(Press-News.org) Motivated by the limitations of scanning approaches to photoacoustic microscopy, an international group supervised by Emmanuel Bossy of Université Grenoble Alpes experimented with structured illumination using known and unknown speckle patterns. One of their experiments produced the first demonstration of the use of blind structured illumination for photoacoustic imaging through a diffuser.
The group’s research was published Jan. 11 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.
The research article concludes that “photoacoustic microscopy can harness many of the structured illumination methods developed initially for pure optical methods such as fluorescence microscopy simply by replacing light detection with acoustic detection.”
One type of structured illumination is speckle illumination, which looks just how it sounds. Speckle illumination belongs to a class of illumination patterns that seem random but can be described statistically. It can be generated using equipment that is cheaper and more flexible than the spatial light modulators needed to generate other types of structured illumination.
In biomedical applications, speckle illumination has two advantages. One is that spreading out and thus reducing the intensity of the illumination can reduce damage to the targeted tissue. Another is that, if the sample is sparse enough, the necessary measurements can be collected faster.
Some devices used for minimally invasive endoscopic surgery produce their own speckle illumination. Previous research suggested exploiting this illumination and demonstrated the principle with fluorescent microscopy, but not photoacoustic microscopy.
The authors hope to see more research in the area of photoacoustic microscopy as acoustic detectors become more sensitive.
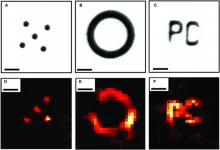
In one set of experiments, the authors used three different popular methods to reconstruct photoacoustic images that were created using speckle illumination patterns. They used a correlation approach, a pseudo-inverse approach, and a compressed sensing approach for each experimental setup. In one setup, they used an optical diffuser to create the speckle patterns. In another setup, they used a multimode optical fiber with a special fiber optic sensor attached. In both of these setups, they calibrated the equipment to collect data that could be used to reconstruct the image.
In another set of experiments, the authors relied on a phenomenon known as the optical memory effect, which allowed them to reconstruct the image without first calibrating the equipment. The authors believe the images produced by their blind structured illumination optical diffuser setup are the first of their kind.
Photoacoustic imaging, also called optoacoustic imaging, is a technique that measures sound emitted by the target when light is focused on it. The light heats the target, causing a temporary size increase that produces a sound wave.
Scanning implementations of photoacoustic microscopy require a sensor to observe every part of the target in a straightforward sequence. One drawback of this approach is that it can take a long time. Thus, researchers looked to optical microscopy for more efficient methods that might also work well in the acoustic domain.
In optical microscopy, the alternative to scanning is variously called single-pixel imaging, ghost imaging, structured illumination, or structured detection. What these methods have in common, in contrast to scanning methods, is a more sophisticated spatial sampling strategy that requires image reconstruction after data is captured. Previous research proposed and demonstrated that such optical microscopy methods can also be used for photoacoustic microscopy.
Bossy’s co-authors on this paper are Antonio M. Caravaca-Aguirre, Florian Poisson, Dorian Bouchet, Philippe Moreau and Irene Wang of CNRS, Grenoble, France; Nicolino Stasio, Claire Prada and Demetri Psaltis of EPFL, Lausanne, Switzerland; Edward Zhang and Paul Beard of University College London; Christophe Moser of CNRS, Paris, France; and Ori Katz of Hebrew University of Jerusalem.
END
Speckle-illumination proves useful in photoacoustic microscopy
2023-03-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Carnegie Mellon researchers develop head-worn device to control mobile manipulators
2023-03-20
More than five million people in the United States live with some form of paralysis and may encounter difficulties completing everyday tasks, like grabbing a glass of water or putting on clothes. New research from Carnegie Mellon University's Robotics Institute (RI) aims to increase autonomy for individuals with such motor impairments by introducing a head-worn device that will help them control a mobile manipulator.
Teleoperated mobile manipulators can aid individuals in completing daily activities, but many existing technologies like hand-operated joysticks or web interfaces require a user to have substantial fine motor skills to effectively ...
Excess calories during development alters the brain and spurs adult overeating
2023-03-20
People whose mothers are overweight during pregnancy and nursing may become obese as adults because early overnutrition rewires developing brains to crave unhealthy food, according to a Rutgers study in Molecular Metabolism.
Rutgers researchers traced this link from mother to child in mice with an experiment that began by letting some mice get obese on unlimited high-fat food during pregnancy and breastfeeding while keeping others slim on limitless healthy food. They found that mice born to obese mothers stay slim in adulthood on unlimited healthy food but overeat more than mice born to lean mothers when given access to unhealthy food.
The ...
Federal-local immigration enforcement policies designed to reduce crime found to raise victimization among Latinos
2023-03-20
Efforts to understand the effects of immigration enforcement on crime have largely been informed by police crime statistics. In a new study, researchers used longitudinal data from the U.S. National Crime Victimization Survey (NCVS) to assess the impact of federal immigration policies on local communities. They found that activation of two policies—the Secure Communities Program and 287(g) task force agreements—significantly increased the risk of violent victimization among Latinos.
The study, by researchers at Penn State University and the University of Maryland (UMD) at College Park, ...
Developing postoperative delirium is associated with a faster rate of cognitive decline
2023-03-20
BOSTON, MA -- Research published today in the JAMA Internal Medicine finds that developing postoperative delirium is associated with a 40% faster rate of cognitive decline over those who do not develop delirium.
“Delirium is associated with faster cognitive decline,” said Zachary J. Kunicki, PhD, MS, MPH Assistant Professor located at the Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, the first author. “Whether delirium causes this faster rate of decline, or is simply a marker of those who are at risk of experiencing faster ...
Daily step counts before, after onset of COVID-19
2023-03-20
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest a consistent, widespread, and significant decline in activity following the onset of COVID-19 in the United States. Vulnerable populations, including individuals at a lower socioeconomic status and those reporting worse mental health in the early COVID-19 period, were at the highest risk of reduced activity. The researchers found a significant decline in daily step counts that persisted even after most COVID-19–related restrictions were relaxed, suggesting COVID-19 affected long-term behavioral choices. It is currently unknown whether this reduction is steps is clinically meaningful over time.
Authors: Evan L. ...
Gender disparity in NIH funding among surgeon-scientists
2023-03-20
About The Study: The results of this study of National Institutes of Health (NIH)-funded surgeons suggest that women surgeons remained underrepresented among surgeon-scientists over a 25-year period despite early career success in receiving NIH funding. These findings suggest that substantial additional support for women surgeon-scientists is necessary to achieve a gender-diverse surgical research workforce.
Authors: Mytien Nguyen, M.S., of the Yale School of Medicine in New Haven, Connecticut, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.3630)
Editor’s ...
Patients overwhelmingly prefer immediate access to test results, even when the news may not be good
2023-03-20
BOSTON – In April 2021, new federal rules went into effect mandating that healthcare providers make nearly all test results and clinical notes immediately available to patients. Evidence suggests that patients may gain important clinical benefits by reviewing their medical records, and access through electronic patient portals has been advocated as a strategy for empowering patients to manage their health care and for strengthening patient-clinician relationships. However, concerns remain about the effects of releasing test results to patients before clinicians offer counsel or interpretation.
In ...
PLOS announces newest joiners to the CRL/NERL Agreement
2023-03-20
SAN FRANCISCO – The Public Library of Science (PLOS) welcomes several new participants to its ongoing three-year consortial agreement with Center for Research Libraries (CRL) and the Northeast Research Libraries (NERL) program. Joining twenty fellow member institutions who signed on during the first year, newly participating institutions for the second year include Duke University, Macalester College, University of Arizona, University of Denver, and University of Southern California, University of Texas at Austin, and University of Washington.
This agreement provides researchers with unlimited publishing privileges in PLOS journals without incurring fees. All PLOS journals are underpinned ...
Link between chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular disease explained
2023-03-20
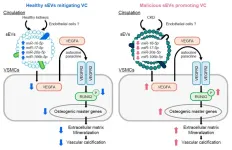
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have uncovered a link between cardiovascular disease and chronic kidney disease, revealing novel disease biomarkers and therapeutic targets
Tokyo, Japan – Chronic kidney disease is linked to the formation of mineral deposits on blood vessel walls, known as “calcification”, causing cardiovascular disease. Small extracellular vesicles (sEVs)—small, enclosed structures outside cells—can transmit signaling molecules between cells, but their biological roles are not fully understood. Now, “malicious” sEVs ...
We have better solutions than chemical warfare to tackle climate-related pests and diseases
2023-03-20
Published on 10 March 2023 in Agronomy journal, the TMG Research gGmbH study team traced a highly destructive desert locust invasion in the Eastern Africa and Horn region between 2019-2021. Ethiopia and Kenya sprayed well over a million hectares of territory with damaging nerve agents malathion and chlorpyrifos, both from the organophosphate family of pesticides. The scale of the invasion – and subsequent choice of control measures – was magnified by unprecedented breeding due to changing climate conditions. Due to the inaccessible location of the breeding grounds, the scale of the threat ...