(Press-News.org) The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology sent recommendations to the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services related to the agency’s proposed changes to petition processing fees. The USCIS proposed increasing its filing fees for employment-based visas by up to 2,050%, a measure intended to remedy financial deficits at USCIS and ramp up hiring to improve services. The ASBMB expressed concern about how “the proposed rule is likely to harm the retention of highly skilled foreign-born scientific researchers.”
The society made three recommendations:
Reevaluate the Asylum Program Fee
Phase in scheduled fee increases
Eliminate petition and visa backlogs
“It’s important for the scientific community to be engaged in topics like proposed changes to the visa process because the U.S. research enterprise relies and thrives on attracting foreign-born scientists and students,” said Sarina Neote, public affairs director for the ASBMB. “This compelled us to work with our committee members to submit a response to USCIS; scientists must be represented in these vital policy decisions.”
Immigrant scientists make up more than half of STEM graduate students and the doctoral-level scientific workforce in the United States.
“(T)he current visa process makes it difficult for them to remain in the U.S. to work and contribute to the U.S. economy after their research training is complete,” the society wrote. “This squanders the substantial investment made in these scientists by the U.S. research enterprise and contradicts their tremendous value to U.S. competitiveness and innovation.”
The proposed changes include instituting a $600 Asylum Program Fee to be paid by employers for each I-129 or I-140 petition. The ASBMB expressed concern that this fee may burden nonprofit research organizations disproportionally. The society wrote: “While for-profit companies are likely to easily absorb this additional filing cost, nonprofit organizations and educational institutions are more financially constrained.”
The society emphasized that this asylum fee will be particularly burdensome for academics as temporary grants rarely align with visa-processing timelines. This misalignment often requires multiple submissions of I-129 and I-140 petitions as employees secure additional federal grants. Industry scientists do not typically have funding restrictions. Rather than burden the nation’s brightest and their nonprofit employers, the ASBMB recommended that USCIS seek more federal funding to cover these costs.
“(T)he ASBMB is concerned that the $600 Asylum Program Fee will deter institutes of higher education and other nonprofit research organizations from supporting I-129 and I-140 petitions for their employees,” the society wrote. “This could increase the barriers to retaining scientific talent in the U.S. research workforce at a time when U.S. competitiveness is crucial for the nation to remain a global leader in technology and innovation.”
In addition, the society cautioned against instituting immediate fee increases as this would financially hinder many organizations. Instead, the ASBMB suggested that, if fee increases are necessary, then the USCIS should phase them in over multiple years to allow STEM organizations to adjust their budgets.
Finally, the ASBMB called upon the USCIS to use any new funds raised by fee increases to “remove backlogs, combat fraudulent activity, and reduce processing times that currently burden temporary visa holders in the U.S. scientific workforce.” Some consulates have student visa backlogs approaching one year long, which can prevent foreign-born scientists from completing their education and training in the U.S. thus harming the bioeconomy.
END
ASBMB cautions against drastic immigration fee increases
Society opposes new asylum fees, calls for removing visa backlogs
2023-03-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A new sight for the electrochemical stability in halide electrolytes
2023-03-21
They published their work on February in Energy Material Advances.
"Constructing an efficient ionic/electronic framework is crucial for the development of high-performance solid-state batteries," said Dr. Chuang Yu, a professor at the State Key Laboratory of Advanced Electromagnetic Engineering and Technology at Huazhong University of Science and Technology. "Currently, the application of solid-state batteries with inorganic electrolytes is challenging because most solid electrolytes have an unsatisfactory low oxidation potential."
According to Dr. Yu, halide electrolytes have been found to be cathode-stable materials with relatively wide electrochemical ...
Study confirms nitrate can release uranium into groundwater
2023-03-21
Eight years ago, the data was sound but only suggestive, the evidence strong but circumstantial.
Now, the University of Nebraska–Lincoln’s Karrie Weber and colleagues have experimentally confirmed that nitrate, a compound common in fertilizers and animal waste, can help transport naturally occurring uranium from the underground to groundwater.
Their new research backs a 2015 Weber-led study showing that aquifers contaminated with high levels of nitrate — including the High Plains Aquifer residing beneath Nebraska — also contain uranium concentrations far exceeding a threshold set by the Environmental Protection Agency. Uranium concentrations above that EPA threshold ...
PNAS announces six 2022 Cozzarelli Prize recipients
2023-03-21
WASHINGTON, DC – The Editorial Board of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) has selected six papers published by PNAS in 2022 to receive the Cozzarelli Prize, an award that recognizes outstanding contributions to the scientific disciplines represented by the National Academy of Sciences (NAS). Papers were chosen from more than 3,200 research articles that appeared in the journal last year and represent the six broadly defined classes under which the NAS is organized. Additionally, the Editorial ...
Using optics to trace the flow of microplastics in oceans
2023-03-21
Microplastics are tiny plastic particles less than 5 mm in diameter that have emerged as a novel marine environment pollutant. Microplastics usually result from a breakdown of larger plastic debris but can also be generated from plastic microbeads used in personal care products. Over the years, there has been a significant buildup of microplastic pollutants in our oceans, with a recent estimate that the world’s oceans contain over 24.4 trillion pieces of microplastics weighing between 82,000 and 578,000 tons. It is highly likely that ...
First results from ESO telescopes on the aftermath of DART’s asteroid impact
2023-03-21
Using ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT), two teams of astronomers have observed the aftermath of the collision between NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) spacecraft and the asteroid Dimorphos. The controlled impact was a test of planetary defence, but also gave astronomers a unique opportunity to learn more about the asteroid’s composition from the expelled material.
On 26 September 2022 the DART spacecraft collided with the asteroid Dimorphos in a controlled test of our asteroid deflection capabilities. The impact took place 11 million kilometres away ...
Obesity risk may pass from mothers to daughters
2023-03-21
WASHINGTON—Women with obesity may share risk for the disease with their daughters, but not their sons, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society’s Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Obesity is a common, serious and costly disease affecting nearly half of the adults and 20 percent of children in the United States. It costs an estimated $173 billion in medical care costs. People with obesity are at higher risk of developing diabetes, high blood pressure, heart ...
New program for veterans with high cholesterol, associated cardiovascular disease
2023-03-21
DALLAS, March 21, 2023 — More than 2 million veterans are living with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) and require management of their high cholesterol, according to the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). Left unaddressed, high cholesterol increases the chance of experiencing heart attack and stroke. To control high cholesterol among veterans, the American Heart Association, the world’s leading nonprofit organization focused on heart and brain health for all, in collaboration with the VA, ...
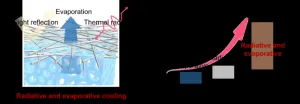
An integrated approach to cool: how evaporation and radiation can cool the world
2023-03-21
Large-scale, effective, and passive: these descriptions are aptly given to the integrated radiative and evaporative chiller (IREC), designed and tested by researchers at Tsinghua University in Beijing, China. The goal of this technology is to come up with an energetically affordable method of cooling to aid in the rising consumption of energy while still minimizing carbon emissions through the process.
“Energy scarcity is a universal challenge to global development. The demand for ...
TAMEST names MD Anderson’s Dr. Florencia McAllister recipient of the 2023 Mary Beth Maddox Award & Lectureship
2023-03-21
TAMEST (The Texas Academy of Medicine, Engineering, Science and Technology) has announced Florencia McAllister, M.D., The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, as the recipient of the 2023 Mary Beth Maddox Award and Lectureship in cancer research. She was chosen for her seminal discoveries at the intersection of microbes, the immune system and pancreatic cancer, leading to insights into early detection, prevention and therapeutic strategies to fight the disease.
The Mary Beth Maddox Award and Lectureship ...
Family Heart Foundation research finds high-risk Americans who do not maintain guideline recommend LDL-C targets have 44% higher rate of cardiovascular events
2023-03-21
SAN ANTONIO, March 21, 2023 – A real-world, retrospective analysis by the Family Heart Foundation, a leading non-profit research and advocacy organization, found that high-risk Americans who do not maintain levels of LDL-cholesterol (LDL-C) recommended in the 2018 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association cholesterol treatment guidelines, had a 44% higher rate of cardiovascular events compared to those who did achieve and maintained recommended LDL-C levels. The study findings, which were based on data from the Family Heart DatabaseTM of more than 300 million Americans, will be ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Researchers determine structural motifs of water undecamer cluster
Researchers enhance photocatalytic hydrogen evolution performance of covalent organic frameworks by constitutional isomer strategy
Molecular target drives immunogenicity in cancer immunotherapy
Plant cell structure could hold key to cancer therapies and improved crops
Sustainable hydrogen peroxide production: Breakthroughs in electrocatalyst design for on-site synthesis
Cash rewards for behavior change: A review of financial incentives science in one health contexts and implications
One Health antimicrobial resistance modelling: from science to policy
Artificial feeding platform transforms study of ticks and their diseases
Researchers uncover microscopic mechanism of alkali species dissolution in water clusters
Methionine restriction for cancer therapy: A comprehensive review of mechanisms and clinical applications
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
[Press-News.org] ASBMB cautions against drastic immigration fee increasesSociety opposes new asylum fees, calls for removing visa backlogs