(Press-News.org) Consumption of a traditional Mediterranean-type diet – rich in foods such as seafood, fruit, and nuts – is associated with a reduced risk of dementia, reports a study published in BMC Medicine. Individuals with a higher adherence to a Mediterranean diet had up to 23% lower risk for dementia compared with those who had lower adherence to a Mediterranean diet.
Diet may be an important modifiable risk factor for dementia that could be targeted for disease prevention and risk reduction but previous studies exploring the impact of a Mediterranean diet have typically been limited to small sample sizes and low numbers of dementia cases. Oliver Shannon and colleagues analysed data from 60,298 individuals from the UK Biobank who had completed a dietary assessment. The authors scored individuals using two measures for adherence to the Mediterranean diet. During the mean follow-up of 9.1 years there were 882 cases of dementia. The authors also considered each individual’s genetic risk for dementia by estimating their polygenic risk, a measure of all the different genes that are related to risk of dementia.
The authors found that participants with the highest adherence to the Mediterranean diet had a 23% lower risk of developing dementia in comparison with those with the lowest adherence score, equivalent to an absolute risk reduction of 0.55%. There was no significant interaction between the polygenic risk for dementia and adherence to a Mediterranean diet, which the authors suggest may indicate that the association of greater adherence to a Mediterranean diet and a reduced dementia risk remains, irrespective of the individual genetic risk for dementia. This finding was not consistent across all the sensitivity analyses and the authors propose further research is needed to assess the interaction between diet and genetics on dementia risk.
The authors caution that their analysis is limited to individuals who self-reported their ethnic background as white, British or Irish, as genetic data was only available based on European ancestry, and that further research is needed in a range of populations to determine the potential benefit. They conclude that, based on their data, a Mediterranean diet that has a high intake of healthy plant-based foods may be an important intervention to incorporate into future strategies to reduce dementia risk.
###
Media contact:
Tara Eadie
Press Officer
Springer Nature
T: +44 (0)2034 263329
E: tara.eadie@springernature.com
Notes to editor:
1. Research article:
Mediterranean diet adherence is associated with lower dementia risk, independent of genetic predisposition: findings from the UK Biobank prospective cohort study
For an embargoed copy of the research article please contact Tara Eadie.
After the embargo lifts, the article will be available here: https://www.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12916-023-02772-3
Please name the journal in any story you write. If you are writing for the web, please link to the article. All articles are available free of charge, according to BMC's open access policy.
2. BMC Medicine is the flagship medical journal of the BMC series. An open access, transparent peer-reviewed general medical journal, BMC Medicine publishes outstanding and influential research in all areas of clinical practice, translational medicine, medical and health advances, public health, global health, policy, and general topics of interest to the biomedical and sociomedical professional communities. We also publish stimulating debates and reviews as well as unique forum articles and concise tutorials.
3. A pioneer of open access publishing, BMC has an evolving portfolio of high quality peer-reviewed journals including broad interest titles such as BMC Biology and BMC Medicine, specialist journals such as Malaria Journal and Microbiome, and the BMC series. At BMC, research is always in progress. We are committed to continual innovation to better support the needs of our communities, ensuring the integrity of the research we publish, and championing the benefits of open research. BMC is part of Springer Nature, giving us greater opportunities to help authors connect and advance discoveries across the world.
END
Great apes spinning behaviours could provide clues about the role of altered states for the origins of the human mind.
Online videos observed great apes spin themselves to deliberately make themselves dizzy.
Researchers say these new findings suggest that the behaviour could be used to understand when humans evolved the desire to seek altered mental states and actively manipulate their mood and perception of reality.
Great apes deliberately spin themselves in order make themselves dizzy, academics at the University ...
Eating a traditional Mediterranean-type diet – rich in foods such as seafood, fruit, and nuts – may help reduce the risk of dementia by almost a quarter, a new study has revealed.
Experts at Newcastle University found that individuals who ate a Mediterranean-like diet had up to 23% lower risk for dementia than those who did not.
This research, published today in BMC Medicine, is one of the biggest studies of its kind as previous studies have typically been limited to small sample sizes and low numbers ...
AUGUSTA, Ga. (March 14, 2023) – The vascular smooth muscle cells that normally give blood vessel walls strength and flexibility proliferate and become destructive in pulmonary hypertension, a typically rapidly progressing condition that makes it hard to get blood inside our lungs and oxygen to our bodies.
Now scientists have found that inhibiting a gene essential to making DNA so the cells can take on this uncharacteristic growth, can significantly reduce the destructive cell proliferation and disease progression, they report in the European Heart Journal.
The findings point toward a ...
Endometriosis is a painful, complex condition affecting about 1 in 10 women of reproductive age, but it is poorly understood. A new clinical review published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.220637 provides an overview of the causes, diagnosis and management of endometriosis based on the latest evidence, to help clinicians and patients.
The review is timely, as March is Endometriosis Awareness Month.
Endometriosis, defined as the presence of endometrial-like tissue outside the uterus, is one of the most common gynecologic conditions. It is estimated to affect approximately 1 million women ...
A new analysis by researchers at UCLA and UC Riverside shows that even in Blue state California, political attacks on public schools are pervasive and growing, hindering learning and the role schools play in a diverse democracy. Political division and community-level conflict is negatively impacting student interactions, and many California students are experiencing hostility and intolerance in school. Troublingly, the research finds high levels of hostile comments toward LGBTQ students, and racist remarks targeting Latino, and in particular, African American ...
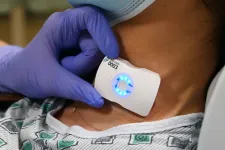
El Camino Health is the first health system in the world to adopt FloPatch, an innovative new technology that monitors blood flow in real time. Developed by Flosonics Medical, FloPatch is the world’s first wireless, wearable Doppler ultra-sound system that helps clinicians better manage intravenous (IV) fluid therapy earlier in the sepsis care pathway.
“Timing is crucial when caring for patients with sepsis. Our nurses have seen firsthand how effective FloPatch is in monitoring the effectiveness of treatment in deteriorating patients, especially those with sepsis and low blood pressure,” said Cheryl Reinking, chief nursing officer at El Camino Health. “We ...
Scientists reveal a potential new approach to treating liver cancer
Results in cell and mouse studies may have implications for the development of a new class of anticancer drugs
Scientists at the National Institutes of Health and Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston have uncovered a potential new approach against liver cancer that could lead to the development of a new class of anticancer drugs. In a series of experiments in cells and mice, researchers found that an enzyme produced in liver cancer ...
FINDINGS
A new study published in Science Immunology points to a promising therapeutic approach for future cancer treatments based on natural killer cells (NK), which are immune cells that bind to tumor cells and destroy them.
City of Hope scientists created a knockout mouse model for a protein called XBP1s to explore the molecule’s effect on NK cells and its role in fighting cancer. Earlier studies showed that XBPIs strengthened the survival of NK cells, but precisely how was unclear.
The team identified a previously unknown mechanism in which interleukin-15 (IL-15) — a protein naturally ...
With a high-speed camera and the luck of being in the right place at the right time, physicist Marcelo Saba, a researcher at Brazil’s National Space Research Institute (INPE), and PhD candidate Diego Rhamon obtained a unique image of lightning strikes showing details of the connections to nearby buildings.
The image is so special that it appeared on the cover of the 28 December 2022 issue of Geophysical Research Letters (GRL) – one of the most important scientific journals in the field –, which featured an article with Saba as first author. ...
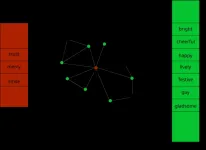
Word lists are the basis of so much research in so many fields. Researchers at the Complexity Science Hub have now developed an algorithm that can be applied to different languages and can expand word lists significantly better than others.
Many projects start with the creation of a word list. Not only in companies when mind maps are created, but also in all areas of research. Imagine you want to find out on which days people are in a particularly good mood by analyzing Twitter postings. Just looking for the word "happy" wouldn't be enough.
Instead, you would have to use an algorithm that detects all tweets that indicate that someone is happy. "So ...