(Press-News.org) Trapped electrons traveling in circular loops at extreme speeds inside graphene quantum dots are highly sensitive to external magnetic fields and could be used as novel magnetic field sensors with unique capabilities, according to a new study.
Electrons in graphene (an atomically thin form of carbon) behave as if they were massless, like photons, which are massless particles of light. Although graphene electrons do not move at the speed of light, they exhibit the same energy-momentum relationship as photons and can be described as “ultra-relativistic.” When these electrons are confined in a quantum dot, they travel at high velocity in circular loops around the edge of the dot.
“These current loops create magnetic moments that are very sensitive to external magnetic fields,” explained Jairo Velasco Jr., associate professor of physics at UC Santa Cruz. “The sensitivity of these current loops stems from the fact that graphene electrons are ultra-relativistic and travel at high velocity.”
Velasco is a corresponding author of a paper on the new findings, published March 6 in Nature Nanotechnology. His group at UC Santa Cruz used a scanning tunneling microscope (STM) to create the quantum dots in graphene and study their properties. His collaborators on the project include scientists at the University of Manchester, U.K., and the National Institute for Materials Science in Japan.
“This was highly collaborative work,” Velasco said. “We did the measurements in my lab at UCSC, and then we worked very closely with theoretical physicists at the University of Manchester to understand and interpret our data.”
The unique optical and electrical properties of quantum dots—which are often made of semiconductor nanocrystals—are due to electrons being confined within a nanoscale structure such that their behavior is governed by quantum mechanics. Because the resulting electronic structure is like that of atoms, quantum dots are often called “artificial atoms.” Velasco’s approach creates quantum dots in different forms of graphene using an electrostatic “corral” to confine graphene’s speeding electrons.
“Part of what makes this interesting is the fundamental physics of this system and the opportunity to study atomic physics in the ultra-relativistic regime,” he said. “At the same time, there are interesting potential applications for this as a new type of quantum sensor that can detect magnetic fields at the nano scale with high spatial resolution.”
Additional applications are also possible, according to co-first author Zhehao Ge, a UCSC graduate student in physics. “The findings in our work also indicate that graphene quantum dots can potentially host a giant persistent current (a perpetual electric current without the need of an external power source) in a small magnetic field,” Ge said. “Such current can potentially be used for quantum simulation and quantum computation.”
The study looked at quantum dots in both monolayer graphene and twisted bilayer graphene. The graphene rests on an insulating layer of hexagonal boron nitride, and a voltage applied with the STM tip creates charges in the boron nitride that serve to electrostatically confine electrons in the graphene.
Although Velasco’s lab uses STM to create and study graphene quantum dots, a simpler system using metal electrodes in a cross-bar array could be used in a magnetic sensor device. Because graphene is highly flexible, the sensor could be integrated with flexible substrates to enable magnetic field sensing of curved objects.
“You could have many quantum dots in an array, and this could be used to measure magnetic fields in living organisms, or to understand how the magnetic field is distributed in a material or a device,” Velasco said.
The co-first authors of the paper are Zhehao Ge, a graduate student in Velasco’s lab at UCSC, and Sergey Slizovskiy at the University of Manchester. Vladimir Fal’ko at the University of Manchester is a corresponding author, and the other coauthors include Peter Polizogopoulos, Toyanath Joshi, and David Lederman at UC Santa Cruz, and Takashi Taniguchi and Kenji Watanabe at the National Institute for Materials Science in Japan. This work was supported in part by the National Science Foundation and the Army Research Office.
END
Graphene quantum dots show promise as novel magnetic field sensors
Physicists found that speeding electrons trapped in circular loops in graphene quantum dots are highly sensitive to external magnetic fields
2023-03-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Parental nonadherence to recommendations for COVID-19 prevention among children
2023-03-06
About The Study: In this survey study of U.S. parents, one-quarter engaged in misrepresentation or nonadherence regarding public health measures for their children. The most common reason was to preserve parental autonomy. Additional reasons included wanting to resume a normal life for their child and the inability to miss work or other responsibilities, among other reasons.
Authors: Andrea Gurmankin Levy, Ph.D., M.B.E., of Middlesex Community College in Middletown, Connecticut, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our ...
Mineral particles and their role in oxygenating the Earth’s atmosphere
2023-03-06
Mineral particles played a key role in raising oxygen levels in the Earth’s atmosphere billions of years ago, with major implications for the way intelligent life later evolved, according to new research.
Up to now, scientists have argued that oxygen levels rose as the result of photosynthesis by algae and plants in the sea, where oxygen was produced as a by-product and released into the atmosphere.
But a research ...
Two-dimensional quantum freeze
2023-03-06
Glass nanoparticles trapped by lasers in extreme vacuum are considered a promising platform for exploring the limits of the quantum world. Since the advent of quantum theory, the question at which sizes an object starts being described by the laws of quantum physics rather than the rules of classical physics has remained unanswered.
A team formed by Lukas Novotny (Zurich), Markus Aspelmeyer (Vienna), Oriol Romero-Isart (Innsbruck), and Romain Quidant (Zurich) is attempting to answer precisely this question within the ERC-Synergy project Q-Xtreme. A crucial step ...
Scientists twist chemical bonds beyond their limits
2023-03-06
A group of scientists from Durham University and University of York have twisted molecules to their breaking point in order to challenge the understanding of chemical bonds.
The researchers explored how far the chemical bonding in an aromatic ring can be twisted before its aromatic bonding breaks.
They achieved this by making overcrowded aromatic rings. Rather than benzene, they used tropylium, which shares electrons around a ring of seven carbon atoms.
Each of these carbon atoms can be functionalised and having seven attachment points in the ring, rather than the six carbon atoms of benzene, allowed ...
Siblings should be screened in cases of suspected child physical abuse
2023-03-06
Siblings of a child suspected of experiencing physical abuse should also be screened for abusive injuries, according to a new international consensus statement led by researchers at UCL (University College London) and Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children (GOSH).
The team of 27 researchers, from six different continents, are calling for a policy change to stop inconspicuous injuries being missed in contact children (i.e. siblings, cohabiting children, or children who are under the same care), and to help prevent further ...
Rewarding accuracy instead of partisan pandering reduces Republican-Democrat divide over the truth – study
2023-03-06
Offering a tiny cash reward for accuracy, or even briefly appealing to personal integrity, can increase people’s ability to tell the difference between misinformation and the truth, according to a new study.
The findings suggest that fake news thrives on social media not only because people are tricked into believing it, but also due to a motivational imbalance: users have more incentive to get clicks and likes than to spread accurate content.
Social psychologists from the University of Cambridge and New York University argue that their study, published in the journal ...
New study compares human contributions to Mississippi river delta land loss, hints at solutions
2023-03-06
Research from scientists at Louisiana State University and Indiana University reveals new information about the role humans have played in large-scale land loss in the Mississippi River Delta—crucial information in determining solutions to the crisis.
The study published today in Nature Sustainability compares the impacts of different human actions on land loss and explains historical trends. Until now, scientists have been unsure about which human-related factors are the most consequential, and why the most rapid land loss in the Mississippi River Delta occurred between the 1960s and 1990s and ...
UCLA engineers design solar roofs to harvest energy for greenhouses
2023-03-06
As countries around the globe seek sustainable energy sources and the U.S. endeavors to become a net-zero emissions economy by 2050, renewable energy sources such as solar panels are in high demand.
However, solar panels can take up significant space and are often difficult to scale. Enter the new field of agrivoltaics, which focuses on the simultaneous use of land for both solar power generation and agriculture. For example, replacing the glass in greenhouses with solar panels could power the lamps and water controls in the greenhouse, or even the whole farm. But how does one build solar panels that can absorb energy from sunlight without blocking the light ...
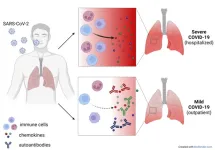
'Good autoantibodies' could help against long Covid
2023-03-06
Sometimes in the laboratory there are unexpected results. "Previously it had been observed that autoantibodies are common in severe Covid patients, those who end up in intensive care," says Jonathan Muri, postdoctoral fellow at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB, affiliated with the Università della Svizzera italiana) and co-author of the study. "Instead, in this case we discovered the opposite."
The autoantibodies in question neutralize chemokines, molecules that direct immune cell trafficking. "Chemokines are a bit like traffic lights: they tell our immune cells when and where to go in the case ...
Drones and deep learning: researchers develop a new technique to quantify rice production
2023-03-06
Rice, a major food crop, is cultivated on nearly 162 million hectares of land worldwide. One of the most commonly used methods to quantify rice production is rice plant counting. This technique is used to estimate yield, diagnose growth, and assess losses in paddy fields. Most rice counting processes across the world are still carried out manually. However, this is extremely tedious, laborious, and time-consuming, indicating the need for faster and more efficient machine-based solutions.
Researchers from China ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
Researchers find that landowner trust, experience influence feral hog management
Breaking down the battery problem
[Press-News.org] Graphene quantum dots show promise as novel magnetic field sensorsPhysicists found that speeding electrons trapped in circular loops in graphene quantum dots are highly sensitive to external magnetic fields