nursing.
The study published recently in the American Cancer Society Journal Cancer, followed over 2000 women between the ages of 50 to 75, from 16 countries, who were aware they had a BRCA mutation ...
February 24, 2023 – Plastic surgery procedures performed to correct cleft lip and palate deformities in infants and children are economically undervalued, relative to pediatric craniofacial procedures, concludes an analysis in the March issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
The study finds unbalanced allocation of relative value units (RVUs) used in billing and compensation for cleft surgery in children, compared to craniofacial procedures, report Roberto L. Flores, MD, of Hansjörg ...
People who suffer from insomnia were 69% more likely to have a heart attack compared to those who didn’t have the sleep disorder during an average nine years of follow-up, according to new research being presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session Together With the World Congress of Cardiology. In addition, when looking at sleep duration as an objective measure of insomnia, researchers found that people who clocked five or fewer hours of sleep a night had the greatest risk of experiencing a heart attack. People with ...
Rising rates of adverse pregnancy outcomes, such as hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, preterm birth and low birthweight, over the past 10 years are largely attributable to the health status of a person before they get pregnant, rather than age, according to a study presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session Together With the World Congress of Cardiology.
The study found that the average age of pregnant individuals rose from 27.9 years in 2011 to 29.1 years in 2019, yet age accounted for only a small portion of the marked increase ...
People who became pregnant using assisted reproductive technologies were found to be over twice as likely to develop preeclampsia than those with traditional pregnancies, according to a study presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session Together With the World Congress of Cardiology.
The study, based on an analysis of health records from over 2.2 million patients, is the first to assess how reproductive technologies may affect the risk of cardiovascular complications during pregnancy on a national scale. Preeclampsia is a pregnancy-related complication involving new onset high ...
People who used marijuana daily were found to be about one-third more likely to develop coronary artery disease (CAD) compared with people who have never used the drug, according to a study presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session Together With the World Congress of Cardiology.
As cannabis becomes legal in an increasing number of U.S. states, this study is among the largest and most comprehensive to date to examine the potential long-term cardiovascular implications of using the drug. CAD is the most common form of heart disease and occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart ...
People with Type 2 diabetes who were given a smartphone app that delivers personalized cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) saw significantly greater reductions in their blood sugar and less need for higher doses of diabetes medications at six months compared with those who only received standard diabetes care and a control app, in a study presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session Together With the World Congress of Cardiology. A clear “dose effect” was seen, with patients completing more CBT lessons seeing the greatest benefits.
“When studied in a large randomized controlled ...
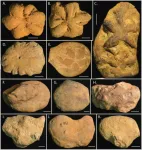
More than 100 years ago, Charles Doolittle Walcott from the Smithsonian Institution was asked to examine strange star-shaped fossils with lobes hailing from the ~ 514-million-year-old Conasauga Formation in Alabama. Walcott described these odd fossils as jellyfish that likely floated in the middle Cambrian seas of what is now the southeastern United States. Little did he know that the Cambrian fossil he named would cause over 100 years of controversy.
The controversy hinged on the interpretation of what Brooksella really was: Was it truly a jellyfish ...