(Press-News.org) NEW YORK – For a functioning brain to develop from its embryonic beginnings, so much has to happen and go exactly right with exquisite precision, according to a just-so sequence in space and time. It’s like starting with a brick that somehow replicates and differentiates into a hundred types of building materials that also replicate, while simultaneously self-assembling into a handsome skyscraper replete with functioning thermal, plumbing, security and electrical systems.
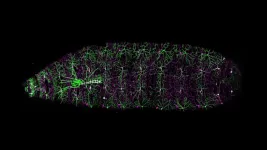
The accompanying microscope image, from the Zuckerman Institute laboratory of Wesley Grueber, PhD, highlights a single moment in the two-week development drama of a fruit fly larva. Two types of sensory nerve cells, or neurons, in the larva’s body wall have been imaged in action. Here, they’re wiring into the fly’s emerging central nervous system with a precision that ultimately enables the fly to tell the difference between gentle mechanical stimuli, like breezes, and painful ones, like a hard knock or noxious heat.
The diaphanous arborizations are the cells’ stimulus-detecting dendrites in the body wall. The dendrites glowing in magenta denote sensory neurons that detect irritating stimuli. The dendrites glowing in green belong to the type of sensory neurons that pick up gentle stimuli.
The denser millipede-like structure on the left? That’s where the researchers spied something previously unknown. Along with other data, a detailed analysis of this structure reveals how signal-conveying axons of these two types of sensory cells interact as they grow and wire into the fly’s central nervous system. Without these axon-axon interactions, the researchers found, crucial brain wiring gets jumbled, which could, in turn, hobble the fly’s ability to discern and respond to different kinds of sensory information.
“Growing axons that arrive first in a particular location appear to deflect later-arriving axons to set them up in their right places,” says Dr. Grueber. “These kinds of axon-axon interactions are likely used very widely to drive appropriate wiring and next we would like to understand the genes that control these processes."
To learn more, read the paper "Axon-axon interactions determine modality-specific wiring and subcellular synaptic specificity in a somatosensory circuit," published today in Development. The full list of authors includes Samantha E. Galindo, Abby J. Wood, Patricia C. Cooney, Luke A. Hammond and Wesley G. Grueber.
END
Magnificent wiring
The process by which neurons connect into functioning brains, even in fruit flies, is an epic exercise of developmental minutiae that could not matter more
2023-03-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Self-driven laboratory, AlphaFlow, speeds chemical discovery
2023-03-15
A team of chemical engineering researchers has developed a self-driven lab that is capable of identifying and optimizing new complex multistep reaction routes for the synthesis of advanced functional materials and molecules. In a proof-of-concept demonstration, the system found a more efficient way to produce high-quality semiconductor nanocrystals that are used in optical and photonic devices.
“Progress in materials and molecular discovery is slow, because conventional techniques for discovering new chemistries rely on varying ...
Minimizing electric vehicles’ impact on the grid
2023-03-15
National and global plans to combat climate change include increasing the electrification of vehicles and the percentage of electricity generated from renewable sources. But some projections show that these trends might require costly new power plants to meet peak loads in the evening when cars are plugged in after the workday. What’s more, overproduction of power from solar farms during the daytime can waste valuable electricity-generation capacity.
In a new study, MIT researchers have found that it’s possible to mitigate or eliminate both these problems without the need for ...
Estimated COVID-19 mRNA vaccine effectiveness, illness severity during Omicron BA.4 and BA.5 periods
2023-03-15
About The Study: In this case-control study of COVID-19 vaccines and illness, vaccine effectiveness associated with protection against medically attended COVID-19 illness was lower with increasing time since last dose; estimated vaccine effectiveness was higher after receipt of one or two booster doses compared with a primary series alone.
Authors: Ruth Link-Gelles, Ph.D., M.P.H., of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention COVID-19 Response Team in Atlanta, is the corresponding ...
Effect of sleep changes on health-related quality of life in healthy children
2023-03-15
About The Study: Results of this secondary analysis of a randomized trial involving 100 healthy children ages 8 to 12 indicated that even 39 minutes less of sleep per night for one week significantly reduced several facets of health-related quality of life in children. This finding shows that ensuring children receive sufficient good-quality sleep is an important child health issue.
Authors: Rachael W. Taylor, Ph.D., of the University of Otago in Dunedin, New Zealand, is the corresponding ...
New definitions of multimorbidity may improve clinical decision-making for older surgical patients
2023-03-15
Key Takeaways
New definitions surpass conventional definitions: The new study developed and validated better surgical, specialty-specific, multimorbidity definitions based on distinct characteristics of older inpatient general, orthopedic, and vascular surgery patients.
Mortality risk is higher for some patients: For some types of surgery, patients with certain combinations of comorbidities face significantly higher 30-day mortality risk than patients who are lower risk.
Helping assess overall risk: Researchers anticipate that the new multimorbidity definitions will help surgeons better explain the risks associated with any given procedure to ...
New research establishes how and why western diets high in sugar and fat cause liver disease
2023-03-15
New research from the University of Missouri School of Medicine has established a link between western diets high in fat and sugar and the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, the leading cause of chronic liver disease.
The research, based in the Roy Blunt NextGen Precision Health Building at MU, has identified the western diet-induced microbial and metabolic contributors to liver disease, advancing our understanding of the gut-liver axis, and in turn the development of dietary and microbial interventions for this global ...
Filling a niche: Neural stem cells help maintain their microenvironment
2023-03-15
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) shed new light on the characteristics of the niche in which neural stem cells reside in the developing brain
Tokyo, Japan – When it comes to cell types, stem cells have unlimited potential – literally. These self-renewing cells, which are capable of giving rise to any cell type in the body, reside in specialized microenvironments known as niches. Now, researchers in Japan have shed new insight into the dynamics of the neural stem cell niche, the ...
PCR panels reduce costs, hospitalizations and antibiotic use for acute GI infections
2023-03-15
Washington, DC – Acute gastroenteritis afflicts adults of all ages, causing significant suffering and inflicting significant costs on the American healthcare system. A new study encompassing nearly 40,000 hospital visits from a geographically diverse healthcare database shows that sampling a single stool, using multiple polymerase chain reaction (PCR) panels, can identify more pathogens, notably diarrhea-causing E. coli and enteric viruses, and do so more rapidly than a conventional workup. The research is published in Journal of Clinical Microbiology, a publication of the American Society for Microbiology.
Using ...
FAU Harbor Branch receives $2.8 million gift to create a queen conch farm in Grand Bahama
2023-03-15
Florida Atlantic University Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institute has received $2.8 million to establish a queen conch hatchery in Grand Bahama. This support expands FAU Harbor Branch’s extensive aquaculture and food security program focused on replenishing queen conch populations throughout the Caribbean. It also enables development of a conceptual master plan for a 25-acre innovation hub on Grand Bahama for researchers working to solve issues of island sustainability.
The project is built on a network of collaborations to secure local support and participation. FAU Harbor Branch will partner with the Bahamian community of Grand Bahama on a pilot-scale queen conch ...
Largest catalog of exploding stars now available
2023-03-15
Celestial phenomena that change with time such as exploding stars, mysterious objects that suddenly brighten and variable stars are a new frontier in astronomical research, with telescopes that can rapidly survey the sky revealing thousands of these objects.
The largest data release of relatively nearby supernovae (colossal explosions of stars), containing three years of data from the University of Hawaiʻi Institute for Astronomy’s (IfA) Pan-STARRS telescope atop Haleakalā on Maui, is publicly available via the Young Supernova Experiment (YSE). The project, which began in 2019, surveyed ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Magnificent wiringThe process by which neurons connect into functioning brains, even in fruit flies, is an epic exercise of developmental minutiae that could not matter more