(Press-News.org) The cells that make up the human brain begin developing long before the physical shape of the brain has formed. This early organizing of a network of cells plays a major role in brain health throughout the course of a lifetime. Numerous studies have found that mothers with low iron levels during pregnancy have a higher risk of giving birth to a child that develops cognitive impairments like autism, attention deficit syndrome, and learning disabilities. However, iron deficiency is still prevalent in pregnant mothers and young children.
The mechanisms by which gestational iron deficiency (GID) contributes to cognitive impairment are not fully understood. The laboratory of Margot Mayer- Proschel, PhD, a professor of Biomedical Genetics and Neuroscience at the University of Rochester Medical Center, was the first to demonstrated that the brains of animals born to iron-deficient mice react abnormally to excitatory brain stimuli, and that iron supplements giving at birth does not restore functional impairment that appears later in life. Most recently, her lab has made a significant progress in the quest to find the cellular origin of the impairment and have identified a new embryonic neuronal progenitor cell target for GID. This study was recently published in the journal Development.
“We are very excited by this finding,” Mayer-Proschel said, who was awarded a $2 million grant from the National Institute of Child Health & Human Development in 2018 to do this work. “This could connect gestational iron deficiency to these very complex disorders. Understanding that connection could lead to changes to healthcare recommendations and potential targets for future therapies.”
Building the map
Michael Rudy, PhD, and Garrick Salois, who were both graduate students in the lab and co-first authors of the study, worked backward to make this connection. By looking at the brains of adults and young mice born with known GID, they found disruption of interneurons, cells that control the balance of excitation and inhibition and ensure that the mature brain can respond appropriately to incoming signals. These interneurons are known to develop in a specific region of the embryonic brain called the medial ganglionic eminence—where specific factors define the fate of early neuronal progenitor cells that then divide, migrate, and mature into neurons that populate the developing cerebral cortex. The researchers found that this specific progenitor cell pool was disrupted in embryonic brains exposed to GID. These findings provide evidence that GID affects the behavior of embryonic progenitor cells causing the creation of a suboptimal network of specialized neurons later in life.
“As we looked back, we could identify when the progenitor cells started acting differently in the iron-deficient animals compared to iron normal controls,” Mayer-Proschel said. “This confirms that the correlation between the cellular change and GID happens in early utero. Translating the timeline to humans would put it in the first three months of gestation before many women know they are pregnant.”
Moving the next model closer to humans
Having identified cellular targets in a mouse model of GID, Neuroscience graduate student Salois in the Mayer-Proschel lab is now establishing a human model of iron deficiency using brain organoids—a mass of cells, in this case that represent a brain. These “mini brains” that look more like tiny balls that need a microscope to be studied, can be instructed to form specific regions of the ganglionic eminences of the embryonic human brain. With these researchers can mimic the development of the neuronal progenitor cells that are targeted by GID in the mouse.
“We believe this model will not only allow us to determine the relevance of our finding in the mouse model for the human system but will also enable us to find new cellular targets for GID that are not even present in mouse models,” said Mayer-Proschel. “Understanding such cellular targets of this prevalent nutritional deficiency will be imperative to take the steps necessary to make changes to how we think of maternal health. Iron is an important part of that, and the limited impact of iron supplementation after birth makes it necessary to identify alternative approaches,”
Additional authors include Janine Cubello, PhD, and Robert Newell at the University of Rochester. This research was supported by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development at the National Institute of Health, the Toxicology training grant of the Environmental Health Department at the University of Rochester, the New York Stem Cell Training Grant, and the Kilian J. and Caroline F. Schmitt Foundation through the Del Monte Institute for Neuroscience Pilot Program.
END
Iron & the brain: Where and when neurodevelopmental disabilities may begin during pregnancy
Researchers identify possible cellular origin for impairments associated with gestational iron deficiency
2023-03-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Long-term intermittent fasting reduces COVID-19 heart failure complications and death in patients with previous heart disease
2023-03-06
Intermittent fasting, especially when done over the course of decades, can have positive effects on metabolic and cardiovascular health. Now, a new study by researchers at Intermountain Health in Salt Lake City finds that it may also add an extra layer of protection from heart-related COVID-19 complications in people who had already sought cardiac care.
“We already know that regular fasting over long periods of time can lead to overall health improvements. Here we found that it may also lead to better outcomes in COVID-19 patients who required a cardiac catheterization,” said Benjamin Horne, PhD, director of cardiovascular and genetic epidemiology ...
Study finds residual inflammation after statin therapy strongly predicted cardiovascular events, death
2023-03-06
New evidence released today from a study of 31,245 patients already taking statin therapy indicates that inflammation may be a more powerful predictor of risk of future cardiovascular events—such as heart attack and stroke — than “bad” cholesterol. Treatments that aggressively lower vascular inflammation need to be incorporated into daily practice if doctors are to maximize patient outcomes, according to the study’s corresponding author, Paul Ridker, MD, a preventive cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General ...
Study finds exhaled breath could enhance detection, diagnosis of COVID-19 and variants
2023-03-06
The emergence of new COVID-19 variants has led to reduced accuracy across current rapid testing methods, but a recent University of Michigan study suggests that a patient’s breath might hold the key to a more precise diagnosis.
Investigators from the University of Michigan’s Max Harry Weil Institute for Critical Care Research and Innovation, including faculty and students from the College of Engineering and Michigan Medicine, used portable gas chromatography to examine breath samples collected during the pandemic’s Delta ...
Some ‘allies’ don’t want gay neighbors
2023-03-06
In a survey of 545,531 people, 8.5% of those who said they were ‘fully accepting’ of gay people did not want gay neighbors.
First study to explore stigmatizing behaviors expressed by avid supporters of sexual minorities
‘Simple legal inclusion can help mobilize the accepting population to their fullest potential’
CHICAGO --- When legal systems choose to offer no protections to sexual minorities, even avid LGBTQ supporters would reject their gay neighbors, reports a new Northwestern Medicine study.
The study examined ...
An innovative twist on quantum bits: Tubular nanomaterial of carbon makes ideal home for spinning quantum bits
2023-03-06
Scientists find that a tubular nanomaterial of carbon makes for ideal host to keep quantum bits spinning in place for use in quantum information technologies.
Scientists are vigorously competing to transform the counterintuitive discoveries about the quantum realm from a century past into technologies of the future. The building block in these technologies is the quantum bit, or qubit. Several different kinds are under development, including ones that use defects within the symmetrical structures of diamond and silicon. They may one day transform computing, accelerate drug discovery, generate unhackable networks and more.
Working with researchers from several universities, scientists ...
LOINC continues facilitating health data interoperability with biannual issuance of new concepts
2023-03-06
INDIANAPOLIS -- LOINC® from Regenstrief Institute is issuing its semi-annual release, which contains 608 new concepts to help health systems, laboratories and other health organizations accurately exchange medical data. Some of the new information has been released in coordination with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Association of Public Health Laboratories.
“Aligning the release of LOINC with emerging healthcare trends is an important component of our mission and critical in promoting effective health information exchange among providers, patients and health systems,” said Marjorie Rallins, ...
New study uncovers key culprit behind pediatric brain cancer metastasis
2023-03-06
New research pinpoints a key cause of metastasis from an aggressive form of brain cancer in children and provides a potential new therapy for treating these tumors in the future.
In a paper, published in Nature Cell Biology, physician-scientists from the University of Pittsburgh and UPMC Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh discovered that medulloblastomas hijack a skill that normal brain cells use during their early development and then manipulate it to help tumors spread.
“Children with medulloblastomas that have not yet metastasized may have a high likelihood of long-term survival, but if ...
Can artificial intelligence help find life on Mars or icy worlds?
2023-03-06
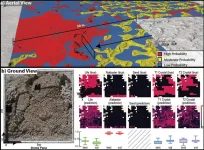
March 6, 2023, Mountain View, CA – Wouldn’t finding life on other worlds be easier if we knew exactly where to look? Researchers have limited opportunities to collect samples on Mars or elsewhere or access remote sensing instruments when hunting for life beyond Earth. In a paper published in Nature Astronomy, an interdisciplinary study led by SETI Institute Senior Research Scientist Kim Warren-Rhodes, mapped the sparse life hidden away in salt domes, rocks and crystals at Salar de Pajonales at the boundary of the Chilean Atacama Desert and Altiplano. Then they trained a machine learning model to recognize the patterns and rules associated with their distributions ...
Geosciences at the Crossroads of America
2023-03-06
Boulder, Colo., USA: Oklahoma State University is hosting the 57th annual meeting of the Geological Society of America’s South-Central Section on 13–14 March. The meeting will have a diverse program of workshops, technical sessions, short courses, and field trips that covers a spectrum of geologic disciplines.
The list below highlights a selection of environmental-related session topics you might like:
· Tar Creek Superfund Site Field Trip (Field Trip)
Managed Aquifer Recharge in the Arbuckle Simpson Aquifer (Field Trip)
Geoscience Career Workshop: Career Planning and Networking
· Hydrogeologic Challenges and Roles ...
Gene and cell therapies to combat pancreatic cancer
2023-03-06
Pancreatic cancer is an incurable form of cancer, and gene therapies are currently in clinical testing to treat this deadly disease. A comprehensive review of the gene and cell biotherapies in development to combat pancreatic cancer is published in the peer-reviewed journal Human Gene Therapy. Click here to read the article now
The article titled “Pancreatic Cancer Cell and Gene Biotherapies: Past, Present and Future,” contributed by corresponding author Pierre Cordelier, from the University of Toulouse, and coauthors, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
[Press-News.org] Iron & the brain: Where and when neurodevelopmental disabilities may begin during pregnancyResearchers identify possible cellular origin for impairments associated with gestational iron deficiency