(Press-News.org) March 14, 2023-- The COVID-19 pandemic has had a long-lasting impact on adolescent mental health and substance use according to a new population-based study are based on survey responses from a nationwide sample of over 64,000 13–18-year-old North American and Icelandic adolescents assessed prior to and up to two years into the pandemic. The study was conducted by faculty at Columbia University Teachers College and Mailman School of Public Health and a team of Icelandic and other North American clinical, behavioral and social scientists. The findings are published in published in The Lancet Child & Adolescent Health.
This same research team published a population-based study in The Lancet Psychiatry in 2021 showing an increase in depressive symptoms and decrease in mental well-being among 13–18-year-old adolescents within one year of the global spread of the COVID-19 pandemic. A decline in substance use, in particular cigarette smoking, e-cigarette use and alcohol intoxication, was also observed. Expanding on these findings, this new study shows that the negative effect on adolescent mental health has been persisted up to two years into the pandemic.
“It is worrisome that we still see an increase in mental health problems among adolescents two years into the pandemic. And this is occurring despite social restrictions having been eased in Iceland,” said Thorhildur Halldorsdottir, assistant professor of psychology at Reykjavik University and senior author of the study.
The initial decrease in cigarette smoking and e-cigarette use observed shortly after the arrival of the pandemic was also maintained up to two years into the pandemic. The frequency of adolescent alcohol intoxication, however, appeared to be returning to pre-pandemic levels. “It is of course positive to see that the reduction in cigarette smoking and vaping has been maintained,” said Dr. Ingibjorg Eva Thorisdottir, chief data analyst at Planet Youth and lead author of the study. She continued: “We will need to monitor alcohol intoxication among adolescents in years to come, especially given the increase in mental health problems.”
The association of immigration status, residency, parental social support and nightly sleep duration with adolescent mental health and substance use was also examined in this study. Parental social support and an average of 8 hours or more of sleep per night was associated with better mental health and less substance use among adolescents. The relationship between immigration status and residency with adolescent mental health was less clear. These findings suggest that stress exposure, like the COVID-19 pandemic, affects all adolescents to some extent rather than only vulnerable subgroups.
As such, policy makers should consider implementing large-scale evidence-based prevention efforts focusing on depressive symptoms to mitigate the negative effect of the pandemic,” said John Allegrante, the Charles Irwin Lambert Professor of Health Behavior and Education at Teachers College and professor of sociomedical sciences at Columbia Mailman School of Public Health, and a senior collaborating investigator on the study.
The research was supported by the Icelandic Research Fund.
Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health
Founded in 1922, the Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health pursues an agenda of research, education, and service to address the critical and complex public health issues affecting New Yorkers, the nation and the world. The Columbia Mailman School is the fourth largest recipient of NIH grants among schools of public health. Its nearly 300 multi-disciplinary faculty members work in more than 100 countries around the world, addressing such issues as preventing infectious and chronic diseases, environmental health, maternal and child health, health policy, climate change and health, and public health preparedness. It is a leader in public health education with more than 1,300 graduate students from 55 nations pursuing a variety of master’s and doctoral degree programs. The Columbia Mailman School is also home to numerous world-renowned research centers, including ICAP and the Center for Infection and Immunity. For more information, please visit www.mailman.columbia.edu.
END
COVID-19 pandemic has long-lasting effects on adolescent mental health and substance use
2023-03-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Learning behavior differs between OCD and problem gambling
2023-03-14
Shinsuke Suzuki at The University of Melbourne, Australia reports distinct patterns of reward-seeking behavior between obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) and problem gambling, in a study publishing in the open access journal PLOS Biology on March 14th. OCD is associated with lower-than-normal learning rates when rewards are less than expected. On the other hand, people with problem gambling exhibit boosted and blunted learning from rewards higher and lower than expected, respectively.
Understanding the differences between obsessive and addictive behaviors is essential for developing treatments for conditions like problem gambling ...
Global maternal Strep B vaccination program could save millions and prevent thousands of deaths worldwide
2023-03-14
A global maternal immunization program for group B Streptococcus - strep B - would save millions in healthcare costs by reducing death and disability, but without tiered pricing, equitable access would likely not be achieved. Several vaccines are currently under development, and an assessment of the impact and value of a global program is publishing March 14th in the open access journal PLOS Medicine. It finds that this could avert over 200,000 cases and more than 31,000 deaths, and reduce disability in children.
Strep B can infect pregnant women and their babies, causing sepsis and meningitis in newborns, and sometimes leading to death or disability. ...
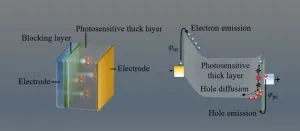
Dark current modeling of thick perovskite X-ray detectors
2023-03-14
X-ray detection is widely used in medical imaging, radioactivity detection, security checking, industrial flaw inspection, and so on. In recent years, metal halide perovskites have demonstrated excellent performances in the detection of X-rays and gamma-rays. However, most studies focus on perovskite single-pixel devices. To achieve the application goal of X-ray imagers, the detectors should be integrated with pixel circuits. This means that the device dark current is an important figure of merit to be considered. The low dark current can guarantee ...
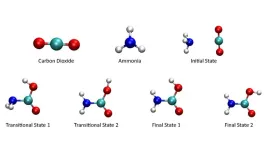
Cleaning up the atmosphere with quantum computing
2023-03-14
WASHINGTON, March 14, 2023 – The amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere increases daily with no sign of stopping or slowing. Too much of civilization depends on the burning of fossil fuels, and even if we can develop a replacement energy source, much of the damage has already been done. Without removal, the carbon dioxide already in the atmosphere will continue to wreak havoc for centuries.
Atmospheric carbon capture is a potential remedy to this problem. It would pull carbon dioxide out of the air and store it permanently to reverse the effects of climate change. Practical carbon capture technologies are still in the early stages of development, with the most promising involving ...
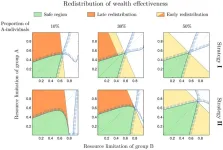
Fighting intolerance with physics
2023-03-14
WASHINGTON, March 14, 2023 – In a world experiencing growing inequality and intolerance, tools borrowed from science and mathematics could be the key to understanding and preventing prejudice.
In Chaos, by AIP Publishing, Luis A. Martinez-Vaquero of the Polytechnic University of Madrid applied evolutionary game theory, which combines techniques from economics and biology, and complex system analysis to investigate the relationship between inequality and intolerance. He found that inequality boosts intolerance and that redistribution ...
Association between California’s state insurance gender nondiscrimination act and utilization of gender-affirming surgery
2023-03-14
About The Study: Implementation in California of its Insurance Gender Nondiscrimination Act was associated with a significant increase in utilization of gender-affirming surgery in California compared with the control states Washington and Arizona. These data might inform state legislative efforts to craft policies preventing discrimination in health coverage for state residents, including transgender and gender-diverse patients.
Authors: Anna Schoenbrunner, M.D., of Ohio State University in Columbus, is ...
COVID-19–related stress and postpartum maternal mental health, infant outcomes
2023-03-14
About The Study: In this study of 318 mothers in Australia, the U.K., and the U.S., antenatal COVID-19–related stress was significantly associated with poor postpartum maternal mental health outcomes and increased negative affectivity among infants. Pregnant individuals should be classified as a vulnerable group during pandemics and should be considered a public health priority, not only in terms of physical health but also mental health.
Authors: Susanne Schweizer, Ph.D., of the University of Cambridge in Cambridge, United Kingdom, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link ...
Intimate partner violence, mental health symptoms, and modifiable health factors in women during the pandemic
2023-03-14
About The Study: The results of this study showed that intimate partner violence experiences at the start of the pandemic were associated with worse mental health symptoms and modifiable health factors for female participants younger than age 60. Screening and interventions for intimate partner violence and related health factors are needed to prevent severe, long-term health consequences.
Authors: Arielle A. J. Scoglio, Ph.D., of the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health in Boston, ...
Extra pounds put kids at higher risk for hypertension
2023-03-14
PASADENA, Calif. — A Kaiser Permanente study of more than 800,000 young people between the ages of 3 and 17 showed that youth at the upper range of average weight had a 26% higher risk of developing hypertension than those closer to what is considered average weight. The study was published March 14, 2023, in JAMA Network Open.
“Hypertension during youth tracks into adulthood and is associated with cardiac and vascular organ damage. Since the organ damage can be irreversible, preventing hypertension in our young people is critically important,” said the lead author, Corinna Koebnick, PhD, of the ...
Simulating cuts and burns reveals wound healing and clearing power of fibroblasts
2023-03-14
WASHINGTON, March 14, 2023 – Burn wounds are notoriously prone to bacterial infection and typically lead to a larger amount of scar tissue than laceration wounds.
In APL Bioengineering, by AIP publishing, researchers from Boston University and Harvard University created a biomimetic model to study wound healing in burn and laceration wounds. They discovered that fibroblasts – normally considered building cells that give shape and strength to tissues and organs – clear away damaged tissue before depositing new material. This ...