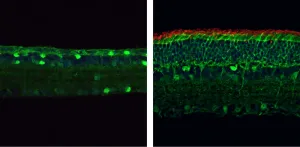
(Press-News.org) Researchers in China have successfully restored the vision of mice with retinitis pigmentosa, one of the major causes of blindness in humans. The study, to be published March 17 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine, uses a new, highly versatile form of CRISPR-based genome editing with the potential to correct a wide variety of disease-causing genetic mutations.
Researchers have previously used genome editing to restore the vision of mice with genetic diseases, such as Leber congenital amaurosis, that affect the retinal pigment epithelium, a layer of non-neuronal cells in the eye that supports the light-sensing rod and cone photoreceptor cells. However, most inherited forms of blindness, including retinitis pigmentosa, are caused by genetic defects in the neural photoreceptors themselves.
“The ability to edit the genome of neural retinal cells, particularly unhealthy or dying photoreceptors, would provide much more convincing evidence for the potential applications of these genome-editing tools in treating diseases such as retinitis pigmentosa,” says Kai Yao, a professor at the Wuhan University of Science and Technology.
Retinitis pigmentosa can be caused by mutations in over 100 different genes and is estimated to impair the vision of 1 in 4,000 people. It begins with the dysfunction and death of dim light-sensing rod cells, before spreading to the cone cells required for color vision, eventually leading to severe, irreversible vision loss.
Yao and colleagues attempted to rescue the vision of mice with retinitis pigmentosa caused by a mutation in the gene encoding a critical enzyme called PDE6β. To do this, Yao’s team developed a new, more versatile CRISPR system called PESpRY, which can be programmed to correct many different types of genetic mutation, regardless of where they occur within the genome.
When programmed to target the mutant PDE6β gene, the PESpRY system was able to efficiently correct the mutation and restore the enzyme’s activity in the retinas of mice. This prevented the death of rod and cone photoreceptors and restored their normal electrical responses to light.
Yao and colleagues performed a variety of behavioral tests to confirm that the gene-edited mice retained their vision even into old age. For example, the animals were able to find their way out of a visually guided water maze almost as well as normal, healthy mice and showed typical head movements in response to visual stimuli.
Yao cautions that much work still needs to be done to establish both the safety and efficacy of the PESpRY system in humans. “However, our study provides substantial evidence for the in vivo applicability of this new genome-editing strategy and its potential in diverse research and therapeutic contexts, in particular for inherited retinal diseases such as retinitis pigmentosa,” Yao says.
Qin et al. 2023. J. Exp. Med. https://rupress.org/jem/article-lookup/doi/10.1084/jem.20220776?PR
# # #
About Journal of Experimental Medicine
Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM) publishes peer-reviewed research on immunology, cancer biology, stem cell biology, microbial pathogenesis, vascular biology, and neurobiology. All editorial decisions on research manuscripts are made through collaborative consultation between professional scientific editors and the academic editorial board. Established in 1896, JEM is published by Rockefeller University Press, a department of The Rockefeller University in New York. For more information, visit jem.org.
Visit our Newsroom, and sign up for a weekly preview of articles to be published. Embargoed media alerts are for journalists only.
Follow JEM on Twitter at @JExpMed and @RockUPress.
END
New gene-editing technique reverses vision loss in mice
2023-03-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Machine intelligence and humanity benefit from ‘spiral’ of mutual learning, says AI researcher and proponent of ‘cognitive physics’
2023-03-17
Deyi Li from the Chinese Association for Artificial Intelligence believes that humans and machines have a mutually beneficial relationship. His paper on machine intelligence, which was published Feb. 15 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal, builds on five groundbreaking works by Schrödinger, the father of quantum mechanics, Turing, the father of artificial intelligence, and Wiener, the father of cybernetics.
Schrödinger and beyond: Machines can think and interact with the world as time goes by. ...
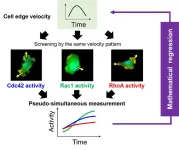
Miracle math determines the dynamically coordinated regulation of edge velocity by Rho GTPases
2023-03-17
Ikoma, Japan – Rho GTPases have a crucial role in the orchestration of cell movements. Cells use Rho GTPases to coordinate cytoskeletal reorganization in dynamically changing environments. Among these RhoGTPases, Cdc42 and Rac1 promote cytoskeletal formation, whereas RhoA is involved in myosin II-mediated cytoskeletal retraction and formation.
Simultaneous live observations of multiple GTPase activities and cell morphology changes by specific biosensors and the resulting spatiotemporal data might help to determine the coordinated regulation of ...
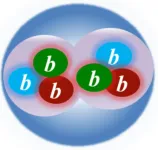
The most beautiful strongly bound dibaryon
2023-03-17
Dibaryons are the subatomic particles made of two baryons. Their formations through baryon-baryon interactions play a fundamental role in big-bang nucleosynthesis, in nuclear reactions including those within stellar environments, and provide a connection between nuclear physics, cosmology and astrophysics. Interestingly, the strong force, which is the key to the existence of nuclei and provides most of their masses, allows formations of numerous other dibaryons with various combinations of quarks. However, we do not observe them abound -- deuteron is the only known stable dibaryon.
To resolve this apparent dichotomy, it is essential to investigate ...
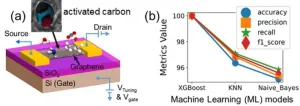
New machine-learning approach enables to identify one molecule in a billion molecules selectively with graphene sensors
2023-03-17
Graphene’s 2D nature, single molecule sensitivity, low noise, and high carrier concentration have generated a lot of interest in its application in gas sensors. However, due to its inherent non-selectivity, and huge p-doping in atmospheric air, its applications in gas sensing are often limited to controlled environments such as nitrogen, dry air, or synthetic humid air. While humidity conditions in synthetic air could be used to achieve controlled hole doping of the graphene channel, this does not adequately mirror the situation ...
ETRI introduces AI tutor who teaches foreign language reading
2023-03-17
The Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute(ETRI) has developed a reading comprehension education AI technology that allows you to learn foreign language listening, speaking, and reading by talking to an artificial intelligence (AI) tutor. It is expected to be of great help in the spread of AI-based language education services.
The Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute(ETRI) introduced a reading comprehension AI tutor, an artificial intelligence technology for reading education, that introduced deep learning-based dialog processing technology to reading comprehension education for the first time in the world. Through ...
Burt's Bees nature-based products improve photodamaged and hyperpigmented facial skin
2023-03-17
DURHAM, N.C., March 17, 2023 – Burt’s Bees, the #1 dermatologist recommended natural skin care brand,* announced its latest research findings on the benefits of a topical bakuchiol-containing sunscreen in treating redness and pigmentation of photodamaged facial skin. Burt’s Bees also published research findings on a topical treatment in improving the appearance of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation associated with acne. These studies, available online via ePoster, have been developed for the American Academy of Dermatology 2023 Annual Meeting (AAD) Mar. 17–21, 2023, ...
Resistant bacteria are a global problem. Now researchers may have found the solution
2023-03-17
Staphylococcus aureus. You may have had it in connection with a wound infection. In most cases, it will pass without treatment, while severe cases may require antibiotics, which kills the bacteria. This is the case for the majority of the population. In fact, many of us – though we feel perfectly fine – carry staphylococci in the nose, a good, moist environment in which the bacteria thrive.
However, more and more staphylococci are becoming resistant to antibiotics (also known as multi resistant staphylococcus aureus or MRSA), and these infections can be difficult to treat.
“Antibiotics resistance ...
An elegant new orchid hiding in plain sight
2023-03-17
It is extremely rare for a new plant species to be discovered in Japan, a nation where flora has been extensively studied and documented. Nevertheless, Professor SUETSUGU Kenji and his associates recently uncovered a stunning new species of orchid whose rosy pink petals bear a striking resemblance to glasswork (Fig. 1). Since it was initially spotted near Hachijo Island in Tokyo Prefecture, the new species has been given the name Spiranthes hachijoensis. Interestingly, it can be found in familiar environments such as lawns and parks, and even in private gardens and on balconies. This research suggests ...
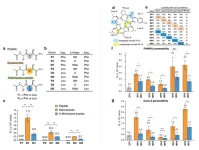
Investigating the effects on amide-to-ester substitutions on membrane permeability of cyclic peptides
2023-03-17
Cyclic peptides often exhibit low membrane permeability which can be significantly improved via amide-to-ester substitutions—as demonstrated by researchers from Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech). The utilization of substitutions shown in this study can be used to develop cyclic peptides with high membrane permeability and oral bioavailability for clinical and therapeutic applications.
Interest in cyclic peptides, a class of organic molecules, has reached a new high recently. Their ability as inhibitors has made them ...
EHRA 2023: The hottest science in heart rhythm disorders
2023-03-17
Date: 17 March 2023
16 to 18 April in Barcelona, Spain and online
Discover what’s new and on the horizon in the prevention and treatment of heart rhythm disorders at EHRA 2023, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).
The annual congress of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA), a branch of the ESC, will be held 16 to 18 April at the Fira Gran Via, Hall 8, in Barcelona, Spain and online. Explore the scientific programme.
Novel research ...