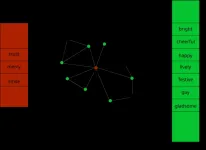
(Press-News.org) With a high-speed camera and the luck of being in the right place at the right time, physicist Marcelo Saba, a researcher at Brazil’s National Space Research Institute (INPE), and PhD candidate Diego Rhamon obtained a unique image of lightning strikes showing details of the connections to nearby buildings.
The image is so special that it appeared on the cover of the 28 December 2022 issue of Geophysical Research Letters (GRL) – one of the most important scientific journals in the field –, which featured an article with Saba as first author. Saba’s research on this topic was supported by FAPESP.
“The image was captured on a summer evening in São José dos Campos [in São Paulo state] while a negatively charged lightning bolt was nearing the ground at 370 km per second. When it was a few dozen meters from ground level, lightning rods and tall objects on the tops of nearby buildings produced positive upward discharges, competing to connect to the downward strike. The final image prior to the connection was obtained 25 thousandths of a second before the lightning hit one of the buildings,” Saba said. This is the spectacular image featured on the cover of the journal.
He used a camera that takes 40,000 frames per second. When the video is played back in slow motion, it shows how lightning discharges behave and also how dangerous they can be if the protection system is not properly installed: although there are more than 30 lightning rods in the vicinity, the strike connected not to them but to a smokestack on top of one of the buildings. “A flaw in the installation left the area unprotected. The impact of a 30,000-amp discharge did enormous damage,” he said.
On average, 20% of all lightning strikes involve an exchange of electrical discharges between clouds and the ground. The other 80% occur inside clouds. Almost all strikes that touch the soil are cloud-to-ground discharges. Upward strikes also occur but are rare and start at the top of tall structures such as mountains, skyscrapers, towers and antennas. Lightning strikes can also be classified as negative or positive depending on the charge transferred to the ground.
“Lightning strikes can be as long as 100 km and transport currents as strong as 30,000 amps, equivalent to the current used simultaneously by 30,000 100-watt bulbs. In some cases, the current can reach 300,000 amps. The temperature of a typical lightning strike is 30,000 °C, five times the Sun’s surface temperature,” Saba said.
How lightning strikes are formed
It all begins with cloud electrification, he explained. The mechanism is poorly understood but basically involves friction between particles of ice, water drops and hail, releasing charges and creating polarities between different cloud regions, with differences in electrical potential ranging from 100 million volts to 1 billion volts.
“Bear in mind that storm clouds are huge structures. The bottom is 2 km to 3 km from the ground, the top can reach 20 km in altitude, and the diameter can be 10 km to 20 km,” he said.
Lightning strikes branch out as the electrical charges seek the path of least resistance, rather than the shortest path, which would be a straight line. The path of least resistance, usually a zigzag, is determined by different electrical characteristics of the atmosphere, which is not homogeneous. “A lightning strike made up of several discharges can last up to 2 seconds. However, each discharge lasts only fractions of milliseconds,” Saba said.
Lightning rods neither attract nor repel strikes, he added. Nor do they “discharge” clouds, as used to be believed. They simply offer lightning an easy and safe route to the ground.
Because it is not always possible to rely on the protection of a lightning rod, and most atmospheric discharges occur in summer in the tropics, it is worth considering Saba’s advice. “Storms are more frequent in the afternoon than in the morning, so be careful about outdoor activities on summer afternoons. Find shelter if you hear thunder, but never under a tree or pole, and never under a rickety roof,” he said. “If you can’t find a safe place to shelter, stay in the car and wait for the storm to blow over. If no car or other shelter is available, squat down with your feet together. Don’t stand upright or lie flat. Indoors, avoid contact with appliances and fixed-line telephones.”
It is possible to survive being struck by lightning, and there are many examples. The odds increase if the person receives care quickly. “Cardiac arrest is the only cause of death. In this case, cardiopulmonary resuscitation is the recommended treatment,” he said.
Saba began systematically studying lightning with high-speed cameras in 2003, ever since building a collection of videos of lightning filmed at high speed that has become the world’s largest. Between them, he and his students have been awarded 17 grants and scholarships by FAPESP.
About São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP)
The São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) is a public institution with the mission of supporting scientific research in all fields of knowledge by awarding scholarships, fellowships and grants to investigators linked with higher education and research institutions in the State of São Paulo, Brazil. FAPESP is aware that the very best research can only be done by working with the best researchers internationally. Therefore, it has established partnerships with funding agencies, higher education, private companies, and research organizations in other countries known for the quality of their research and has been encouraging scientists funded by its grants to further develop their international collaboration. You can learn more about FAPESP at www.fapesp.br/en and visit FAPESP news agency at www.agencia.fapesp.br/en to keep updated with the latest scientific breakthroughs FAPESP helps achieve through its many programs, awards and research centers. You may also subscribe to FAPESP news agency at http://agencia.fapesp.br/subscribe.
END
Unique image obtained by Brazilian scientists with high-speed camera shows how lightning rods work
The image captured with a high-speed camera shows several lightning rods trying to connect to the downward discharge. The two descending branches seen in the image are part of the same lightning strike, which ended up hitting the building on the right.
2023-03-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A new and better way to create word lists
2023-03-13
Word lists are the basis of so much research in so many fields. Researchers at the Complexity Science Hub have now developed an algorithm that can be applied to different languages and can expand word lists significantly better than others.
Many projects start with the creation of a word list. Not only in companies when mind maps are created, but also in all areas of research. Imagine you want to find out on which days people are in a particularly good mood by analyzing Twitter postings. Just looking for the word "happy" wouldn't be enough.
Instead, you would have to use an algorithm that detects all tweets that indicate that someone is happy. "So ...
The immune system does battle in the intestines to keep bacteria in check
2023-03-13
Yersinia bacteria cause a variety of human and animal diseases, the most notorious being the plague, caused by Yersinia pestis. A relative, Yersinia pseudotuberculosis, causes gastrointestinal illness and is less deadly but naturally infects both mice and humans, making it a useful model for studying its interactions with the immune system.
These two pathogens, as well as a third close cousin, Y. enterocolitica, which affects swine and can cause food-borne illness if people consume infected meat, have many traits in common, particularly their knack for interfering with the immune system’s ability to respond to infection.
The plague pathogen is blood-borne and transmitted by infected ...
Switching to hydrogen fuel could prolong the methane problem
2023-03-13
Hydrogen’s potential as a clean fuel could be limited by a chemical reaction in the lower atmosphere, according to research from Princeton University and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Association.
This is because hydrogen gas easily reacts in the atmosphere with the same molecule primarily responsible for breaking down methane, a potent greenhouse gas. If hydrogen emissions exceed a certain threshold, that shared reaction will likely lead to methane accumulating in the atmosphere — with decades-long climate consequences.
“Hydrogen is theoretically the fuel of the future,” said Matteo Bertagni, a postdoctoral researcher at the High ...
Normalizing tumor blood vessels may improve immunotherapy against brain cancer
2023-03-13
BOSTON – A type of immune therapy called chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy has revolutionized the treatment of multiple types of blood cancers but has shown limited efficacy against glioblastoma—the deadliest type of primary brain cancer—and other solid tumors.
New research led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and published in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer March 10, 2023, suggests that drugs that correct abnormalities in a solid tumor’s blood vessels can improve the delivery and function of CAR-T cell therapy.
With CAR-T cell therapy, immune cells are taken from a ...
Wayne State researchers develop new technology to easily detect active TB
2023-03-13
DETROIT – A team of faculty from Wayne State University has discovered new technology that will quickly and easily detect active Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) infection antibodies. Their work, “Discovery of Novel Transketolase Epitopes and the Development of IgG-Based Tuberculosis Serodiagnostics,” was published in a recent edition of Microbiology Spectrum, a journal published by the American Society for Microbiology. The team is led by Lobelia Samavati, M.D., professor in the Center for Molecular Medicine and Genetics in the School of Medicine. ...
Mahoney Life Sciences Prize awarded to UMass Amherst biologist Lynn Adler
2023-03-13
AMHERST, Mass. – University of Massachusetts Amherst biologist Lynn Adler has won the Mahoney Life Sciences Prize for her research demonstrating that different kinds of wildflowers can have markedly different effects on the health and reproduction rate of bumblebees.
“My lab studies the role that flowers play in pollinator health and disease transmission,” says Adler. “Flowers are of course a food source for pollinators, but, in some cases, nectar or pollen from specific plants can be medicinal. However, flowers are also high-traffic areas, and just like with humans, high-traffic areas can be hotspots for disease transmission. We’re tracing how different populations ...
Research highlights gender bias persistence over centuries
2023-03-13
New research from Washington University in St. Louis provides evidence that modern gender norms and biases in Europe have deep historical roots dating back to the Middle Ages and beyond, suggesting that DNA is not the only thing we inherit from our ancestors.
The findings — published on March 13, 2023 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) — highlight why gender norms have remained stubbornly persistent in many parts of the world despite significant strides made by the international ...
Swan populations grow 30 times faster in nature reserves
2023-03-13
Populations of whooper swans grow 30 times faster inside nature reserves, new research shows.
Whooper swans commonly spend their winters in the UK and summers in Iceland.
In the new study, researchers examined 30 years of data on swans at 22 UK sites – three of which are nature reserves managed by the Wildfowl and Wetlands Trust (WWT).
Survival rates were significantly higher at nature reserves, and population growth was so strong that many swans moved to non-protected sites.
Based on these findings, the research team – led by the universities of Exeter and Helsinki – project that nature reserves could help double the number ...
FSU researchers find decaying biomass in Arctic rivers fuels more carbon export than previously thought
2023-03-13
The cycling of carbon through the environment is an essential part of life on the planet.
Understanding the various sources and reservoirs of carbon is a major focus of Earth science research. Plants and animals use the element for cellular growth. It can be stored in rocks and minerals or in the ocean. Carbon in the form of carbon dioxide can move into the atmosphere, where it contributes to a warming planet.
A new study led by Florida State University researchers found that plants and small organisms in Arctic rivers could be responsible for more than half the particulate organic matter flowing to the Arctic Ocean. That’s a significantly ...
Statins may reduce heart disease in people with sleep apnea
2023-03-13
NEW YORK, NY (March 13, 2023)--A new study by Columbia University researchers suggests that cholesterol-lowering drugs called statins have the potential to reduce heart disease in people with obstructive sleep apnea regardless of the use of CPAP machines during the night.
CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure) therapy improves sleep quality and reduces daytime fatigue in people with obstructive sleep apnea. But based on findings from several recent clinical trials, CPAP does not improve heart health as physicians originally hoped.
Alternative ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How periodontitis-linked bacteria accelerate osteoporosis-like bone loss through the gut
Understanding how cells take up and use isolated ‘powerhouses’ to restore energy function
Ten-point plan to deliver climate education unveiled by experts
Team led by UC San Diego researchers selected for prestigious global cancer prize
Study: Reported crop yield gains from breeding may be overstated
Stem cells from human baby teeth show promise for treating cerebral palsy
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
[Press-News.org] Unique image obtained by Brazilian scientists with high-speed camera shows how lightning rods workThe image captured with a high-speed camera shows several lightning rods trying to connect to the downward discharge. The two descending branches seen in the image are part of the same lightning strike, which ended up hitting the building on the right.