(Press-News.org) MADISON – While recent studies and polls indicate the nation is in the midst of a mental health crisis, the situation in academia is even more grim: Within the high-stress, high-pressure, often socially isolated world of advanced education, graduate students experience depression and anxiety at six times the rate of the general population.
Normalizing mindfulness practices within the graduate student experience may be an answer, according to a three-year study conducted by University of Wisconsin–Madison researchers. Their results showed that regular, sustained mindfulness activities can play an important role in improving engineering graduate student emotional well-being.
The research team, which includes UW–Madison engineering and Center for Healthy Minds researchers, published details of the National Science Foundation-funded study in the March 23, 2023 edition of the journal PLOS ONE.
"Because of the state of graduate student mental health nationally, there's a tangible need for a concrete intervention like this," says Susan Hagness, a professor of electrical and computer engineering and one of the study's co-authors. "How do we help our students develop resiliency and a really robust toolbox, both professional and personal, to flourish in an environment where there's inevitably going to be stress? We're getting the word out that investing in self-care is important, and it's normal."
Cultivated through practices such as meditation, yoga or prayer, mindfulness centers around being in the present moment in an open, non-judgmental, curious, accepting way. In recent years, corporate giants like Google, Intel, Nike, General Mills, Target and others have included mindfulness in employee development activities to reduce employee stress and burnout, and enhance their focus, creativity, job satisfaction and wellness.
The UW–Madison research included two studies involving a total of 215 participants across six academic semesters at UW–Madison (and the final four semesters concurrently at the University of Virginia). In the study, engineering graduate student cohorts participated in an hour-long, instructor-led mindfulness training program once a week for eight weeks. This "Mindful Engineer" curriculum was based on an existing Center for Healthy Minds training, "Cultivating Well-Being in the Workplace," and drew on neuroscience-derived concepts described in The Emotional Life of Your Brain, a book co-authored by center founder Richard Davidson, a professor of psychology and psychiatry at UW–Madison.
Each weekly session built on the previous weeks' content; students learned about the brain's neuroplasticity and how it can be trained to change responses to emotions. They explored the six dimensions of emotional style (attention, self-awareness, resilience, outlook, social intuition and sensitivity to context) and learned strategies for creating and maintaining healthy mental and emotional habits. The graduate students also received training in mindfulness meditation and other contemplative practices, cognitive skills and techniques, and each session included time for meditation and cognitive exercises.
In post-training surveys, students reported significantly improved emotional well-being, a more positive outlook, fewer negative emotions and increased mindfulness. Over the same period, the control groups (which received training at a later date) noted steady or decreased well-being. Mindfulness participants also reported they were better able to manage stress and anxiety, deal positively with setbacks, work more effectively with colleagues and focus on their research.
"What was beautiful is that we saw a really consistent pattern of results across all of the cohorts we did this study with," says Pelin Kesebir, an honorary fellow with the Center for Healthy Minds and a study co-author.
Somewhat surprisingly, the researchers also found that engineering graduate students were open to mindfulness training and were not only highly satisfied with it, but also enjoyed the opportunity to connect with other graduate students.
"In the literature, there's evidence that engineers are less likely to seek treatment for mental health issues — so our team wondered if engineers would engage with this," says Wendy Crone, a professor of engineering physics and mechanical engineering and a study co-author. "The answer is that they did, and we had great cohorts throughout the project."
The researchers say they'd like mindfulness training to be integrated into the graduate student experience in the future. In the meantime, they recommend the Healthy Minds Program app, which offers podcast-style lessons and seated and active meditations.
And while the researchers focused on engineering graduate students, they note that adopting a mindfulness practice can be a positive step for anyone.
"Modest investments of your time can result in really significant benefits to your overall well-being," says Hagness. "Small investments in self-care can have long-term rewards."
Wendy Crone is the Karen Thompson Medhi Professor in engineering physics and mechanical engineering. Susan Hagness is the Philip Dunham Reed Professor and chair of the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering.
Other authors on the paper include Center for Healthy Minds collaborator Beverly Hays; Shilagh Mirgain, a psychologist in the Department of Orthopedics and Rehabilitation; and Richard Davidson, the William James and Vilas Professor of Psychology and Psychiatry at UW–Madison. The team's partners at the University of Virginia include Professor David Germano, executive director of the Contemplative Sciences Center; Professor Pamela Norris, former executive dean of the School of Engineering and Applied Science; and Leslie Hubbard, program director in the Contemplative Sciences Center.
# # #
-- Renee Meiller, rlmeiller@wisc.edu, (608) 262-2481
END
For stressed-out grad students, mindfulness makes big difference
2023-03-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Alzheimer's early detection through biomarkers -
2023-03-23
Scientists from Swansea University ‘s Institute for Innovative Materials, Processing and Numerical Technologies (IMPACT) and Japan have been awarded £1.3 million to develop a new “point of care testing” kit that can detect biomarkers for Alzheimer's Disease.
The project follows Dr Sanjiv Sharma’s ground-breaking work in this area and the development of the world’s first COVID-19 ‘smart patch’.
Compared to hypodermic single needles, a ‘smart patch’ consists of a collection of tiny needles - microneedles - created to break the skin barrier in a minimally invasive ...
Rates of autism climb to new highs in the U.S., with California setting record numbers
2023-03-23
New federal studies coauthored by autism experts at Rutgers found that more children have been diagnosed with autism than at any time since monitoring began more than two decades ago.
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), about 4 percent of 8-year-old boys and 1 percent of 8-year-old girls, have autism in the U.S. These estimates are the highest since the CDC’s Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring (ADDM) Network was created in 2000.
Biennial studies from the ADDM Network, which analyzed ...
Study uncovers aspect of how muscular dystrophies progress
2023-03-23
A research study has shed new light on how congenital muscular dystrophies such as Walker-Warburg syndrome progress, bringing hope for better understanding, early diagnosis and treatments of these fatal disorders.
Published in March in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, the research was led by scientists in the lab of Vlad Panin, Ph.D., professor in the Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics in the Texas A&M College of Agriculture and Life Sciences. The study is titled “Protein tyrosine phosphatase 69D is a substrate of protein O-mannosyltransferases 1-2 that is required for the wiring of sensory axons in Drosophila.” ...
Researchers make breakthrough in high-pressure magnetic detection
2023-03-23
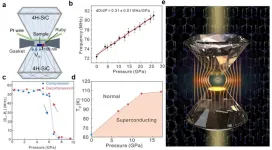
According to a study published in Nature Materials, a collaborative research team from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and the University of Science and Technology of China has developed a research platform to study superconducting magnetic detection and magnetic phase transitions of hydrides under high pressure.
High-resolution in-situ magnetic measurement under high pressure has been a challenge. It has limited the progress of research on the Meissner effect of superconductivity and on magnetic phase transition behavior under high pressure. Using the optically detected ...
Cellular growth rate reshapes cell-fate-decision landscape
2023-03-23
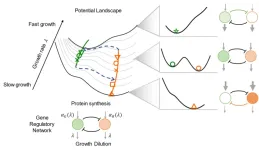
Genes and the regulation relationships among them create complex networks that determine cell differentiation trajectories. However, we still cannot understand and predict the cell-fate-decision process using network topology in a bottom-up manner.
Recently, a research group led by Prof. FU Xiongfei from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has revealed how the global regulation factor, cellular growth rate, reshapes the cell-fate-decision landscape.
The ...
Where does your brain want to have lunch?
2023-03-23
New research published by investigators at Cedars-Sinai advances scientific understanding of how the brain weighs decisions involving what people like or value, such as choosing which book to read, which restaurant to pick for lunch—or even, which slot machine to play in a casino. Published today in the peer-reviewed journal Nature Human Behaviour, this study involved recording the activity of individual human neurons.
The study examined decisions called value-based choices, where there is ...
Microplastics limit energy production in tiny freshwater species
2023-03-23
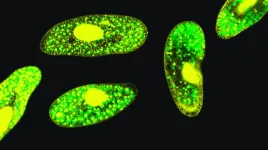
Microplastic pollution reduces energy production in a microscopic creature found in freshwater worldwide, new research shows.
Paramecium bursaria contain algae that live inside their cells and provide energy by photosynthesis.
The new study, by the University of Exeter, tested whether severe microplastic contamination in the water affected this symbiotic relationship.
The results showed a 50% decline in net photosynthesis – a major impact on the algae’s ability to produce energy and release ...
SwRI, JPL study suggests explanation for unusual radar signatures of icy satellites in the outer solar system
2023-03-23
SAN ANTONIO — March 23, 2023 —A study co-authored by Southwest Research Institute Senior Research Scientist Dr. Jason Hofgartner explains the unusual radar signatures of icy satellites orbiting Jupiter and Saturn. Their radar signatures, which differ significantly from those of rocky worlds and most ice on Earth, have long been a vexing question for the scientific community.
“Six different models have been published in an attempt to explain the radar signatures of the icy moons that orbit Jupiter and Saturn,” said Hofgartner, first author of the study, ...
Harnessing power of immune system may lessen reliance on antibiotics for infections like TB
2023-03-23
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 16:00 GMT 23 March 2023
Peer reviewed
Experimental study
Human stem cells
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have found that the body’s process of removing old and damaged cell parts, is also an essential part of tackling infections that take hold within our cells, like TB.
If this natural process can be harnessed with new treatments, it could present an alternative to, or improve use of antibiotics, especially where bacteria have become ...
Newly discovered cell in fruit flies is essential for touch sensation
2023-03-23
The Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 16:00 GMT Thursday 23rd March
Peer reviewed
Experimental
Cells
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have uncovered a key role for a new type of cell in touch detection in the skin of the fruit fly.
Touch allows animals to navigate their environment by gathering information from the outside world. In their study published today in Nature Cell Biology, Dr Federica Mangione and Dr Nicolas Tapon shed light on how touch-sensitive organs assemble during development.
In particular the team studied the development ...