(Press-News.org) The Science
Protons and neutrons, the building blocks of atomic nuclei, are themselves made up of strongly interacting quarks and gluons">quarks and gluons. Because the interactions are so strong, the structure of protons and neutrons is difficult to calculate from theory. Instead, scientists must measure it experimentally. Neutrino experiments use targets that are nuclei made of many protons and neutrons bound together. This complicates interpreting those measurements to infer proton structure. By scattering neutrinos from the protons that are the nuclei of hydrogen atoms in the MINERvA detector, scientists have provided the first measurements of this structure with neutrinos using unbound protons.
The Impact
Researchers are building several large neutrion experiments, including DUNE and the Sanford Underground Research Facility. These experiments will help make precise measurements of neutrino properties. This in turn will answer questions about how neutrinos affected the structure of our Universe. Those experiments require an accurate understanding of how neutrinos interact on the heavy nuclei in the experiments, such as argon in the case of DUNE. Building a theory of those interactions requires separating the effects of neutrino scattering from protons or neutrons and the effects of the binding in the nucleus. By measuring this property of free protons, the results from MINERvA will help to build more complete theories of neutrino interactions.
Summary
The primary challenge in the measurement described in this new research is that the hydrogen in MINERvA's detector is chemically mixed half and half in plastic with carbon atoms. There are six protons in the carbon atom, so the carbon background reaction is much larger. By developing a novel technique to measure the direction of the outgoing neutron in the reaction, anti-muon neutrino on proton creates anti-muon and neutron, researchers can separate the two reaction types. This allows study of the residual backgrounds using the same parallel reaction in a neutrino beam, where no reaction on the hydrogen atoms is possible. This measurement of structure is interpreted as the axial vector form factor of the proton, a technical term for the structure revealed by neutrino scattering, so that it can be used as inputs to predictions of neutrino reactions.
Funding
This work was funded by the Department of Energy Office of Science, Office of High Energy Physics, by the University of Rochester's Messersmith Graduate Fellowships, and by the National Science Foundation's Graduate Research Fellowships. The Fermilab Accelerator Complex that creates the NuMI neutrino beam used for MINERvA and other experiments is a DOE Office of Science user facility.
END
Imaging the proton with neutrinos
The MINERvA experiment in the NuMI beam at Fermilab has made the first accurate image of the proton using neutrinos instead of light as the probe
2023-03-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
To ward off aging, stem cells must take out the trash
2023-03-21
In humanity’s ongoing quest for the elixir of life, the science keeps pointing to stem cells. Research increasingly shows that maintaining stem cell fitness promotes a long healthspan, and new findings show keeping stem cells clean and tidy is an integral step.
In a study published March 21, 2023 in Cell Stem Cell, researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine found that blood stem cells use an unexpected method to get rid of their misfolded proteins, and that this pathway’s ...
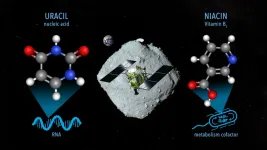
Uracil found in Ryugu samples
2023-03-21
Samples from the asteroid Ryugu collected by the Hayabusa2 mission contain nitrogenous organic compounds, including the nucleobase uracil, which is a part of RNA.
Researchers have analyzed samples of asteroid Ryugu collected by the Japanese Space Agency’s Hayabusa2 spacecraft and found uracil—one of the informational units that make up RNA, the molecules that contain the instructions for how to build and operate living organisms. Nicotinic acid, also known as Vitamin B3 or niacin, which is an important cofactor for metabolism in living organisms, was also detected in the same samples.
This discovery by an international team, led by Associate Professor ...
Honey, the 3D print--I mean, dessert--is ready!
2023-03-21
New York, NY—March 21, 2023—Cooking devices that incorporate three-dimensional (3D) printers, lasers, or other software-driven processes may soon replace conventional cooking appliances such as ovens, stovetops, and microwaves. But will people want to use a 3D printer--even one as beautifully designed as a high-end coffee maker--on their kitchen counters to calibrate the exact micro- and macro-nutrients they need to stay healthy? Will 3D food printing improve the ways we nourish ourselves? What sorts of ...
Albert Einstein College of Medicine and Montefiore Health System awarded $30 million from NIH to support its Institute for Clinical and Translational Research
2023-03-21
March 21, 2023—BRONX, NY—Albert Einstein College of Medicine and Montefiore Health System have received a seven-year, $30 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to continue support for the Harold and Muriel Block Institute for Clinical and Translational Research at Einstein and Montefiore (ICTR). The latest Clinical and Translational Science Award (CTSA) will ensure the ICTR will further its vision to improve health in the Bronx, Westchester, and lower Hudson Valley by accelerating the translation of scientific discoveries into effective and equitable prevention and treatment approaches.
“Since establishing ...
Diet and exercise programs alone won’t tackle childhood obesity
2023-03-21
Focusing on immediate fixes such as diet and exercise programs alone won’t curb the tide of childhood obesity, according to a new study that for the first time maps the complex pathways that lead to obesity in childhood.
Coordinated by the University of Sydney’s Charles Perkins Centre the study finds children whose parents did not complete high school and who live with social disadvantage, were more likely to be affected by overweight or obesity in mid-adolescence. High school completion is a strong indicator of socio-economic status.
These factors were ‘on ramps’ which flow down to influence the body ...
New Yale study evaluates PAXLOVID’s use in Long COVID recovery
2023-03-21
New Haven, Conn. — Yale School of Medicine announces the initiation of a novel, randomized trial that will test whether receiving PAXLOVIDTM (nirmatrelvir tablets; ritonavir tablets) for 15 days can improve the health of highly symptomatic adults with Long COVID.
The trial, led by Yale School of Medicine Professors Harlan Krumholz and Akiko Iwasaki, has a decentralized design, meaning that participants do not have to travel to study sites. It also uses a novel, participant-centric, digital approach to data collection.
Long COVID, also known as post-acute sequelae SARS-CoV-2 ...
ESMT Berlin: New book on how industrial companies can survive deglobalization
2023-03-21
Deglobalization and the unpredictability of global business have led technology-based industries to review their overall strategies. Current geopolitical changes – the war in Ukraine, effects of the pandemic, and greenhouse gas emission targets – revived discussions about the value of globalization. However, international trade of goods and services has been slowing down significantly since 2011, with increasing nationalism being a factor. Additionally, lower salary differentials between developed and emerging economies have reduced overseas product shipments – which are increasingly criticized regarding environmental impact. So, how ...
Scientists find a common thread linking subatomic color glass condensate and massive black holes
2023-03-21
The Science
Physicists have discovered a remarkable correspondence between dense states of gluons—the gluelike carriers of the strong nuclear force within atomic nuclei—and enormous black holes in the cosmos. The dense walls of gluons, known as a color glass condensate (CGC), are generated in collisions of atomic nuclei. This CGC measures a mere 10-19 kilometers across—less than a billionth of a kilometer. Black holes, in contrast, span billions of kilometers across. The new work shows that both systems are made of densely packed, self-interacting force carrier particles. In CGC, those particles are ...
Vocal tract size, shape dictate speech sounds
2023-03-21
WASHINGTON, March 21, 2023 – Only humans have the ability to use speech. Remarkably, this communication is understandable across accent, social background, and anatomy despite a wide variety of ways to produce the necessary sounds.
In JASA, published on behalf of the Acoustical Society of America by AIP Publishing, researchers from University Hospital and Medical Faculty of the RWTH Aachen University explored how anatomical variations in a speaker’s vocal tract affect speech production.
The vocal tract looks like an air duct, starting at the vocal cords and moving vertically through the larynx before bending at the back of the mouth and running ...
Healthy men who have vaginal sex have a distinct urethral microbiome
2023-03-21
Contrary to common beliefs, your urine is not germ free. In fact, a new study shows that the urethra of healthy men is teeming with microbial life and that a specific activity—vaginal sex—can shape its composition. The research, published March 24 in the journal Cell Reports Medicine, provides a healthy baseline for clinicians and scientists to contrast between healthy and diseased states of the urethra, an entrance to the urinary and reproductive systems.
“We know where bugs in the gut come from; they primarily come from our surroundings ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
[Press-News.org] Imaging the proton with neutrinosThe MINERvA experiment in the NuMI beam at Fermilab has made the first accurate image of the proton using neutrinos instead of light as the probe