(Press-News.org) Consuming a diet rich in vitamin A or its analogs may help prevent children and young adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) reduce their risk of developing painful pancreas inflammation during chemotherapy treatment.
Details about this potential dietary solution to prevent a potentially life-threatening adverse event were published March 15, 2023, in Science Translational Medicine. The research team was led by Sohail Husain, MD, chief of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition at Stanford University and Anil Goud Jegga, DVM, MRes, a computational biologist at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center.
For people with ALL, treatment with the enzyme asparaginase helps starve cancer cells by reducing the amount of asparagine circulating in the blood, which the cancer cells need but cannot make themselves. The medication, often used in combination with other chemotherapies, is given via injection into a vein, muscle, or under the skin.
However, an estimated 2% to 10% of asparaginase users develop inflammation of the pancreas in reaction to asparaginase treatment. For a third of these people, the symptoms can be severe.
Jegga and colleagues developed predictive analytics using over 100 million data points encompassing gene expression data, small-molecule data, and electronic health records to understand more of the mechanisms driving asparaginase-associated pancreatitis (AAP) and identify potential interventions to prevent or mitigate AAP.
First, they analyzed massive amounts of gene expression data to reveal that gene activity associated with asparaginase or pancreatitis might be reversed by retinoids (vitamin A and its analogs). The team found more supporting evidence by “mining” millions of of electronic health records from the TriNetX database and the U.S. Federal Drug Administration Adverse Events Reporting System.
This number crunching and predictive analytics work included use of the AERSMine software developed at Cincinnati Children’s by Mayur Sarangdhar, PhD, MRes, and colleagues. The research team also studied data from mice experiments and compared plasma samples from people with ALL who developed pancreatitis and those who did not.
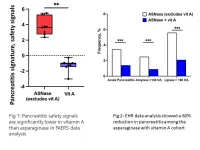
Ultimately, the team established two sets of human “real-world” experiences. They found that only 1.4% of patients treated with asparaginase developed pancreatitis when they were also taking vitamin A in contrast to 3.4% of patients who did not. Concomitant use of vitamin A correlated with a 60% reduction in the risk of AAP. Lower amounts of dietary vitamin A correlated with increased risk and severity of AAP.
“This study demonstrates the potential of mining ‘real-world’ data to identify therapy modifiers for improving patient outcomes. In cases where a primary drug induces toxicity but is critical to therapy, such as asparaginase, therapy modifiers, such as vitamin A and its analogs, may be of immediate relevance to patients on asparaginase and ‘at-risk’ for AAP,” says Sarangdhar, a co-first author of the study.
Says Jegga: "Our study highlights the power of heterogeneous data integration and analysis in translational research. By leveraging existing ‘omics and patient-centric data and a systems approach, we were able to identify new insights into the development of AAP and potential interventions to prevent or mitigate this side effect."
Next steps
In some ways, learnings from this study could be applied immediately to patient care. However, more clinical research is needed to establish how much vitamin A would be needed to protect ALL patients from pancreatitis; and whether a protective level can be achieved by diet or via supplements. In fact, target vitamin levels may need to vary according to individual differences in metabolism.
END
Vitamin A may reduce pancreatitis risk during ALL treatment
2023-03-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UAF scientist offers evidence that Venus is volcanically active
2023-03-15
Embargoed: Not for release until 2 p.m. U.S. Eastern time Wednesday, March 15, 2023
Venus appears to have volcanic activity, according to a new research paper that offers strong evidence to answer the lingering question about whether Earth’s sister planet currently has eruptions and lava flows.
Venus, although similar to Earth in size and mass, differs markedly in that it does not have plate tectonics. The boundaries of Earth’s moving surface plates are the primary locations of volcanic activity.
New research by University of Alaska Fairbanks Geophysical Institute research professor Robert Herrick revealed ...
A nonnative tree species reclaims its prominence after extreme weather
2023-03-15
The long-term effects on forests of more extreme climate events, plus other drivers of forest change, are highly uncertain. A new study of the tropical forests across Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands (USVI), spanning 19 years, found that after Hurricane Maria in 2017, the total biomass of a fast-growing nonnative species, the African tulip Tree (Spathodea campanulata), may again be overtaking that of the most common group of native tree species, even though, at least for young and small trees, nonnatives ...
Antidepressant medication may be key to help people stop use of cocaine while in treatment for opioid use disorder
2023-03-15
For some people receiving methadone for treatment of opioid use disorder (OUD), the co-use of opioids and stimulants such as cocaine is an issue. Now, a new study led by Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers found that bupropion, an antidepressant medication also used for smoking cessation, may help people stop using cocaine while in treatment for OUD.
The results of the study were published March 15 in JAMA Network Open.
For this double-blind randomized study, the researchers used an adaptive treatment design, meaning that it allowed ...
Zook joins The Gerontological Society of America’s Board of Directors
2023-03-15
The Gerontological Society of America (GSA) — the nation’s largest interdisciplinary organization devoted to the field of aging — has named David Zook of Faegre Drinker LLP as an at-large member of its Board of Directors.
GSA’s Board of Directors provides governance oversight, establishes Society policy, sets the organization’s strategic plan, and oversees implementation thereof. It comprises 12 members representing the broad diversity of the Society’s membership. Zook’s three-year term became effective January 1.
“GSA is very effective in applying knowledge to policymaking as the role of older individuals in our society continues to evolve,” ...
Breakthrough drug combination remains safe and effective in patients with cystic fibrosis after four years
2023-03-15
Patients with cystic fibrosis (CF) face difficulty breathing and a decline in lung function and are at risk of early death. CF is an inherited condition that results in thick mucus build-up, persistent infection and inflammation in the lungs.
Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC) researcher Patrick Flume, M.D., was lead author of a recent Journal of Cystic Fibrosis article reporting the findings of a trial of a two-drug combination for treating CF. The study demonstrated long-term safety and clinical benefit of the combination therapy. Flume is director of the ...
Remains of a modern glacier found near mars’ equator implies water ice possibly present at low latitudes on Mars even today
2023-03-15
March 15, 2023, Mountain View, California – In a groundbreaking announcement at the 54th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference held in The Woodlands, Texas, scientists revealed the discovery of a relict glacier near Mars' equator. Located in Eastern Noctis Labyrinthus at coordinates 7° 33' S, 93° 14' W, this finding is significant as it implies the presence of surface water ice on Mars in recent times, even near the equator. This discovery raises the possibility that ice may still exist at shallow depths in the ...
Associations between teacher and student mathematics, science, and literacy anxiety in fourth grade
2023-03-15
Educational Impact and Implications Statement
We investigated associations among teachers’ and students’ anxiety in mathematics, science, and literacy. We found that teachers’ anxiety in mathematics and science was associated with the mathematics and science anxiety of their low-SES students. Results highlight STEM content areas as contexts in which transmission of negative emotions between teachers and students may take place, as well as highlight the particular impacts these processes might have on students from underserved socioeconomic backgrounds.
The ...
Kerin Adelson, M.D., named MD Anderson Chief Quality and Value Officer
2023-03-15
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center today announced Kerin Adelson, M.D., as the institution’s chief quality and value officer. An accomplished clinician and researcher with extensive leadership experience in delivering high-quality and value-based cancer care, Adelson will begin her role March 20. She also will hold a faculty appointment in Breast Medical Oncology.
As chief quality and value officer, Adelson will partner with Chief Administrative Quality Officer José Rivera to lead MD Anderson’s medical practice quality improvement efforts and ...
For the first time, controlling the degree of twist in nanostructured particles
2023-03-15
Images
Micron-sized "bow ties," self-assembled from nanoparticles, form a variety of different curling shapes that can be precisely controlled, a research team led by the University of Michigan has shown.
The development opens the way for easily producing materials that interact with twisted light, providing new tools for machine vision and producing medicines.
While biology is full of twisted structures like DNA, known as chiral structures, the degree of twist is locked in—trying to change it breaks the structure. Now, researchers can engineer the degree of twist.
Such materials ...
Study unravels a cause of resistance to novel drug in patients with acute leukemia
2023-03-15
BOSTON – A new targeted drug has not only sparked remissions in patients with a common form of leukemia but also induced the cancer cells to reveal one of their schemes for resisting the drug, investigators at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and other research centers report in a new pair of studies in the journal Nature.
One of the papers presents results of a clinical trial in which approximately 40% of patients with acute leukemia subtypes had a complete response – a disappearance of all signs of cancer – to treatment with the drug revumenib. The other paper uncovers a molecular countermove by which leukemia cells come to sidestep the drug and reassert their growth.
The ...