Designing antennas for 6G V2X (Vehicle to Everything) communication
2023-03-24
(Press-News.org)
Researchers at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) are working on designing antennas that can empower 6G technology, which is instrumental in realising efficient V2X (Vehicle to Everything) communications.
In a recent study, the team, led by Debdeep Sarkar, Assistant Professor at the Department of Electrical Communication Engineering, shows how self-interference in full-duplex communication antennas can be reduced, and consequently the movement of signals across the communication network can be faster and more bandwidth-efficient. Such full-duplex antennas are particularly helpful for applications that require almost instantaneous relay of commands, like driverless cars.
Full-duplex antennas consist of a transmitter and a receiver to send and receive radio signals. Traditional radio transceivers are half duplex, which means that they either use signals of different frequencies for sending and receiving or there is a time lag between the signal transmitted and the signal received. This time lag is needed to ensure that there is no interference – the signals going back and forth should not cross paths with each other, similar to two people talking to each other at the same time, without pausing to listen to the other. But this also compromises the efficiency and speed of signal transfer.
In order to transmit data much faster and more efficiently, full-duplex systems are required, where both the transmitter and receiver can operate signals of the same frequency simultaneously. For such systems, eliminating self-interference is key. This is what Sarkar and his IoE-IISc postdoctoral fellow, Jogesh Chandra Dash, have been working on for the past few years.
“The broad objective of the research is that we want to eliminate the signal that is coming as self-interference,” says Sarkar. There are two ways to cancel self-interference – passive and active. Passive cancellation is done without any additional instrument, by just designing the circuit in a certain way (for example, increasing the distance between the two antennas). Active cancellation relies on additional components like signal processing units to cancel out the self-interference. But the components needed for these steps can make the antenna bulky and expensive. What is needed, instead, is a compact, cost-efficient antenna which can be easily integrated into the rest of the circuitry of any device.
The antenna developed by Sarkar and Dash, by virtue of its design, relies on passive interference, allowing it to operate as a full-duplex system. It consists of two ports, either of which can act as transmitter or receiver. The two ports are isolated from each other by electromagnetic tools called metallic vias. Metallic vias are holes drilled into the metal surface of the antenna which disrupt the electric field. In this way, the team managed to cancel out most of the interference passively, alongside achieving a cost-effective and compact design.
“We are eliminating all the conventional techniques for self-interference cancellation, and we are integrating a very simple structure that can be installed in a car,” says Dash.
In the immediate future, the team plans to optimise their device so that it can entirely remove passive interference, and reduce the overall size of the antenna. Then, it can easily be fixed onto a vehicle where it can transmit and receive data at very high speeds, bringing driverless operation as well as 6G mobile connectivity closer to reality.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-03-24
A parasite which has devasting impacts on agriculture and human health is the first pathogen to have its proteins located and mapped within its cells – providing clues to their function and helping to identify potential drug targets.
African trypanosomes are parasites transmitted by tsetse flies that cause sleeping sickness in humans (presenting as fever, anaemia and, in serious cases, death) and a similar disease celled nagana in cattle. These parasites have made large areas of Africa unsuitable for ...
2023-03-24
Graphene is the strongest of all materials. On top of that, it is exceptionally good at conducting heat and electrical currents, making it one of the most special and versatile materials we know. For all these reasons, the discovery of graphene was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2010. Yet, many properties of the material and its cousins are still poorly understood – for the simple reason that the atoms they are made up of are very difficult to observe. A team of researchers from the University of Amsterdam and New York University have now ...
2023-03-24
A new high resolution model of the CA1 region of the human hippocampus has been developed by the Institute of Biophysics of the Italian National Research Council (CNR-IBF) and University of Modena e Reggio Emilia (UNIMORE), part of the Human Brain Project. The single-cell resolution model, which replicates the structure and architecture of the area, along with the position and relative connectivity of the neurons, was developed from a full-scale dataset of high resolution images. The dataset is available in the BigBrain Atlas and it will be soon available on EBRAINS. According to the study, published in the journal ...
2023-03-24
Moderate and severe ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) developed in 1.14% of Chinese women of reproductive age between 2013 and 2017. Moreover, women under 35 years of age receiving assisted reproductive technology (ART) should be monitored for OHSS more closely compared with other age groups.
These findings were concluded from the first report on the incidence of moderate and severe OHSS in China recently published in Health Data Science, a Science Partner Journal.
OHSS constitutes the most severe iatrogenic ...
2023-03-24
Hailey-Hailey disease is a rare, inherited condition characterized by patches of blisters appearing mainly in the skin folds of the arm pits, groin and under the breasts. It is caused by a mutation in the gene that codes for a specific protein involved in the transportation of calcium and manganese ions from the cell cytoplasm and into a sac-like organelle called the Golgi apparatus. Scientists at Tohoku University, together with colleagues in Japan, have uncovered some aspects of this protein's structure that could help researchers understand how it works. The findings, published ...
2023-03-24
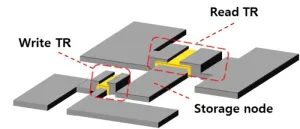
ChatGPT's impact extends beyond the education sector and is causing significant changes in other areas. The AI language model is recognized for its ability to perform various tasks, including paper writing, translation, coding, and more, all through question-and-answer-based interactions. The AI system relies on deep learning, which requires extensive training to minimize errors, resulting in frequent data transfers between memory and processors. However, traditional digital computer systems' von Neumann architecture separates the storage and computation of information, resulting in increased ...
2023-03-24
A research team at POSTECH led by Professor Chulhong Kim (Department of Electrical Engineering, Department of Convergence IT Engineering, and Department of Mechanical Engineering) has compiled the findings from innovative research on contrast-enhanced photoacoustic imaging conducted over the last four years. These findings were recently featured in Chemical Reviews, a highly authoritative journal.
For decades, the scientific community has been investigating the potential of photoacoustic imaging as a biomedical imaging modality. However, despite its enhanced optical contrast and ultrasonic spatiotemporal resolution, photoacoustic imaging faces ...
2023-03-24
FINDINGS
MitoQ, a mitochondrial antioxidant that is available to the public as a diet supplement, was found in a mouse study to reverse the detrimental effects that HIV and antiretroviral therapy (ART) have on mitochondria in the brain, heart, aorta, lungs, kidney and liver.
The researchers used a molecular method to measure the ratio of human and murine mitochondrial (mtDNA) to nuclear DNA (ntDNA) ratio, a measure of mitochondrial dysfunction. Reduction in this ratio reflects mitochondrial dysfunction. Compared to uninfected mice, HIV infected mice treated with ART had mitochondrial dysfunction in the human immune cells in the brain, ...
2023-03-24
DALLAS, March 24, 2023 — High levels of lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] are an independent, predominantly inherited and causal risk factor for cardiovascular disease, the leading cause of death and disability worldwide, according to a recent American Heart Association scientific statement. It is estimated that 1 in 5 Americans have high Lp(a) levels. Studies have shown that elevated Lp(a) — a low-density lipoprotein variant containing a protein called apolipoprotein(a) — is a risk factor for atherosclerosis (buildup of fatty material in artery walls) and related ...
2023-03-24
Dr. Natalie Uy, a leading pediatric nephrologist, has been named chief of the Division of Pediatric Nephrology in the Department of Pediatrics at Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian Komansky Children’s Hospital, effective April 17.
The Division of Pediatric Nephrology provides compassionate care for newborns, children and young adults with complex kidney diseases and urologic conditions. Services provided include dialysis and kidney transplantation for patients with end-stage kidney disease.
Dr. Uy was recruited to Weill Cornell Medicine as an assistant professor of pediatrics ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Designing antennas for 6G V2X (Vehicle to Everything) communication