(Press-News.org) SAN ANTONIO — March 23, 2023 —A study co-authored by Southwest Research Institute Senior Research Scientist Dr. Jason Hofgartner explains the unusual radar signatures of icy satellites orbiting Jupiter and Saturn. Their radar signatures, which differ significantly from those of rocky worlds and most ice on Earth, have long been a vexing question for the scientific community.
“Six different models have been published in an attempt to explain the radar signatures of the icy moons that orbit Jupiter and Saturn,” said Hofgartner, first author of the study, which was published this month in Nature Astronomy. “The way these objects scatter radar is drastically different than that of the rocky worlds, such as Mars and Earth, as well as smaller bodies such as asteroids and comets.”
The objects are also extremely bright, even in areas where they should be darker.
“When we look up at Earth's moon it looks like a circular disk, even though we know it's a sphere. Planets and other moons similarly look like disks through telescopes,” Hofgartner said. “While making radar observations, the center of the disk is very bright and the edges much darker. The change from center to edge is very different for these icy satellites than for rocky worlds.”
In collaboration with Dr. Kevin Hand of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Hofgartner argues that the extraordinary radar properties of these satellites, such as their reflectiveness and polarization (the orientation of light waves as they propagate through space) is very likely to be explained by the coherent backscatter opposition effect (CBOE).
“When you’re at opposition, the Sun is positioned directly behind you on the line between you and an object, the surface appears much brighter than it would otherwise,” Hofgartner said. “This is known as the opposition effect. In the case of radar, a transmitter stands in for the Sun and a receiver for your eyes.”
An icy surface, Hofgartner explained, has an even stronger opposition effect than normal. For every scattering path of light bouncing through the ice, at opposition there is a path in the exact opposite direction. Because the two paths have precisely the same length, they combine coherently, resulting in further brightening.
In the 1990s, studies were published stating that the CBOE was one explanation for the anomalous radar signatures of icy satellites, but other explanations could explain the data equally well. Hofgartner and Hand improved the polarization description of the CBOE model and also showed that their modified CBOE model is the only published model that can explain all of the icy satellite radar properties.
“I think that tells us that the surfaces of these objects and their subsurfaces down to many meters are very tortured,” Hofgartner said. “They’re not very uniform. Icy rocks dominate the landscape, perhaps looking somewhat like the chaotic mess after a landslide. That would explain why the light is bouncing in so many different directions, giving us these unusual polarization signatures.”
The radar observations Hofgartner and Hand used were from the Arecibo Observatory, which was one of only two telescopes making radar observations of icy satellites until it was severely damaged by the collapse of its support structure, antenna and dome assembly and subsequently decommissioned. The researchers hope to make follow-up observations when possible and plan to study additional archival data that may shed even more light on icy satellites and the CBOE, as well as radar studies of ice at the poles of Mercury, the Moon, and Mars.
The paper “An icy-satellite radar-properties continuum that requires the coherent backscatter effect,” appears in Nature Astronomy: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41550-023-01920-2
For more information, visit https://www.swri.org/planetary-science.
END
SwRI, JPL study suggests explanation for unusual radar signatures of icy satellites in the outer solar system
Researchers present answers for long-debated mysterious radar properties of moons of Jupiter and Saturn
2023-03-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Harnessing power of immune system may lessen reliance on antibiotics for infections like TB
2023-03-23
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 16:00 GMT 23 March 2023
Peer reviewed
Experimental study
Human stem cells
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have found that the body’s process of removing old and damaged cell parts, is also an essential part of tackling infections that take hold within our cells, like TB.
If this natural process can be harnessed with new treatments, it could present an alternative to, or improve use of antibiotics, especially where bacteria have become ...
Newly discovered cell in fruit flies is essential for touch sensation
2023-03-23
The Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 16:00 GMT Thursday 23rd March
Peer reviewed
Experimental
Cells
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have uncovered a key role for a new type of cell in touch detection in the skin of the fruit fly.
Touch allows animals to navigate their environment by gathering information from the outside world. In their study published today in Nature Cell Biology, Dr Federica Mangione and Dr Nicolas Tapon shed light on how touch-sensitive organs assemble during development.
In particular the team studied the development ...
Researchers discover a way to fight the aging process and cancer development
2023-03-23
A protein complex prevents the repair of genome damage in human cells, in mice and in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, a team of researchers at the University of Cologne has discovered. They also successfully inhibited this complex for the first time using a pharmaceutical agent.
“When we suppress the so-called DREAM complex in body cells, various repair mechanisms kick in, making these cells extremely resilient towards all kinds of DNA damage,” said Professor Dr Björn Schumacher, Director of the Institute for Genome Stability in Aging ...
A new, sustainable source for a promising cancer killer
2023-03-23
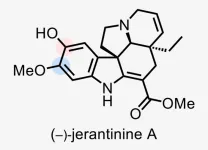
Plants produce all types of curious chemicals. Some deter predators. Some smell wonderful. Some even have medicinal value. One of these hidden gems is (–)-jerantinine A (JA), a molecule with remarkable anticancer properties, produced by a plant called Tabernaemontana corymbosa. Unfortunately, access to this Malaysian jungle plant and its promising chemical compound has been limited. Until now.
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) chemists, led by Professor John E. Moses, have created a way to safely, quickly, and sustainably synthesize JA in the lab. To cancer biologists at CSHL, this breakthrough could mean future ...
Disparities in the research effort to combat animal-borne diseases amid climate change
2023-03-23
Whether it’s diseases from bats, birds, pigs, or mosquitoes, climate change brings with it an increased risk of animal-borne (or “zoonotic”) diseases that can transmit to humans.
Digital Science, a technology company serving stakeholders across the research ecosystem, has today released its analysis of the global research response to climate change and zoonotic diseases, in the context of the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) on climate and health.
Using data from Dimensions, Dr Briony Fane, Ann Campbell and Dr Juergen Wastl from Digital Science have explored published research, ...
Patient-specific cells generated from thymus organoids
2023-03-23
Researchers have used pluripotent stem cells to make thymus organoids that support the development of patient-specific T-cells, researchers report March 23rd in the journal Stem Cell Reports. The proof-of-concept work provides the basis for studying human thymus function, T-cell development, and transplant immunity.
“We have established the framework for further basic science and translational research interrogating human thymus development and function in vitro, and in a patient-specific manner,” says senior author Holger Russ, of the University ...
Early European farmers borrowed genes from hunter-gatherers to survive disease
2023-03-23
When early Stone Age farmers first moved into Europe from the Near East about 8,000 years ago, they met and began mixing with the existing hunter-gatherer populations. Now genome-wide studies of hundreds of ancient genomes from this period show more hunter-gatherer ancestry in adaptive-immunity genes in the mixed population than would be expected by chance.
The findings, reported in Current Biology on March 23, suggest that mixing between the two groups resulted in mosaics of genetic variation that were acted upon by natural selection, a process through which all organisms, including humans, adapt and change ...
Deceptive daisy’s ability to create fake flies explained
2023-03-23
A male fly approaches a flower, lands on top of what he thinks is a female fly, and jiggles around. He’s trying to mate, but it isn’t quite working. He has another go. Eventually he gives up and buzzes off, unsuccessful. The plant, meanwhile, has got what it wanted: pollen.
A South African daisy, Gorteria diffusa, is the only daisy known to make such a complicated structure resembling a female fly on its petals. The mechanism behind this convincing three-dimensional deception, complete ...
Ancient genomes reveal immunity adaptation in early farmers
2023-03-23
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 15:00hrs GMT 23 March 2023
Peer reviewed
Observational study
People
Research from the Francis Crick Institute published today in Current Biology has revealed that diversity in genes coding for immunity may have facilitated adaptation to farming lifestyles in prehistoric periods.
Researchers at the Ancient Genomics Laboratory at the Crick studied available genome-wide DNA from 677 individuals dating to Stone Age Europe, spanning the movement of Neolithic farmers from the Near East into Europe about 8000 years ago, where they mixed with Mesolithic hunter-gatherers already in Europe.
They were interested in whether ...
Vaccination halves risk of long COVID, largest study to date shows
2023-03-23
Being vaccinated against Covid halves people’s risk of developing long Covid, according to new research from the University of East Anglia.
Long Covid still affects some two million people in the UK, and new research published today reveals the risk factors associated with developing the condition.
Overweight people, women, smokers and those over the age of 40 are also more likely to suffer from long Covid according to the study - which includes more than 860,000 patients and is thought to be the largest of its kind.
The study also finds that co-morbidities such as asthma, COPD, Type 2 Diabetes, coronary heart disease, immunosuppression, anxiety ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
Predicting extreme rainfall through novel spatial modeling
The Lancet: First-ever in-utero stem cell therapy for fetal spina bifida repair is safe, study finds
Nanoplastics can interact with Salmonella to affect food safety, study shows
Eric Moore, M.D., elected to Mayo Clinic Board of Trustees
NYU named “research powerhouse” in new analysis
New polymer materials may offer breakthrough solution for hard-to-remove PFAS in water
Biochar can either curb or boost greenhouse gas emissions depending on soil conditions, new study finds
Nanobiochar emerges as a next generation solution for cleaner water, healthier soils, and resilient ecosystems
Study finds more parents saying ‘No’ to vitamin K, putting babies’ brains at risk
Scientists develop new gut health measure that tracks disease
Rice gene discovery could cut fertiliser use while protecting yields
Jumping ‘DNA parasites’ linked to early stages of tumour formation
[Press-News.org] SwRI, JPL study suggests explanation for unusual radar signatures of icy satellites in the outer solar systemResearchers present answers for long-debated mysterious radar properties of moons of Jupiter and Saturn