(Press-News.org)
“Selective protection of normal cells may transform therapy of cancer.”
BUFFALO, NY- March 13, 2023 – A new review paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on March 11, 2023, entitled, “Selective protection of normal cells from chemotherapy, while killing drug-resistant cancer cells.”
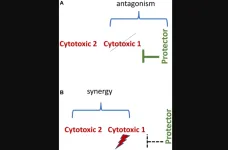
Cancer therapy is limited by toxicity in normal cells and drug-resistance in cancer cells. In his latest review, Mikhail V. Blagosklonny, M.D., Ph.D., from Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center discusses the theory that cancer resistance to certain therapies can be exploited for protection of normal cells—simultaneously enabling the selective killing of resistant cancer cells by using antagonistic drug combinations, which include cytotoxic and protective drugs.
“No cancer cell, no matter how resistant it is, can survive chemotherapy in a cell culture. In the organism, however, therapy of cancer is limited by killing or damaging normal cells. Selective protection of normal cells from chemotherapy would increase the therapeutic window, improving the therapeutic outcome. Needless to say, reduction of side effects and better quality of life are very important for a cancer patient.”
Depending on the mechanisms of drug-resistance in cancer cells, the protection of normal cells can be achieved with inhibitors of CDK4/6, caspases, Mdm2, mTOR, and mitogenic kinases. When normal cells are protected, the selectivity and potency of multi-drug combinations can be further enhanced by adding synergistic drugs, in theory, eliminating the deadliest cancer clones with minimal side effects.
“I also discuss how the recent success of Trilaciclib may foster similar approaches into clinical practice, how to mitigate systemic side effects of chemotherapy in patients with brain tumors and how to ensure that protective drugs would only protect normal cells (not cancer cells) in a particular patient.”
Read the full review: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28382
Correspondence to: Mikhail V. Blagosklonny
Emails: Blagosklonny@oncotarget.com, Blagosklonny@rapalogs.com
Keywords: oncology, resistance, cyclotherapy, trilaciclib, rapamycin
About Oncotarget: Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
To learn more about Oncotarget, visit Oncotarget.com and connect with us on social media:
Twitter
Facebook
YouTube
Instagram
LinkedIn
Pinterest
LabTube
Soundcloud
For media inquiries, please contact: media@impactjournals.com.
Oncotarget Journal Office
6666 East Quaker Str., Suite 1A
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957 (option 2)
###
END
Insect pests which attack crops have extraordinary powers to develop resistance to greener pesticides and a new way to manage resistance risks is needed, according to analysis by University of Stirling scientists.
For more than 70 years, agriculture’s response to pesticide resistance has been to seek new pesticides in an endless race to keep up with evolving pests.
Researchers now propose a new way to step off this treadmill as farmers embrace the ongoing green revolution in pest control by switching to biopesticides derived from natural organisms.
The evolution of resistance to biopesticides - a crucial tool in ...
Racial minorities in the United States are less likely to receive treatment for prostate cancer and, overall, have worse survival outcomes compared to individuals who are white. Typically, patient-level and physician-level factors have been used to explain the racial and socioeconomic differences in prostate cancer disparities. However, a new study led by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, investigated the role of facilities themselves ...
-With pictures-
Scientists have demonstrated in a new study that carbon-based molecules can be much more dynamic than previously thought.
When a carbon atom forms four bonds to different groups, the molecule can exist in two mirror image forms. These mirror image forms are vital in medicine because they have different biological activities.
Usually, it is impossible to interconvert between these ‘enantiomers’ because to do so would require a bond to be broken, a process that needs too much energy.
The researchers ...
A new study of Antarctic minke whales reveals a minimum size limit for whales employing the highly efficient “lunge-feeding” strategy that enabled the blue whale to become the largest animal on Earth.
Lunge feeding whales accelerate toward a patch of prey, engulf a huge volume of water, and then filter out the prey through the baleen plates in their mouths. This strategy is used by the largest group of baleen whales, known as rorquals, which includes blue, fin, humpback, and minke whales.
The ability ...
Scientists have discovered why breast cancer cells that have spread to the lungs may ‘wake up’ following years of sleep - forming incurable secondary tumours.
Their research, funded by Breast Cancer Now, reveals the mechanism that triggers this breast cancer 'time bomb' – and suggests a strategy to defuse it.
Patients with oestrogen receptor positive (ER+) breast cancer – the most common type – have a continued risk of their cancer recurring in another part of their body for many years or even decades after their original ...
Not all probiotics are created equal. In a new study, researchers found that certain enzymes within a class known as bile salt hydrolases (BSHs) can restrict Clostridioides difficile (C. diff.) colonization by both altering existing bile acids and by creating a new class of bile acids within the gut's microbial environment. The work could lead to “designer” probiotics that protect against disease by introducing specific BSHs to the gut after antibiotic treatment.
Selecting the right suite of BSH-producing bacteria is critical, because the study found that interactions between BSHs and bile acids ...
New York, NY (March 13, 2023) – Researchers have identified two previously unknown genes linked to schizophrenia and newly implicated a third gene as carrying risk for both schizophrenia and autism. Led by the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, the multi-center study further demonstrated that the schizophrenia risk conferred by these rare damaging variants is conserved across ethnicities. The study may also point to new therapeutics.
The findings were published in the March 13 online issue of Nature ...
A new study has highlighted how and when changes to the environment result in animal-borne disease thresholds being breeched, allowing for a better understanding and increased capacity to predict the risk of transmissions.
For the first time, researchers from Griffith University, Stanford University and the University of California used cumulative pressure mapping and machine learning to better understand how six vector-borne diseases (those transmitted by biting insects) found in different environments responded to the effects of human pressures.
Published in Nature Sustainability, the research found diseases associated with ...
How does an iPhone predict the next word you’re going to type in your messages? The technology behind this, and also at the core of many AI applications, is called a transformer; a deep-learning algorithm that detects patterns in datasets.
Now, researchers at EPFL and KAIST have created a transformer for Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs), a class of porous crystalline materials. By combining organic linkers with metal nodes, chemists can synthesize millions of different materials with potential applications in energy storage and gas separation.
The “MOFtransformer” is designed to be the ChatGPT for researchers that study MOFs. It’s architecture is based ...
HOUSTON – (March 13, 2023) – Physicists were surprised by the 2022 discovery that electrons in magnetic iron-germanium crystals could spontaneously and collectively organize their charges into a pattern featuring a standing wave. Magnetism also arises from the collective self-organization of electron spins into ordered patterns, and those patterns rarely coexist with the patterns that produce the standing wave of electrons physicists call a charge density wave.
In a study published this week in Nature Physics, Rice University physicists Ming Yi and Pengcheng Dai, and many of their collaborators from the 2022 ...