A simpler way to track the spread of infectious diseases
New computational method simplifies the analysis of social contacts
2023-02-24
(Press-News.org)
How society organizes affects different phenomena, from the transmission of information to the spread of contagious diseases. The more links we establish with each other via social and transportation networks, the more spread is favored. To study the dynamics of complex systems, such as society, we can infer these networks – in which nodes, representing individuals, connect through lines – from real-world data. However, these networks are usually large, dense, and cumbersome to manipulate.
In previous work, Luís M. Rocha’s group at the Instituto Gulbenkian de Ciência (IGC) found a way to simplify networks by extracting their backbones. The principle behind this method is quite simple: it finds the shortest path to reach every other point in a network and deletes redundant alternatives. But how do we find these shorter paths? Rion B. Correia, a postdoc at the IGC, explains: “In the three-dimensional world we live in, we are used to thinking in terms of shortest paths, for instance, how to go from home to work through the shortest/fastest possible route. But in multi-dimensional systems (adding traffic, multiple modes of transportation, and road constructions), the shortest path is not necessarily the direct path between two points”. Even if there are infinite ways to get from A to B, with this method researchers can focus on the most important paths. Since then, the researchers have applied it to study a variety of networks, from gene interactions to essential communication pathways in the brain.
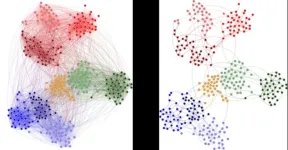
Now, the team took this method to a whole new level by testing it on real human contacts. For this, they used previously recorded contacts between nearly 3000 individuals using wearable proximity sensors in a variety of social settings, including schools, a hospital and an art exhibit. Then, they transformed this contact data into social networks, where links represent the amount of time people spent together.
The researchers concluded that the backbones of social contact networks were very small. “This means that a lot of connections in human communities are redundant”, Rion, first author of this study, explains. Surprisingly, this backbone still preserved the community structure, stemming from people’s tendency to cluster in groups. And it did it much better than other methods.
Reduced to 6-20% of the original networks, the backbones make it much easier to understand how communities organize and study simple transmission dynamics. In this study, the researchers demonstrated that the backbone is a reliable tool to explain how processes such as viral infection spread in a population, as well as to identify the most relevant social contacts to stop contagion. But the implications of the backbone of social systems go much beyond epidemiology. “The recent pandemic demonstrated that our social lives and overall public health depends heavily on interactions that cross scales from the molecular network of minute pathogens to all our transportation, health, economy, ecology, and governance networks”, Luís highlights. “Our basic research on backbones adds another tool in the study of networks that link the tiniest virus to the most potent economy. It is only through the fundamental understanding of how these systems interact that we can solve these XXI century problems”, he concludes.
This study was developed by the Instituto Gulbenkian de Ciência (IGC) in collaboration with the State University of New York at Binghamton, Aix Marseille Univ, Université de Toulon, CNRS, CPT, Turing Center for Living Systems, France, and partially funded by National Institutes of Health, National Library of Medicine Program, Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR), a Fulbright Commission fellowship (LMR), and a CAPES Foundation fellowship.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-02-24
Attention editors: Under embargo by the journal Current Biology until Friday, February 24 at 11 a.m. eastern
Scientists who study the origins and evolution of the plague have examined hundreds of ancient human teeth from Denmark, seeking to address longstanding questions about its arrival, persistence and spread within Scandinavia.
In the first longitudinal study of its kind, focusing on a single region for 800 years (between 1000-1800AD), researchers reconstructed Yersinia pestis genomes, the bacterium responsible for the plague, and showed that it was reintroduced into the Danish population from other parts of Europe again and again, perhaps via ...
2023-02-24
OAKLAND, Calif. — Long-term exposure to air pollution is tied to an increased risk of having a heart attack or dying from heart disease — with the greatest harms impacting under-resourced communities, new Kaiser Permanente research shows.
The study, published February 24 in JAMA Network Open, is one of the largest to date to look at the effects of long-term exposure to fine particle air pollution, which is emitted from sources such as vehicles, smokestacks, and fires. Fine particle air pollution, also known as PM2.5, are fine particles that are 2.5 micrometers in diameter or smaller. The ...
2023-02-24
About The Study: In this case series study that analyzed 44,000 confirmed COVID-19 cases in Tokyo, cases identified in nightlife settings were associated with a higher likelihood of spreading COVID-19 than household and health care cases. Surveillance and interventions targeting nightlife settings should be prioritized to disrupt COVID-19 transmission, especially in the early stage of an epidemic.
Authors: Michihiko Yoshida, Ph.D., of the Minato Public Health Center in Tokyo, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.0589)
Editor’s ...
2023-02-24
About The Study: In this study including 3.7 million adults in California, long-term fine particulate air pollution (PM2.5) exposure at moderate concentrations was associated with increased risks of heart attack, ischemic heart disease mortality and cardiovascular disease mortality. The findings add to the evidence that the current regulatory standard is not sufficiently protective.
Authors: Stacey E. Alexeeff, Ph.D., of the Kaiser Permanente Division of Research in Oakland, California, is the corresponding author.
To access ...
2023-02-24
Gestational diabetes and preeclampsia may be linked to slower biological development in infants, according to a new study led by USC.
The research, published today in JAMA Network Open, found that newborns exposed to these two pregnancy complications were biologically younger than their chronologic gestational age. The infants’ biological or “epigenetic” age is based on molecular markers in their cells.
The results raise intriguing questions about how common pregnancy complications may affect infants and health outcomes later in childhood. Could they create developmental delays? Could some exposures advance biological ...
2023-02-24
A team of researchers has highlighted human-wildlife conflict as one of the globe’s most pressing human development and conservation dilemmas.
New research published in Communications Biology looked at 133 countries where 18 large carnivores ranged, and found that a person farming with cattle in developing countries such as Kenya, Uganda or India were up to eight times more economically vulnerable than those living in developed economies such as Sweden, Norway or the U.S.
Duan Biggs from Northern Arizona University’s School of Earth and Sustainability is the senior author of the study. He partnered with organizations throughout the world to conduct ...
2023-02-24
Researchers from the UCL Cancer Institute have provided important molecular understanding of how injury may contribute to the development of a relatively rare but often aggressive form of brain tumour called a glioma.
Previous studies have suggested a possible link between head injury and increased rates of brain tumours, but the evidence is inconclusive. The UCL team have now identified a possible mechanism to explain this link, implicating genetic mutations acting in concert with brain tissue inflammation to change the behaviour of cells, making them more likely to become cancerous. Although this study was largely carried out in mice, it suggests ...
2023-02-24
SAN FRANCISCO, CA (February 24, 2023) — The history of life on Earth has been punctuated by several mass extinctions, the greatest of these being the Permian-Triassic extinction event, also known as the “Great Dying”, which occurred 252 million years ago. While scientists generally agree on its causes, exactly how this mass extinction unfolded—and the ecological collapse that followed—remains a mystery. In a study published today in Current Biology, researchers analyzed marine ecosystems before, during, and after the Great Dying ...
2023-02-24
A small but significant metabolic difference between human and mouse lung tumor cells, has been discovered by Weill Cornell Medicine researchers, explaining a discrepancy in previous study results, and pointing toward new strategies for developing cancer treatments.
The work, published Jan. 30 in Cancer Discovery, focuses on lung adenocarcinoma, a common but often difficult to treat cancer that researchers have long studied in mouse models. However, those models didn’t quite align with human clinical observations in some instances. The new paper shows why; a specific gene mutation has opposite effects on tumor ...
2023-02-24
Led by scientists at The University of Manchester, a series of new stable, porous materials that capture and separate benzene have been developed. Benzene is a volatile organic compound (VOC) and is an important feedstock for the production of many fine chemicals, including cyclohexane. But, it also poses a serious health threat to humans when it escapes into the air and is thus regarded as an important air pollutant.
The research published today in journal Chem, demonstrates the high adsorption of benzene at low pressures and concentrations, as well as the efficient separation of benzene and cyclohexane. This was achieved by the design and successful preparation ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A simpler way to track the spread of infectious diseases
New computational method simplifies the analysis of social contacts