Researchers develop biodegradable, biorecyclable glass
2023-03-17
(Press-News.org)
Everyone is familiar with glass—from putting on eyeglasses, pushing open the window, standing in front of a mirror, to holding a water glass. Glass is ubiquitous in nature and essential to human life.
But the widespread use of persistent, non-biodegradable glass that cannot be naturally eliminated causes long-term environmental hazards and social burdens.
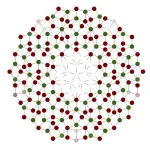
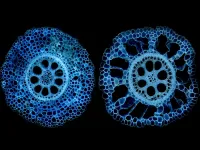
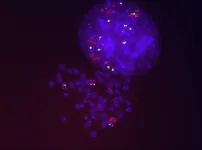
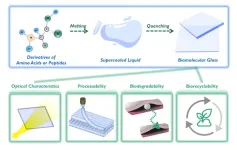
To solve this problem, a research group led by Prof. YAN Xuehai from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a family of eco-friendly glass of biological origin fabricated from biologically derived amino acids or peptides. The proposed glass is biodegradable and biorecyclable.
This study was published in Science Advances on Mar. 17.
Traditional glass, such as commercial inorganic glass and poly (methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) organic glass, etc., is biologically incompatible and not readily degraded in nature. The development of biodegradable and biorecyclable glass is expected to have a minimal environmental footprint.
Unfortunately, manufacturing such eco-friendly glass of biological origin is very challenging because biomolecules possess poor thermal stability and decompose easily at the high temperatures typically used in glass manufacturing.
In this study, the researchers used chemically modified amino acids and peptides to fabricate biomolecular glass with biodegradability and biorecyclability features through the classic "heating-quenching" procedure.
The researchers tracked the glass-forming ability, glass-transition-related kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of the material, as well as glass performance in vitro and in vivo.
Surprisingly, the biomolecular glass based on derivatives of amino acids or peptides showed a unique combination of functional properties and eco-friendly features, including excellent optical characteristics, good mechanical properties and flexible processability, as well as the desired biodegradability and biorecyclability. "The concept of biomolecular glass, beyond the commercially-used glasses or plastics, may underlie a green-life technology for a sustainable future," said Prof. YAN. "However, the biomolecular glass is currently in the laboratory stage, and far from large-scale commercialization."
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-03-17
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., March 17, 2023 — Research using a quantum computer as the physical platform for quantum experiments has found a way to design and characterize tailor-made magnetic objects using quantum bits, or qubits. That opens up a new approach to develop new materials and robust quantum computing.
“With the help of a quantum annealer, we demonstrated a new way to pattern magnetic states,” said Alejandro Lopez-Bezanilla, a virtual experimentalist in the Theoretical Division at Los Alamos National Laboratory. ...
2023-03-17
LA JOLLA—(March 17, 2023) Cancer treatments have long been moving toward personalization—finding the right drugs that work for a patient’s unique tumor, based on specific genetic and molecular patterns. Many of these targeted therapies are highly effective, but aren’t available for all cancers, including non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLCs) that have an LKB1 genetic mutation. A new study led by Salk Institute Professor Reuben Shaw and former postdoctoral fellow Lillian Eichner, now an assistant professor ...
2023-03-17
DURHAM, N.C. – A research team at Duke Health has identified a set of biomarkers that could help distinguish whether cysts on the pancreas are likely to develop into cancer or remain benign.
Appearing online March 17 in the journal Science Advances, the finding marks an important first step toward a clinical approach for classifying lesions on the pancreas that are at highest risk of becoming cancerous, potentially enabling their removal before they begin to spread.
If successful, the biomarker-based approach could address the biggest impediment to decreasing the ...
2023-03-17
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A new discovery, reported in a global study that encompassed more than a decade of research, could lead to the breeding of corn crops that can withstand drought and low-nitrogen soil conditions and ultimately ease global food insecurity, according to a Penn State-led team of international researchers.
In findings published March 16 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science, the researchers identified a gene encoding a transcription factor – a protein useful for converting DNA into RNA – that triggers a genetic sequence responsible for the development of an important trait enabling corn roots ...
2023-03-17
With more than half of the world’s population active on social media networks, user-generated data has proved to be fertile ground for social scientists who study attitudes about the environment and sustainability.
But several challenges threaten the success of what's known as social media data science. The primary concern, according to a new study from an international research team, is limited access to data resulting from restrictive terms of service, shutdown of platforms, data manipulation, censorship and regulations.
The study, published online March ...
2023-03-17
Even after 27 years of reunification, East Germans are still more likely to be pro-state support than their Western counterparts, a new study published in the De Gruyter journal German Economic Review finds. Of the sample studied, 48% of respondents from the East said it was the government’s duty to support the family compared to 35% from the West.
The study led by Prof. Nicola Fuchs-Schündeln of Goethe University Frankfurt, Germany builds on her earlier work which evaluated results from the German Socio-Economic Panel, a regular survey of around 15,000 households. The survey has been running in the federal ...
2023-03-17
NORTH LOGAN, UTAH - NASA has announced that the launch of the Utah State University Space Dynamics Laboratory and College of Science-led Atmospheric Waves Experiment, or AWE, is scheduled for December 2023. The NASA-funded instrument will launch from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station to the International Space Station.
AWE Principal Investigator Michael Taylor from USU’s College of Science leads a team of scientists that will provide new details about how the weather on Earth interacts with, and affects, space weather. To do that, the AWE instrument, measuring about 54 centimeters by 1 meter and weighing less than 57 kilograms, will peer into Earth’s ...
2023-03-17
Texas Engineers are leading a multi-university research team that will build technology and tools to improve measurement of important climate factors by observing atoms in outer space.
They will focus on the concept of quantum sensing, which use quantum physics principles to potentially collect more precise data and enable unprecedented science measurements. These sensors could help satellites in orbit collect data about how atoms react to small changes in their environment, and using that to infer the ...
2023-03-17
A collaborative study carried out by the groups of Matthias Drosten, principal investigator at the Cancer Research Center (CSIC- University of Salamanca), and Mariano Barbacid, head of the Experimental Oncology group at the CNIO, reveals the mechanisms responsible for the development of tumor resistance to Sotorasib, the first approved inhibitor against the KRAS oncogene.
The study, recently published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, shows that lung tumor cells can rapidly adapt to this drug by increasing the number of copies of the mutated KRAS gene targeted by the treatment and by increased expression of xenobiotic pathways that limit ...
2023-03-17
Fossil site is ‘Rosetta Stone’ for understanding early life
Leading edge technology has uncovered secrets about a world-renowned fossil hoard that could offer vital clues about early life on earth.
Researchers who analysed the 400 million-year-old-cache, found in rural north-east Scotland, say their findings reveal better preservation of the fossils at a molecular level than was previously anticipated.
Fresh scrutiny of the exquisitely preserved treasure trove from Aberdeenshire has enabled scientists to identify the chemical fingerprints of the various organisms within ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers develop biodegradable, biorecyclable glass