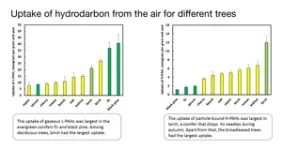
(Press-News.org) Conifers are generally better than broadleaved trees at purifying air from pollutants. But deciduous tree may be better at capturing particle-bound pollution. A new study led by the University of Gothenburg shows that the best trees for air purification depend on the type of pollutant involved.
Trees and other greenery in cities provide many benefits that are important for the well-being of residents. Leaves and needles on trees filter air pollutants and reduce exposure to hazardous substances in the air. But which trees purify the air most effectively? Researchers from the University of Gothenburg have collected leaves and needles from eleven different trees growing in the same place in the Gothenburg Botanical Garden’s arboretum (tree collection) to analyse which substances they have captured.
“This tree collection provides a unique opportunity to test many different tree-species with similar environmental conditions and exposure to air pollutants,” says Jenny Klingberg, a researcher at the Gothenburg Botanical Garden.
Harmful pollutants
A total of 32 different pollutants were analysed, some of which are bound to particles of various sizes. Others are gaseous. There is a proven connection between exposure to air pollutants and increased risk of cardiovascular diseases and airway problems. This project has focused on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). In cities, traffic is the biggest source of these pollutants, which are released due to incomplete combustion in engines.
“Our analyses show that different tree species have different abilities to absorb air pollutants. Conifers generally absorbed more gaseous PAHs than broadleaved trees. Another advantage of conifers is that they also act as air purifiers in winter, when air pollution is usually at its highest,” says Jenny Klingberg.
Needles clean air for many years
The researchers also saw that needles continued to absorb air pollutants for several years, which leaves cannot do for obvious reasons. But broadleaved trees had other advantages. They were more efficient at cleaning the air of particles, which is thought to be due to the leaves having a larger surface area to which particles can attach.
“The various species differed more than we expected. Larch, which is a conifer that sheds its needles each autumn, was best in test. Larch trees absorbed the most particle-bound pollutants, but were also good at capturing gaseous PAHs,” says Jenny Klingberg.
Needles and leaves do not, however, break down pollutants to any greater extent, even if sunlight can start that process. Thus there is a risk that the soil beneath the trees will be contaminated by pollutants when the leaves and needles shed and decompose. This places the ecosystem in the soil at risk of being affected, though this has not been investigated in the current study being published in the journal Ecological Indicators.
“The pollutants do not appear to impact the trees’ photosynthesis; leaf chlorophyll content is just as high in the most polluted areas of Gothenburg compared with trees that grow in less polluted environments. But this likely looks different in cities with even worse air quality,” says project leader Håkan Pleijel, professor of applied environmental science at the University of Gothenburg.
Careful urban planning is needed
However, you should not simply start filling city streets with trees to improve air quality for residents. Several factors determine the benefit. An alley of trees in a narrow street canyon can reduce air flow, negatively affecting dispersion and dilution of the air pollutants and therefore increase concentrations of contaminants locally on busy streets. This means that on narrow streets sheltered from wind, lower-growing vegetation, like hedges, may be preferable. Careful urban planning is necessary, combining different tree species to optimise air purification and to take into account other functions and benefits of trees, according to the researchers.
“This study contributes to improving our understanding of the ability of trees to clean the air and which species are best at absorbing air pollutants,” says Håkan Pleijel. This knowledge is important for urban planning when designing sustainable cities. While trees and greenery can contribute to better air quality in cities, at the end of the day the most important measure is to reduce emissions.
END
A mixture of trees purifies urban air best
2023-03-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
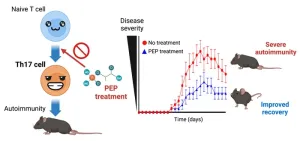
Potential treatment of autoimmune diseases revealed in new study
2023-03-06
Scientists in Japan have revealed a chemical compound that could be used for the treatment of various autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis. These diseases occur when the body’s immune response goes wiry. The immune system, which normally attacks pathogens and infections, instead attacks healthy cells and tissues. For the millions of people who suffer from autoimmune diseases worldwide, the result can be debilitating—rheumatoid arthritis causes excessive joint pain, while multiple sclerosis can disable one’s brain and spinal cord function.
“The key to the development of autoimmune ...
Physical activity and tailored support fails to deliver lasting benefits for smokers not ready to quit
2023-03-06
Promoting physical activity and other behavioural support can help people wanting to reduce their smoking to quit in the short-term.
However, after nine months, physical activity delivers no noticeable benefits – compared with offering no additional support – in the rates of people stopping smoking, according to the findings of a major national study.
The Trial of physical Activity and Reduction of Smoking (TARS) study, led by the University of Plymouth with funding from the National Institute for Health and Care Research, took place across four cities – Plymouth, Nottingham, Oxford and ...
Death rates from lung cancer will fall overall in the EU and UK in 2023, but rise among women in France, Italy and Spain
2023-03-06
A total of 1,261,990 people will die from cancer in 2023 in the EU (EU-27). A further 172,314 people will die from the disease in the UK, according to new research published in the leading cancer journal Annals of Oncology [1] today (Monday).
Researchers led by Carlo La Vecchia (MD), a professor at the University of Milan (Italy), estimate there will be a 6.5% fall in cancer death rates in men and a 3.7% fall in women between 2018 and 2023.
They predict that death rates from the ten most common cancers will continue to fall in most European countries in 2023, although the numbers of people dying will go up ...
As urban populations soar wastewater treatment struggles to find sustainable solutions
2023-03-06
Globally, activated sludge treats the majority of urban wastewaters; yet it is one of the most complex biological processes used. It is a sophisticated microbial process fraught with operational problems leading to occasional failures in achieving required effluent quality standards. With the increasing problem of partially treated and raw sewage entering rivers and estuaries, the pressure on the process to cope with ever increasing volumes of wastewater has never been so great.
With increasing volumes of dilute wastewater entering treatment plants the high variability in hydraulic and organic ...
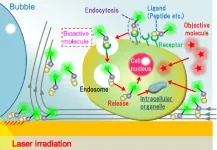
Light-induced acceleration of intracellular delivery
2023-03-06
Cell membranes are barriers that maintain cellular homeostasis, and the intracellular delivery of biologically functional molecules, including peptides, proteins, and nucleic acids to manipulate cellular functions. Conventional intracellular uptake processes require high concentrations of biofunctional molecules with low permeability to pass through the cell membrane. This results in low drug activity because the probability of the biofunctional molecules entering target cells and their organelles is low. In addition, many drugs damage healthy cells as well as the cells that are supposed to target due to poor selectivity, making ...
Physician workforce planning must adjust for aging population, changing practice patterns: New analysis
2023-03-06
Why are Canadians having problems accessing physicians despite historic highs in physician numbers? Factoring in changing demographics and physician work trends can help with physician workforce planning, according to a new analysis in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.221239.
"[T]he increasing [health care] needs of an aging population have been empirically important since around 2005, while the supply of physician service hours has simultaneously declined in a manner that is largely unrelated to the evolving age–sex composition of the physician workforce," writes Dr. Arthur Sweetman, ...
Pregnant people with schizophrenia have threefold risk of interpersonal violence
2023-03-06
Pregnant and postpartum people with schizophrenia have a more than threefold increase in the risk of an emergency department visit for interpersonal violence, compared with those without schizophrenia, according to a new study in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.220689.
Interpersonal violence can include physical, sexual and psychological abuse by a family member, intimate partner, acquaintance or stranger.
"Though we found a threefold increased risk for individuals with schizophrenia, we also found that ...
Testing for ApoB protein may be a more accurate marker for heart disease risk than testing for cholesterol alone
2023-03-05
Getting tested for levels of HDL (the good) and LDL (the bad) cholesterol is part of the annual physical exam. But emerging research is showing that these standard tests may not be the most accurate way to test for heart disease risk.
Instead, emerging data suggest that testing for levels of Apolipoprotein B-100 (ApoB), a protein that carries fat molecules, including LDL cholesterol – the so-called “bad cholesterol” – around the body, may be a more accurate risk predictor of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, which occurs ...
Alert banners dramatically increase prescribing rates of life-saving heart failure medication
2023-03-05
An automated system that flags which patients could most benefit from an underused yet life-saving cardiology drug more than doubled new prescriptions, according to a pilot program test by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine.
“Our findings suggest that tailored electronic notifications can boost the prescription of life-saving drugs,” said study lead author and cardiologist Amrita Mukhopadhyay, MD, a clinical instructor in the Department of Medicine at NYU Langone Health. “By compiling key information in one place, the system may help providers to spend less time searching through medical records during a visit ...
Cardiovascular risk factor prevalence, treatment, control in young adults
2023-03-05
About The Study: In this study of nearly 13,000 U.S. adults ages 20 to 44, diabetes and obesity increased from 2009 to March 2020, while hypertension did not change and hyperlipidemia declined. The data from this study show a high and rising burden of most cardiovascular risk factors in young U.S. adults, especially for Black, Hispanic, and Mexican American individuals.
Authors: Rishi K. Wadhera, M.D., M.P.P., M.Phil., of the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...