(Press-News.org) A team of researchers from the University of British Columbia and BC Cancer have developed an artificial intelligence (AI) model that predicts cancer patient survival more accurately and with more readily available data than previous tools.
The model uses natural language processing (NLP) – a branch of AI that understands complex human language – to analyze oncologist notes following a patient’s initial consultation visit—the first step in the cancer journey after diagnosis. By identifying characteristics unique to each patient, the model was shown to predict six-month, 36-month and 60-month survival with greater than 80 per cent accuracy. The findings were published today in JAMA Network Open.
“Predicting cancer survival is an important factor that can be used to improve cancer care,” said lead author Dr. John-Jose Nunez, a psychiatrist and clinical research fellow with the UBC Mood Disorders Centre and BC Cancer. “It might suggest health providers make an earlier referral to support services or offer a more aggressive treatment option upfront. Our hope is that a tool like this could be used to personalize and optimize the care a patient receives right away, giving them the best outcome possible.”
Traditionally, cancer survival rates have been calculated retrospectively and categorized by only a few generic factors such as cancer site and tissue type. Despite familiarity with these rates, it can be challenging for oncologists to accurately predict an individual patient’s survival due to the many complex factors that influence patient outcomes.
The model developed by Dr. Nunez and his collaborators, which includes researchers from BC Cancer and UBC’s departments of computer science and psychiatry, is able to pick up on unique clues within a patient’s initial consultation document to provide a more nuanced assessment. It is also applicable to all cancers, whereas previous models have been limited to certain cancer types.
“The AI essentially reads the consultation document similar to how a human would read it,” said Dr. Nunez. “These documents have many details like the age of the patient, the type of cancer, underlying health conditions, past substance use, and family histories. The AI brings all of this together to paint a more complete picture of patient outcomes.”
The researchers trained and tested the model using data from 47,625 patients across all six BC Cancer sites located across British Columbia. To protect privacy, all patient data remained stored securely at BC Cancer and was presented anonymously. Unlike chart reviews by human research assistants, the new AI approach has the added benefit of maintaining complete confidentiality of patient records.
“Because the model is trained on B.C. data, that makes it a potentially powerful tool for predicting cancer survival here in the province,” said Dr. Nunez.
In the future, the technology could be applied in cancer clinics across Canada and around the world.
“The great thing about neural NLP models is that they are highly scalable, portable and don’t require structured data sets,” said Dr. Nunez. “We can quickly train these models using local data to improve performance in a new region. I would suspect that these models provide a good foundation anywhere in the world where patients are able to see an oncologist.”
Dr. Nunez is a recipient of the 2022/23 UBC Institute of Mental Health Marshall Fellowship, and is also supported by funding from the BC Cancer Foundation. In another stream of work, Dr. Nunez is examining how to facilitate the best-possible psychiatric and counselling care for cancer patients using advanced AI techniques. He envisions a future where AI is integrated into many aspects of the health system to improve patient care.
“I see AI acting almost like a virtual assistant for physicians,” said Dr. Nunez. “As medicine gets more and more advanced, having AI to help sort through and make sense of all the data will help inform physician decisions. Ultimately, this will help improve quality of life and outcomes for patients.”
Interview language(s): English
END
AI predicts cancer patient survival by reading doctor's notes
2023-03-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
For older adults, every 500 additional steps taken daily associated with lower heart risk
2023-03-02
Research Highlights:
A study of people ages 70 and older found walking an additional 500 steps per day, or an additional quarter mile of walking, was associated with a 14% lower risk of heart disease, stroke or heart failure.
Compared to adults who took less than 2,000 steps per day, adults who took about 4,500 steps per day had a 77% lower observed risk of experiencing a cardiovascular event.
Only about 3.5% of participants who took around 4,500 steps per day had a cardiovascular event, compared to 11.5% of those who took less than 2,000 steps per day, over the 3.5-year follow-up period.
Embargoed until 10:45 a.m. CT/11:45 a.m. ET, ...
American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery supports new clinical guidance on treatment of obesity in children and teens
2023-03-02
The American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) fully supports the new “Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Treatment of Children and Adolescents With Obesity” issued from the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) calling for earlier and more intensive treatment of obesity in children and teens. Published in the journal Pediatrics in February, this is the first comprehensive guideline on obesity in 15 years from the AAP, the largest professional association of pediatricians in the U.S.
According to AAP, more evidence ...
Many firearm owners in the U.S. store at least one gun unlocked, fearing an emergency
2023-03-02
Most firearm owners keep at least one firearm unlocked, with some viewing gun locks as an unnecessary obstacle to quick access in an emergency, according to a Rutgers study. But when they do lock their firearms, Rutgers researchers found that firearm owners are most likely to use gun safes.
In a study published in JAMA Network Open and funded by the Defense Health Agency, researchers surveyed a national sample of 2,152 English-speaking adult firearm owners, asking them what locking devices they used and why.
Unlike previous studies, participants were presented with both words and images describing each ...
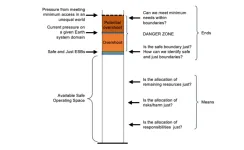
To ensure a safe and just future for people, nature and the planet, Earth System Boundaries must include justice, researchers find
2023-03-02
In a new study published in Nature Sustainability an international team of scientists from the Earth Commission, convened by Future Earth, investigates how global biophysical boundaries need to be adjusted to ensure a safe and just future for people, nature and the planet. The Earth Commission is the scientific cornerstone of the Global Commons Alliance
This new framework integrates methods to reduce harm to people, increase access to resources, address tradeoffs, and challenge powerful interests whilst addressing inequality between generations and between humans and nature ...
Genomic study of indigenous Africans paints complex picture of human origins and local adaptation
2023-03-02
Africa, where humans first evolved, today remains a place of remarkable diversity. Diving into that variation, a new analysis of 180 indigenous Africans from a dozen ethnically, culturally, geographically, and linguistically varied populations by an international scientific team offers new insights into human history and biology, and may inform precision medicine approaches of the future.
The work clarifies human migration histories, both historical and more recent, and provides genetic evidence of adaptation to local environments, ...
Energy: More than two million citizens power Europe’s renewable energy transition
2023-03-02
More than two million citizens across 30 European countries have been involved in thousands of projects and initiatives as part of efforts to transition to renewable energy, according to an analysis published in Scientific Reports. With investments ranging between 6.2 and 11.3 billion Euros, these findings highlight the important role of collective action in the decarbonisation of Europe.
The energy system in Europe is undergoing a significant transition towards renewables and decarbonisation. However, the contribution ...
Performance of outpatient surgical procedures before, after onset of pandemic
2023-03-02
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that despite calls for the expansion of outpatient surgery to mitigate the growing backlog of surgical cases in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, uptake of this practice occurred in only a small subset of operations. Further studies should explore potential barriers to the uptake of this approach, particularly for procedures that have been shown to be safe when performed in an outpatient setting.
Authors: Cornelius A. Thiels, D.O., M.B.A., of the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, is the corresponding author
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.1198)
Editor’s ...
Trends, variation in the use of active surveillance for management of low-risk prostate cancer
2023-03-02
About The Study: The results of this study of more than 20,000 men with low-risk prostate cancer suggest that active surveillance rates are rising nationally but are still suboptimal, and wide variation persists across practices and practitioners. Continued progress on this critical quality indicator is essential to minimize overtreatment of low-risk prostate cancer and by extension to improve the benefit-to-harm ratio of national prostate cancer early detection efforts.
Authors: Matthew R. Cooperberg, M.D., M.P.H., of the UCSF Helen Diller Family Comprehensive Cancer Center in San Francisco, is the corresponding ...
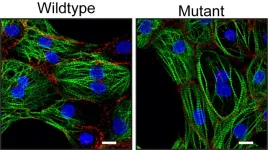
New mutation in the desmoplakin gene leads to ACM
2023-03-02
Researchers from the group of Eva van Rooij in collaboration with the UMC Utrecht identified a new mutation that leads to the cardiac disease arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy (ACM). They assessed the effect of this mutation on heart muscle cells and obtained new insights into the underlying mechanism that causes the disease. The results of this study, published on March 2nd in Stem Cell Reports, could contribute to the development of new treatments for ACM.
Desmosomes
Millions of heart muscle cells contract to let the heart fulfill ...
PCORI launches pioneering initiative offering up to $50 million to boost uptake of practice-changing health research findings in real-world settings
2023-03-02
WASHINGTON, DC – The Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) today kicked off a multiyear initiative with an initial investment of $50 million to advance the uptake of practice-changing comparative clinical effectiveness research results into health care practice with the selection of 42 U.S. health systems to participate in its groundbreaking Health Systems Implementation Initiative (HSII). In addition, PCORI initiated the first in two stages of HSII funding, focusing on initial capacity-building efforts.
The array of participating health systems representing a wide range of care settings and populations will develop and implement ...