New laser technology developed by EPFL and IBM
2023-03-15
(Press-News.org)
Scientists at EPFL and IBM have developed a new type of laser that could have a significant impact on optical ranging technology. The laser is based on a material called lithium niobate, often used in the field of optical modulators, which controls the frequency or intensity of light that is transmitted through a device.
Lithium niobate is particularly useful because it can handle a lot of optical power and has a high “Pockels coefficient”, which means that it can change its optical properties when an electric field is applied to it.
The researchers achieved their breakthrough by combining lithium niobate with silicon nitride, which allowed them to produce a new type of hybrid integrated tunable laser. To do this, the team manufactured integrated circuits for light (“photonic integrated circuits”) based on silicon nitride at EPFL, and then bonded them with lithium niobate wafers at IBM.
The approach produced a laser with low frequency noise (a measure of how stable the laser's frequency is) and simultaneously with fast wavelength tuning – both great qualities for a laser used in light detection and ranging (LiDAR) applications. Then they performed an optical ranging experiment where they used the laser to measure distances with high precision.
Beyond integrated lasers, the hybrid platform has the potential to realize integrated transceivers for telecommunications as well as microwave-optical transducers for use in quantum computing.
"What is remarkable about the result is that the laser simultaneously provides low phase noise and fast petahertz-per-second tuning, something that has never before been achieved with such a chip-scale integrated laser," says Professor Tobias J. Kippenberg, who led the EPFL side of the project.
The chip samples were fabricated in the EPFL center of MicroNanoTechnology (CMi) and the Binnig and Rohrer Nanotechnology Center (BRNC) at IBM Research.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:


ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-03-15
A single cell contains 2-3 meters of DNA, meaning that the only way to store it is to package it into tight coils. The solution is chromatin: a complex of DNA wrapped around proteins called histones. In the 3D space, this complex is progressively folded into a multi-layered organization composed of loops, domains, and compartments, which makes up what we know as chromosomes. The organization of chromatin is closely linked to gene expression and the cell’s proper function, so any problems in chromatin structure can have detrimental effects, including the development of cancer.
A common event in around 30% of all human cancers is “whole genome doubling” ...
2023-03-15
NEW YORK – For a functioning brain to develop from its embryonic beginnings, so much has to happen and go exactly right with exquisite precision, according to a just-so sequence in space and time. It’s like starting with a brick that somehow replicates and differentiates into a hundred types of building materials that also replicate, while simultaneously self-assembling into a handsome skyscraper replete with functioning thermal, plumbing, security and electrical systems.
The accompanying microscope image, from ...
2023-03-15
A team of chemical engineering researchers has developed a self-driven lab that is capable of identifying and optimizing new complex multistep reaction routes for the synthesis of advanced functional materials and molecules. In a proof-of-concept demonstration, the system found a more efficient way to produce high-quality semiconductor nanocrystals that are used in optical and photonic devices.
“Progress in materials and molecular discovery is slow, because conventional techniques for discovering new chemistries rely on varying ...
2023-03-15
National and global plans to combat climate change include increasing the electrification of vehicles and the percentage of electricity generated from renewable sources. But some projections show that these trends might require costly new power plants to meet peak loads in the evening when cars are plugged in after the workday. What’s more, overproduction of power from solar farms during the daytime can waste valuable electricity-generation capacity.
In a new study, MIT researchers have found that it’s possible to mitigate or eliminate both these problems without the need for ...
2023-03-15
About The Study: In this case-control study of COVID-19 vaccines and illness, vaccine effectiveness associated with protection against medically attended COVID-19 illness was lower with increasing time since last dose; estimated vaccine effectiveness was higher after receipt of one or two booster doses compared with a primary series alone.
Authors: Ruth Link-Gelles, Ph.D., M.P.H., of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention COVID-19 Response Team in Atlanta, is the corresponding ...
2023-03-15
About The Study: Results of this secondary analysis of a randomized trial involving 100 healthy children ages 8 to 12 indicated that even 39 minutes less of sleep per night for one week significantly reduced several facets of health-related quality of life in children. This finding shows that ensuring children receive sufficient good-quality sleep is an important child health issue.
Authors: Rachael W. Taylor, Ph.D., of the University of Otago in Dunedin, New Zealand, is the corresponding ...
2023-03-15
Key Takeaways
New definitions surpass conventional definitions: The new study developed and validated better surgical, specialty-specific, multimorbidity definitions based on distinct characteristics of older inpatient general, orthopedic, and vascular surgery patients.
Mortality risk is higher for some patients: For some types of surgery, patients with certain combinations of comorbidities face significantly higher 30-day mortality risk than patients who are lower risk.
Helping assess overall risk: Researchers anticipate that the new multimorbidity definitions will help surgeons better explain the risks associated with any given procedure to ...
2023-03-15
New research from the University of Missouri School of Medicine has established a link between western diets high in fat and sugar and the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, the leading cause of chronic liver disease.
The research, based in the Roy Blunt NextGen Precision Health Building at MU, has identified the western diet-induced microbial and metabolic contributors to liver disease, advancing our understanding of the gut-liver axis, and in turn the development of dietary and microbial interventions for this global ...
2023-03-15
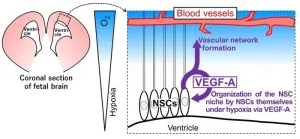
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) shed new light on the characteristics of the niche in which neural stem cells reside in the developing brain
Tokyo, Japan – When it comes to cell types, stem cells have unlimited potential – literally. These self-renewing cells, which are capable of giving rise to any cell type in the body, reside in specialized microenvironments known as niches. Now, researchers in Japan have shed new insight into the dynamics of the neural stem cell niche, the ...
2023-03-15
Washington, DC – Acute gastroenteritis afflicts adults of all ages, causing significant suffering and inflicting significant costs on the American healthcare system. A new study encompassing nearly 40,000 hospital visits from a geographically diverse healthcare database shows that sampling a single stool, using multiple polymerase chain reaction (PCR) panels, can identify more pathogens, notably diarrhea-causing E. coli and enteric viruses, and do so more rapidly than a conventional workup. The research is published in Journal of Clinical Microbiology, a publication of the American Society for Microbiology.
Using ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New laser technology developed by EPFL and IBM