(Press-News.org) Electrification is seen as having an important role to play in the fossil-free aviation of tomorrow. But electric aviation is battling a trade-off dilemma: the more energy-efficient an electric aircraft is, the noisier it gets. Now, researchers at Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, have developed a propeller design optimisation method that paves the way for quiet, efficient electric aviation.
In recent years, electrification has been described as having an important role in reducing emissions from future aviation. Due to the challenges posed by longer ranges, interest is chiefly focused on electric propeller planes covering shorter distances. Propellers connected to electric motors are considered the most efficient propulsion system for regional and domestic flights.
But while airplanes are electric, propellers cause another kind of emission – noise. The noise from the propeller blades wouldn’t just disturb air passengers. Future electric aircraft will need to fly at relatively low altitudes, with noise disturbance reaching residential areas and animal life.
Battling a trade-off dilemma
This is where the research community faces a dilemma. The ambition of developing electric aircraft that are both quiet and energy-efficient is somewhat thwarted by a trade-off problem.
“We can see that the more blades a propeller has, the lower the noise emissions. But with fewer blades, propulsion becomes more efficient and the electric aircraft can fly for longer. In that sense, there is a trade-off between energy efficiency and noise. This is something of an obstacle for electric aircrafts that are both quiet and efficient,” explains Hua-Dong Yao, Associate Professor and researcher in fluid dynamics and marine technology at Chalmers University of Technology.
An optimised design for quiet and efficient propellers
But now, Hua-Dong Yao and his research colleagues may be one step closer to a solution. They have succeeded in isolating and exploring the noise that occurs at the tip of the propeller blades, or “tip vortices”, a known but less well-explored source of noise. In isolating this noise, the researchers were able to fully understand its role in relation to other noise sources generated by propeller blades. By adjusting a range of propeller parameters, such as pitch angle, chord length and number of blades, the team found a way to optimise the propeller design and even out the trade-off effect between efficiency and noise. The method, described in the study published in the journal Aerospace, can now be used in the design process of quieter propellers for future electric aircraft.
“Modern aircraft propellers usually have two to four blades, but we’ve found that by using six blades designed using our optimisation framework, you can develop a propeller that’s both relatively efficient and quiet. The propeller achieves a noise reduction of up to 5-8 dBA* with only a 3.5 per cent thrust penalty, compared to a propeller with three blades. That’s comparable to the noise reduction of someone going from speaking in a normal conversation voice to the sound you would perceive in a quiet room,” says Hua-Dong Yao.
* A-weighted decibel (dBA or dB(A)) is an expression of the relative loudness of sounds as perceived by the human ear. A-weighting gives more value to frequencies in the mid-range of human hearing and less value to frequencies at the edges as compared to a flat audio decibel measurement. A-weighting is the standard for determining hearing damage and noise pollution.
More about the scientific publication
The study Blade-Tip Vortex Noise Mitigation Traded-Off against Aerodynamic Design for Propellers of Future Electric Aircraft was published in the journal Aerospace.
The authors are Hua-Dong Yao, Zhongjie Huang, Lars Davidson, Jiqiang Niu and Zheng-Wei Chen.
The researchers are active at Chalmers University of Technology, Volvo Cars, School of Mechanical Engineering, Southwest Jiaotong University and The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, China.
The research project has been funded by the Transport Area of Advance at Chalmers University of Technology.
Link to the study: https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace9120825
For more information, please contact:
Hua-Dong Yao, Associate Professor and researcher in fluid dynamics and marine technology, Department of Mechanics and Maritime Sciences, Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden
huadong.yao@chalmers.se, +46 31 772 14 05
END
Propeller advance paves way for quiet, efficient electric aviation
2023-03-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
People of color have been largely underrepresented among authors published in the American Journal of Archaeology
2023-03-14
A new demographic survey of authorship in the American Journal of Archaeology (AJA) reveals that people of color have been largely underrepresented among the scholars published in the journal. The results of the survey, which also found that authors who are the children of people without advanced degrees were also underrepresented in the journal’s pages, are published in the paper “Demographic Dynamics of Publishing in the American Journal of Archaeology.” The study was conducted ...
Common cold gives children immunity against COVID-19
2023-03-14
During the pandemic, medical doctors and researchers noticed that children and adolescents infected with COVID-19 became less ill than adults. A possible explanation for this is that children already had a prior level of immunity to COVID-19 provided by memory T cells generated by common colds.
After studying unique blood samples from children taken before the pandemic, researchers from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have now identified memory T cells that react to cells infected with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
Four coronaviruses cause common colds
A possible explanation for this immunity in children is that they already had colds caused by one of the four coronaviruses ...
Researchers discover way to reverse infertility by reducing HDL cholesterol
2023-03-14
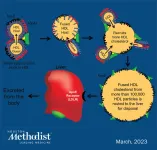
Houston Methodist scientists reversed infertility in sterile mice by reducing high-circulating cholesterol with a bacterial protein, showing further evidence that links high cholesterol to female infertility. This is a promising development, with one in every five women of childbearing age in the U.S. unable to get pregnant after trying for a year.
“We are working with a protein, called serum opacity factor, with unique characteristics,” said Corina Rosales, Ph.D., assistant research professor of molecular biology in medicine with the Houston Methodist ...
UK HealthCare’s Transplant Center celebrates 500th lung transplant
2023-03-14
LEXINGTON, Ky. (March 14, 2023) — The lung transplant team at UK HealthCare’s Transplant Center recently celebrated a major milestone, performing the 500th lung transplant since the lung transplant program was founded in 1991.
“This is an impressive milestone, and our whole staff — physicians, surgeons, nurse practitioners, nurse coordinators, pharmacists, nutritionists, social workers, therapists and support staff — should be very proud of their success,” said Sravanthi Nandavaram, M.D., medical director of the Lung Transplant Program. ...
How neuroimaging can be better utilized to yield diagnostic information about individuals
2023-03-14
Since the development of functional magnetic resonance imaging in the 1990s, the reliance on neuroimaging has skyrocketed as researchers investigate how fMRI data from the brain at rest, and anatomical brain structure itself, can be used to predict individual traits, such as depression, cognitive decline, and brain disorders.
Brain imaging has the potential to reveal the neural underpinnings of many traits, from disorders like depression and chronic widespread pain to why one person has a better memory than another, and why some people’s memories are resilient as they age. But how reliable brain imaging is for detecting traits has been a subject of wide debate.
Prior research ...
NASA’s Webb Telescope captures rarely seen prelude to supernova
2023-03-14
The rare sight of a Wolf-Rayet star – among the most luminous, most massive, and most briefly detectable stars known – was one of the first observations made by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope in June 2022. Webb shows the star, WR 124, in unprecedented detail with its powerful infrared instruments. The star is 15,000 light-years away in the constellation Sagittarius.
Massive stars race through their lifecycles, and only some of them go through a brief Wolf-Rayet phase before going supernova, making Webb’s detailed observations of this rare phase valuable to astronomers. Wolf-Rayet stars are in the process of casting off their outer layers, ...
Potential treatment target for drug-resistant epilepsy identified
2023-03-14
Researchers at Tufts University School of Medicine and colleagues have identified a small molecule that may help treat people with epilepsy whose condition has become resistant to the benzodiazepine drugs usually used in managing seizures. The research, conducted in laboratory cells and rodents, was published online March 7 in Cell Reports Medicine.
Uncontrolled epilepsy can lead to frequent and prolonged seizures lasting five minutes or more that can cause brain cell damage and even death. The condition affects an estimated 3.4 million people in the U.S. and millions more worldwide.
Epilepsy occurs ...
New model provides improved air-quality predictions in fire-prone areas
2023-03-14
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Globally, wildfires are becoming more frequent and destructive, generating a significant amount of smoke that can be transported thousands of miles, driving the need for more accurate air pollution forecasts. A team of Penn State researchers developed a deep learning model that provides improved predictions of air quality in wildfire-prone areas and can differentiate between wildfires and non-wildfires.
“As climate change continues to cause ecological changes and challenges, it is likely that wildfire ...
New study finds early warning signs prior to 2002 Antarctic ice shelf collapse
2023-03-14
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — In 2002, an area of ice about the size of Rhode Island dramatically broke away from Antarctica as the Larsen B ice shelf collapsed. A new study of the conditions that led to the collapse may reveal warning signs to watch for future Antarctic ice shelf retreat, according to a Penn State-led team of scientists.
“The collapse of the Larsen B ice shelf is generally thought of as an independent event,” said Shujie Wang, assistant professor of geography at Penn State. “Our ...
Oncotarget | MTAP loss in metastatic breast cancer patients: Genomic landscape
2023-03-14
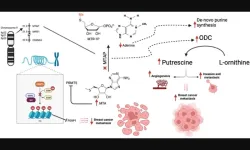
“In breast cancer, MTAP downregulation activates ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) which in turn leads to formation of putrescine which promotes tumor migration, invasion and angiogenesis [15].”
BUFFALO, NY- March 14, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on March 11, 2023, entitled, “Genomic landscape of metastatic breast cancer (MBC) patients with methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAP) loss.”
Homozygous deletion of methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAP) upregulates de novo synthesis ...