(Press-News.org) Disposable plastics are everywhere: Food containers, coffee cups, plastic bags. Some of these plastics, called compostable plastics, can be engineered to biodegrade under controlled conditions. However, they often look identical to conventional plastics, get recycled incorrectly and, as a result, contaminate plastic waste streams and reduce recycling efficiency. Similarly, recyclable plastics are often mistaken for compostable ones, resulting in polluted compost.
Researchers at University College London (UCL) have published a paper in Frontiers in Sustainability in which they used machine learning to automatically sort different types of compostable and biodegradable plastics and differentiate them from conventional plastics.
“The accuracy is very high and allows the technique to be feasibly used in industrial recycling and composting facilities in the future,” said Prof Mark Miodownik, corresponding author of the study.
Up to perfect accuracy
The researchers worked with different types of plastics measuring between 50mm by 50mm and 5mm by 5mm. Conventional plastic samples included PP and PET, often used for food containers and drinking bottles, as well as LDPE, used, among other things, for plastic bags and packaging. Compostable plastic samples included PLA and PBAT, used for cup lids, tea bags, and magazine wraps; as well as palm-leaf and sugarcane, both biomass-derived materials used to produce packaging. The samples were divided into a training set, used to build classification models, and a testing set, used to check accuracy.
Results showed high success rates: The model achieved perfect accuracy for all materials when the samples measured more than 10mm by 10mm. For sugarcane-derived or palm-leaf-based materials measuring 10mm by 10mm or less, however, the misclassification rate was 20% and 40%, respectively.
Looking at pieces measuring 5mm by 5mm, some materials were identified more reliably than others: For LDPE and PBAT pieces the misclassification rate was 20%; and both biomass-derived materials were misidentified at rates of 60% (sugarcane) and 80% (palm-leaf). The model was, however, able to identify PLA, PP and PET pieces without error, regardless of sample measurements.
Beyond the visible
“Currently, most compostable plastics are treated as a contaminant in the recycling of conventional plastics, reducing their value. Trommel and density sorting are applied to screen compost and reduce the presence of other materials. However, the level of contaminants from the current screening process is unacceptably high,” explained Miodownik. “The advantages of compostable packaging are only realized when they are industrially composted and do not enter the environment or pollute other waste streams or the soil.”
To improve accuracy, a team of scientists including Nutcha Teneepanichskul, Prof Helen Hailes and Miodownik from UCL’s Plastic Waste Innovation Hub tested different types of conventional, compostable, and biodegradable plastics, using hyperspectral imaging (HSI) for classification model development. HSI is an imaging technique that detects the invisible chemical signature of different materials while scanning them, producing a pixel-by-pixel chemical description of a sample. AI models were used to interpret these descriptions and make a material identification.
Plastic mismanagement in recycling and industrial composting processes is high, making reliable sorting mechanisms essential. “Currently, the speed of identification is too low for implementation at industrial scale,” Miodownik pointed out. However, “we can and will improve it since automatic sorting is a key technology to make compostable plastics a sustainable alternative to recycling.”
END
Machine learning helps researchers separate compostable from conventional plastic waste with ‘very high’ accuracy
Scientists develop classification models allowing for reliable, automated sorting of plastic types
2023-03-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Observations open door to improved luminous efficiency of organic LEDs
2023-03-14
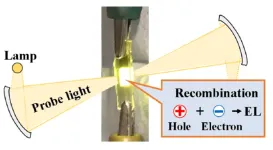
Electroluminescence is the production of light with an electrical current, without relying on heat or chemical reactions. This makes electroluminescent lights reliable and highly efficient: they are used as backlights in digital watches and in the displays of Apollo space shuttle guidance computers. Like OLEDs, light-emitting electrochemical cells (LECs)—which emit light through electroluminescence—have undergone many technological advancements. Close examination of the processes that lead to luminescence is essential ...
Rice labs seek RNA programming for ‘smart’ antibiotics
2023-03-14
HOUSTON – (March 13, 2023) – Synthetic biologists at Rice University are embarking on a three-year project to create “genetically encoded antibiotics,” strands of RNA that bacteria will readily copy and share that will selectively kill only disease-causing, pathogenic bacteria.
“Most bacteria pose no danger to human health,” said James Chappell, an assistant professor of biosciences and bioengineering at Rice. “The question for us as synthetic biologists is, ‘Can we create genetic programs that move through microbial communities and precisely remove only the bad actors from those communities?’”
Thanks ...
Attracting stem cells and facilitating bone regeneration by adhesive protein
2023-03-14
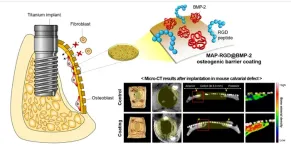
One of the key factors of success in a dental implant is the condition of the periodontium around the implant. A higher long-term success rate of dental implants requires sufficient and healthy alveolar bone. In those cases where lack of alveolar bone renders setting an implant difficult, the bone should be regenerated sufficiently to receive the implant, whether before or during the implant surgery. Development of osteogenic barrier coating material for implants by a Korean research team is expected to improve the success rate of alveolar bone grafting.
Three research teams led by Professor Hyung Joon Cha of the Chemical Engineering ...
Thousands of native plants are unphotographed, and citizen scientists can help fill the gaps
2023-03-14
Scientists have documented plant species for centuries to help us understand and protect the incredible diversity of flora in our world. But according to new research, many have never actually been photographed in their natural habitats – and that’s a problem.
Researchers from UNSW Sydney and the Australian Institute of Botanical Science, part of the Royal Botanic Gardens and Domain Trust, surveyed 33 major online databases of plant photographs to examine the photographic record of Australian plant species. The findings, published in New Phytologist, reveal out of 21,077 native Australian vascular plant species, almost 20 per cent lack a verifiable photograph.
Lead ...
Study sheds light on concerning new trend in drug advertising: Patient influencers
2023-03-14
Patients-turned-social-media-influencers routinely offer prescription drug advice to their followers and often have close ties with pharmaceutical companies, according to new University of Colorado Boulder research.
But they also tend to have good intentions, the study found.
The study, published this week in the Journal of Medical Internet Research, provides some of the first insights into the burgeoning, loosely regulated world of so-called “patient influencers,” sharing findings from 26 in-depth interviews about why and how they do it.
“The bottom line here is that patient influencers act as a form ...
Checking children’s wellbeing: Before and after COVID-19
2023-03-14
A video game featuring a mystical character named Rumble has helped Griffith University researchers investigate how school kids fared following lockdown disruption.
Dr Jacqueline Allen from Griffith’s School of Criminology and Criminal Justice headed up the team looking at self-reported wellbeing in a sample of primary school-aged children in Queensland, Tasmania and Western Australia.
The team used an innovative video game called Rumble’s Quest, developed wholly within Griffith University, which measures the four key facets of wellbeing, as well as ...
Health: Mediterranean diet associated with decreased risk of dementia
2023-03-14
Consumption of a traditional Mediterranean-type diet – rich in foods such as seafood, fruit, and nuts – is associated with a reduced risk of dementia, reports a study published in BMC Medicine. Individuals with a higher adherence to a Mediterranean diet had up to 23% lower risk for dementia compared with those who had lower adherence to a Mediterranean diet.
Diet may be an important modifiable risk factor for dementia that could be targeted for disease prevention and risk reduction but previous studies exploring the impact of a Mediterranean diet have typically been limited to small sample ...
Dizzy apes provide clues on human need for mind altering experiences
2023-03-14
Great apes spinning behaviours could provide clues about the role of altered states for the origins of the human mind.
Online videos observed great apes spin themselves to deliberately make themselves dizzy.
Researchers say these new findings suggest that the behaviour could be used to understand when humans evolved the desire to seek altered mental states and actively manipulate their mood and perception of reality.
Great apes deliberately spin themselves in order make themselves dizzy, academics at the University ...
Mediterranean diet associated with decreased risk of dementia
2023-03-14
Eating a traditional Mediterranean-type diet – rich in foods such as seafood, fruit, and nuts – may help reduce the risk of dementia by almost a quarter, a new study has revealed.
Experts at Newcastle University found that individuals who ate a Mediterranean-like diet had up to 23% lower risk for dementia than those who did not.
This research, published today in BMC Medicine, is one of the biggest studies of its kind as previous studies have typically been limited to small sample sizes and low numbers ...
Gene essential to making DNA appears to be a good target in minimizing pulmonary hypertension
2023-03-14
AUGUSTA, Ga. (March 14, 2023) – The vascular smooth muscle cells that normally give blood vessel walls strength and flexibility proliferate and become destructive in pulmonary hypertension, a typically rapidly progressing condition that makes it hard to get blood inside our lungs and oxygen to our bodies.
Now scientists have found that inhibiting a gene essential to making DNA so the cells can take on this uncharacteristic growth, can significantly reduce the destructive cell proliferation and disease progression, they report in the European Heart Journal.
The findings point toward a ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Of crocodiles, counting and conferences
AERA announces 2026 award winners in education research
Saving two lives with one fruit drop
Photonic chips advance real-time learning in spiking neural systems
Share of migratory wild animal species with declining populations despite UN treaty protections worsens from 44% to 49% in two years; 24% face extinction, up 2%
One in 20 babies experiences physical abuse, global review finds
Tundra tongue: The science behind a very cold mistake
Targeting a dangerous gut infection
Scientists successfully harvest chickpeas from “moon dirt”
Teen aggression a warning sign for faster aging later in life
Study confirms food fortification is highly cost-effective in fighting hidden hunger across 63 countries
Special issue elevates disease ecology in marine management
A kaleidoscope of cosmic collisions: the new catalogue of gravitational signals from LIGO, Virgo and KAGRA
New catalog more than doubles the number of gravitational-wave detections made by LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA observatories
Antifibrotic drug shows promise for premature ovarian insufficiency
Altered copper metabolism is a crucial factor in inflammatory bone diseases
Real-time imaging of microplastics in the body improves understanding of health risks
Reconstructing the world’s ant diversity in 3D
UMD entomologist helps bring the world’s ant diversity to life in 3D imagery
ESA’s Mars orbiters watch solar superstorm hit the Red Planet
The secret lives of catalysts: How microscopic networks power reactions
Molecular ‘catapult’ fires electrons at the limits of physics
Researcher finds evidence supporting sucrose can help manage painful procedures in infants
New study identifies key factors supporting indigenous well-being
Bureaucracy Index 2026: Business sector hit hardest
ECMWF’s portable global forecasting model OpenIFS now available for all
Yale study challenges notion that aging means decline, finds many older adults improve over time
Korean researchers enable early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva!
Swipe right, but safer
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
[Press-News.org] Machine learning helps researchers separate compostable from conventional plastic waste with ‘very high’ accuracyScientists develop classification models allowing for reliable, automated sorting of plastic types