(Press-News.org) The number of injuries in youth athletics is significantly reduced when coaches and parents have access to digital information on adolescent growth. It also takes twice as long for the first injury to occur. This is shown in a study from Linköping University published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
Many promising athletes have had their careers ruined because of injuries. One thing that almost all events in athletics have in common is a high load for a short time, as in jumping, throwing and running. This leads to overuse injuries such as groin pain and sore shoulders but also sudden injuries such as ankle sprain and hamstring tear.
Jenny Jacobsson is a physiotherapist and visiting researcher at the Athletics Research Center at Linköping University. She has worked as a medical coordinator for the Swedish national athletics team for many years and has seen the impact of injuries on athletes.
“Before the 2008 Beijing Olympics, we saw many injuries in our national team and tried to figure out why. At the time, no survey had been done of injury incidence in athletics athletes. But we wanted to find out what was happening among our elite athletes from age 16 and up, including adult elite athletes,” says Jenny Jacobsson.
The survey of injuries in Swedish athletics showed that one of the main causes of injury was prior injury. This means that the earlier an athlete is injured in their career, the higher the likelihood that they will be injured later and more frequently. But causes of injury in youth sports is a complex matter, associated with everything from training amount and load to equipment, and even sleep.
Together with her colleagues at the Athletics Research Center, Jenny Jacobsson has developed a digital health platform containing information for parents and youth coaches on adolescent growth and how this is affected by training, with a focus on athletics athletes aged 12–15.
To investigate whether this type of platform can prevent injuries, the researchers carried out a study where 21 athletics clubs with athletes aged 12–15 were randomised into two groups: an intervention group and a control group. For four months during the early season, the intervention group parents and coaches were given access to the digital information platform, which at the time was not open to outsiders (but is now open to anyone). They were also regularly encouraged to log in and explore its content.
The researchers noted that the clubs given access to the information showed significantly lower injury incidence and that it took twice as long for the first injury to occur. Moreover, the effect was greater in large clubs. The results, published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine, can point the way to more injury-free athletics.
“We haven’t investigated the mechanism leading to change, but we can see that digital information works when it comes to injury prevention. If coaches and parents learn to recognise the problems, it’s possible to reduce the training load in time. Medically we know what is happening in growing bodies, but getting the information out to those who can benefit from it has been a challenge. This platform may bridge that gap,” says Jenny Jacobsson.
The study was financed by the Swedish Research Council for Sport Science (Centrum för idrottsforskning).
Facts: The digital health platform tested in the study is friskfriidrott.se, which is aimed mainly at youth sports coaches and parents of athletes aged 12–15. More information for other age groups has since been developed. For the duration of the study, the platform was not open to outsiders. It is now open to anyone. Visit friskfriidrott.se/en for further information.
END
Fewer sports injuries with digital information
2023-03-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Getting a good night’s sleep could boost your response to vaccination
2023-03-13
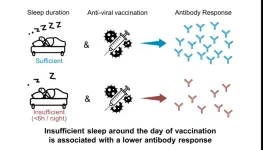
We all know how important sleep is for mental health, but a meta-analysis publishing in the journal Current Biology on March 13 found that getting good shut-eye also helps our immune systems respond to vaccination. The authors found that people who slept less than six hours per night produced significantly fewer antibodies than people who slept seven hours or more, and the deficit was equivalent to two months of antibody waning.
“Good sleep not only amplifies but may also extend the duration of protection of the vaccine,” says senior author Eve Van Cauter, professor emeritus at the University of Chicago who, along ...
Entire populations of Antarctic seabirds fail to breed due to extreme, climate-change-related snowstorms
2023-03-13
The arrival of the new year is a prime time for Antarctic birds like the south polar skua, Antarctic petrel, and snow petrel to build nests and lay their eggs. However, from December 2021 to January 2022, researchers did not find a single skua nest on Svarthamaren, one of the regions where the birds go to raise their young. Similarly, the number of Antarctic petrel and snow petrel nests dropped to almost zero.
In these regions, climate change caused snowfall and snow accumulation to be significantly higher than in previous years. Now, a study published on March 13 in the journal Current Biology shows that these unusually strong snowstorms ...
Assessment of the risk of venous thromboembolism in non-hospitalized patients with COVID-19
2023-03-13
About The Study: In this study of 398,000 adult outpatients with COVID-19, the absolute risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) was low. Several patient-level factors were associated with higher VTE risk; these findings may help identify subsets of patients with COVID-19 who may benefit from more intensive surveillance or VTE preventive strategies.
Authors: Margaret C. Fang, M.D., M.P.H., of the University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.2338)
Editor’s ...
Remote blood pressure management program enhanced care during pandemic
2023-03-13
BOSTON – Hypertension is the leading risk factor for death worldwide. During the COVID-19 pandemic, routine blood pressure assessments decreased because of global disruptions to medical care delivery. However, new research has found that a remote hypertension program, operated by Mass General Brigham since 2019, successfully supported patients through the pandemic in achieving their blood pressure goals, with patients who enrolled during the pandemic reaching and maintaining their goal blood pressures an average of two months earlier than in the pre-pandemic period. The results, published in Journal ...
Too little sleep could make vaccination less effective
2023-03-13
How strongly a vaccine protects you may depend on getting enough sleep in the days before and after inoculation, finds a new meta-analysis examining the relationship between sleep duration and the body’s response to vaccination.
Sleeping fewer than six hours per night around the time of vaccination was associated with a robust decrease in antibody response, according to the multi-institution study published March 13 in Current Biology. Adults are typically recommended to get between seven and nine hours of sleep per night.
The meta-analysis included data on the association between sleep duration and antibody responses for the ...
Not getting enough sleep could blunt antibody response to vaccination, leaving you more vulnerable to infection
2023-03-13
In reviewing data from previous studies, a team lead by researchers at the University of Chicago and the French National Institute of Health and Medical Research (Inserm) found that individuals who had fewer than six hours of sleep per night in the days surrounding vaccination had a blunted antibody response. That indicates efforts to promote heathy sleep duration ahead of an immunization could be an easy way to improve vaccine effectiveness. The study was published March 13 in Current Biology.
The latest work builds off a 2002 study by members of the team showing that restricting sleep ...
A new immune pathway sheds light on ALS
2023-03-13
While drugs are on the market to slow the progression of neurodegenerative diseases, there are still no cures. But researchers at Boston Children’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School are looking for new pathways for slowing neuronal dysfunction and treating amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), a fatal motor neuron disease. The team found that proteins involved in the innate immune system could be at the root of the disease.
“The unmet need for therapies for neurodegenerative diseases is huge, and our work opens up a whole new ...
Study shows how biodiversity of coral reefs around the world changes with depth
2023-03-13
SAN FRANCISCO, CA (March 13, 2023) — In a paper published today in Current Biology, researchers from the California Academy of Sciences Hope for Reefs initiative, along with Brazilian collaborators from the University of São Paulo, Federal University of Espírito Santo, and the Instituto Nacional da Mata Atlântica, show that mesophotic coral reefs function much differently than their shallower counterparts and are unlikely to offer a refuge for shallow water fishes trying to escape climate-change driven warming on the ocean’s surface.
The research is based on hundreds of dives totaling ...
Benefits of the net-zero emissions strategy for Nepal
2023-03-13
Achieving the goals of the Paris Climate Agreement will require the combined efforts of states and companies around the world. How can developing countries achieve carbon neutrality and boost their resilience while pursuing economic growth and improved living standards? A study by the Research Institute for Sustainability (RIFS) draws on the example of Nepal to analyse the benefits of a net-zero emissions strategy.
Nepal is among the 10 countries most vulnerable to climate-change-related disasters and risks. However, its contribution to global greenhouse gas emissions is minor. As Nepal prepares to graduate ...
Pediatric Investigation review takes stock of history and current status of long-acting growth hormone therapy
2023-03-13
In 1957, Maurice Raben successfully isolated and purified the growth hormone (GH) from the pituitary gland, opening up a potential avenue of GH therapies. Children who were born with a deficiency of this hormone could now receive medical intervention in the form of daily injections to substitute the product into their body, thus avoiding the ill-effects of GH deficiency. However, given that it was a product that had to be meticulously extracted from the pituitary of dead bodies, and was time-consuming as well as labor- and resource-intensive process, it remained ...