(Press-News.org) A new study has highlighted how and when changes to the environment result in animal-borne disease thresholds being breeched, allowing for a better understanding and increased capacity to predict the risk of transmissions.
For the first time, researchers from Griffith University, Stanford University and the University of California used cumulative pressure mapping and machine learning to better understand how six vector-borne diseases (those transmitted by biting insects) found in different environments responded to the effects of human pressures.
Published in Nature Sustainability, the research found diseases associated with lower human pressure, including malaria, cutaneous leishmaniasis and visceral leishmaniasis, gave way to diseases associated with high human pressure, such as dengue, chikungunya and Zika.
Human impact on the earth
“People are really good at modifying the earth – as much as 95% of the earth’s surface has been modified in some way by humans,” said Dr Eloise Skinner, the study’s lead researcher from Griffith’s Centre for Planetary Health and Food Security.
“We know that when we modify the earth’s surface we also change the species community, which includes plants, animals and insects.
“What we haven’t known until recently is how these changes to species change the risk of disease to humans.”
Dr Skinner said the findings enhance the ability to anticipate these transitions, would support a dynamic public healthcare infrastructure that could adapt to changes in disease occurrence through space and time.
Vector-borne diseases a global challenge
Vector-borne diseases (VBDs) are highly responsive to environmental changes, but such responses are notoriously difficult to isolate because pathogen transmission depends on a suite of ecological and social responses in vectors and hosts that may differ across species.
With more than half of the global population at risk of being infected with a VBD, Dr Skinner and the team acknowledged how changes to environments impacted on each disease’s unique transmission cycle presented various complexities.
"Often, vectors and pathogens occupy their own unique niche, so that each transmission cycle responds distinctly to environmental change," she said.
“With increasing human pressure, one would expect transitions in the occurrence of different diseases – for example, dengue is a highly urban pathogen while malaria occurs at the frontiers of deforestation.
“But how urban does an area have to be for dengue to become a risk? How much forest has to be converted before we start to see increases in malaria?”
These are some of the research questions the team sought answers to, to highlight the thresholds of land-use transitions that could lead to abrupt shifts in infectious disease burdens and public health needs.
Impact thresholds identified, a first
For the first time, the researchers were able to identify distinct thresholds of human impacts that specific diseases occupied.
Comparing across six vector-borne diseases in Brazil, the team found that in a critical window in which human footprint changed from moderate (4-7) to high (7-12) to intense (>12), disease occurrence abruptly shifted from malaria, cutaneous leishmaniasis, and visceral leishmaniasis to dengue, chikungunya, and Zika (arboviruses transmitted by the urban mosquito Aedes aegypti).
“These are diseases that require distinct responses in vector control, diagnostics, and environmental management,” Dr Skinner said.
“Because biomedical and chemical approaches alone have failed to sustainably eliminate these diseases, managing the socio-ecological settings that promote pathogen transmission is a critical frontier for planetary health.
“In conjunction with climatic pressures, human pressure presents a major risk for disease emergence and transmission and therefore a major threat to human and environmental wellbeing.
“Brazil was an ideal case study for assessing human pressure on disease transmission because it is a large, ecologically and socio-economically diverse country that contains many biogeographic zones, intense and variable land use pressures, high incidence of multiple diseases with contrasting ecologies, and a longstanding nationwide disease surveillance system.”
The research ‘Human footprint is associated with shifts
END
Changing landscapes alter disease-scapes: Study
2023-03-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New AI model transforms understanding of metal-organic frameworks
2023-03-13
How does an iPhone predict the next word you’re going to type in your messages? The technology behind this, and also at the core of many AI applications, is called a transformer; a deep-learning algorithm that detects patterns in datasets.
Now, researchers at EPFL and KAIST have created a transformer for Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs), a class of porous crystalline materials. By combining organic linkers with metal nodes, chemists can synthesize millions of different materials with potential applications in energy storage and gas separation.
The “MOFtransformer” is designed to be the ChatGPT for researchers that study MOFs. It’s architecture is based ...
Magnetism fosters unusual electronic order in quantum material
2023-03-13
HOUSTON – (March 13, 2023) – Physicists were surprised by the 2022 discovery that electrons in magnetic iron-germanium crystals could spontaneously and collectively organize their charges into a pattern featuring a standing wave. Magnetism also arises from the collective self-organization of electron spins into ordered patterns, and those patterns rarely coexist with the patterns that produce the standing wave of electrons physicists call a charge density wave.
In a study published this week in Nature Physics, Rice University physicists Ming Yi and Pengcheng Dai, and many of their collaborators from the 2022 ...
Beheshti conducting tribological study of propulsion shaft materials subjected to advanced surface strengthening treatments
2023-03-13
Ali Beheshti, Assistant Professor, Mechanical Engineering, received funding for the project: "Surface Integrity and Tribological Study of Propulsion Shaft Materials Subjected to Advanced Surface Strengthening Treatments."
In this project, Beheshti and his team are conducting detailed analyses of IN625, a nickel-based superalloy, and Ni-Cu, alloys of copper and nickel, subjected to an advanced laser peening (LP) process. The process uses very high-speed laser generated shock waves applied to the material and results in significant mechanical strength.
Specifically, they are studying unpeened, ...
Gut microbiome plays key role in response to CAR-T cell cancer immunotherapy
2023-03-13
Scientists from German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), together with colleagues from Germany, Israel, and the USA, have found that the gut microbiome may modulate the efficacy of CAR-T cellular immunotherpy CAR-T cells in patients with B cell lymphomas. Individualized microbiome information retreaved from patients‘ gut microbiomes prior to initiation of CAR T therapy could accurately predict their subsequent responsiveness to therapy, but only in the condition that these patients were not pre-treated with broad spectrum ...
IPK researcher use TurboID to uncover new meiotic proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana
2023-03-13
During meiosis, reshuffling of genetic information between homologous chromosomes through meiotic recombination creates variable gametes and hence genetic variation in offsprings. Meiotic recombination occurs in the context of the meiotic chromosome axis, a proteinaceous structure along which sister chromatids are arranged in a loop base array during prophase I. Data across organisms suggests meiotic chromosome axis serving as a scaffold for meiotic recombination.
In the model plant A. thaliana, the axis associated proteins ASY1 and ASY3 are critical for synapsis and meiotic recombination. “Due to the key role of axis proteins such as ...
Superstore MXene: New proton hydration structure determined
2023-03-13
One of the biggest challenges for a climate-neutral energy supply is the storage of electrical energy. Conventional batteries can hold large amounts of energy, but the charging and discharging processes take time. Supercapacitors, on the other hand, charge very quickly but are limited in the amount of stored energy. Only in the last few years has a new class of materials been discussed that combines the advantages of batteries with those of supercapacitors, named pseudocapacitors.
Promising materials: Pseudocapacitors
Among pseudocapacitive materials, so-called MXenes consisting of a large family of 2D transition metal carbides and nitrides appear particularly promising. Their structure ...
Fewer sports injuries with digital information
2023-03-13
The number of injuries in youth athletics is significantly reduced when coaches and parents have access to digital information on adolescent growth. It also takes twice as long for the first injury to occur. This is shown in a study from Linköping University published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
Many promising athletes have had their careers ruined because of injuries. One thing that almost all events in athletics have in common is a high load for a short time, as in jumping, throwing and running. ...
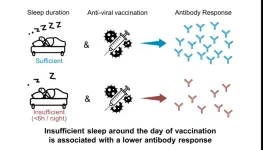
Getting a good night’s sleep could boost your response to vaccination
2023-03-13
We all know how important sleep is for mental health, but a meta-analysis publishing in the journal Current Biology on March 13 found that getting good shut-eye also helps our immune systems respond to vaccination. The authors found that people who slept less than six hours per night produced significantly fewer antibodies than people who slept seven hours or more, and the deficit was equivalent to two months of antibody waning.
“Good sleep not only amplifies but may also extend the duration of protection of the vaccine,” says senior author Eve Van Cauter, professor emeritus at the University of Chicago who, along ...
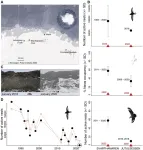
Entire populations of Antarctic seabirds fail to breed due to extreme, climate-change-related snowstorms
2023-03-13
The arrival of the new year is a prime time for Antarctic birds like the south polar skua, Antarctic petrel, and snow petrel to build nests and lay their eggs. However, from December 2021 to January 2022, researchers did not find a single skua nest on Svarthamaren, one of the regions where the birds go to raise their young. Similarly, the number of Antarctic petrel and snow petrel nests dropped to almost zero.
In these regions, climate change caused snowfall and snow accumulation to be significantly higher than in previous years. Now, a study published on March 13 in the journal Current Biology shows that these unusually strong snowstorms ...
Assessment of the risk of venous thromboembolism in non-hospitalized patients with COVID-19
2023-03-13
About The Study: In this study of 398,000 adult outpatients with COVID-19, the absolute risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) was low. Several patient-level factors were associated with higher VTE risk; these findings may help identify subsets of patients with COVID-19 who may benefit from more intensive surveillance or VTE preventive strategies.
Authors: Margaret C. Fang, M.D., M.P.H., of the University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.2338)
Editor’s ...