(Press-News.org) New research shows that people with a lifetime history of mental disorders such as depression, bipolar disorder, or anxiety disorders have blood markers suggesting that they are older than their actual age. This may go some way to explaining why people with mental health problems tend to have shorter lifespans and more age-related diseases than the general population.
Dr Julian Mutz and Prof Cathryn Lewis, from King’s College London, looked at data on 168 different blood metabolites from 110,780 participants in the UK Biobank2. They linked these data to information on whether individuals had a history of mental illness and found that those with a mental illness had a metabolite profile older than would have been expected for their age.
Presenting the work at the European Congress of Psychiatry in Paris, lead researcher Dr Julian Mutz (King’s College London) said:
“It is now possible to predict people’s age from blood metabolites. We found that, on average, those who had a lifetime history of mental illness had a metabolite profile which implied they were older than their actual age. For example, people with bipolar disorder had blood markers indicating that they were around 2 years older than their chronological age.”
People with mental health disorders tend to have shorter lives, and poorer quality health, than the general population3. Estimates of the effect vary according to the mental health condition. Often people with poor mental health show an increased tendency to develop conditions such as heart disease and diabetes, and these conditions tend to worsen with age. A 2019 study found that on average people with mental disorders had shorter life expectancy (in comparison to the general population) by around 10 years for men and seven years for women4.
Dr Mutz continued:
“Our findings indicate that the bodies of people with mental health problems tend to be older than would be expected for an individual their age. This may not explain all the difference in health and life expectancy between those with mental health problems and the general population, but it does mean that accelerated biological ageing may be an important factor. If we can use these markers to track biological ageing, this may change how we monitor the physical health of people with mental illness and how we evaluate the effectiveness of interventions aimed at improving physical health”.
Commenting, Dr Sara Poletti (Istituto Scientifico Universitario Ospedale San Raffaele, Milan) said:
“This is an important work as it gives a possible explanation for the higher prevalence of metabolic and age-related diseases in patients with mental illness. Understanding the mechanisms underlying accelerated biological ageing could be crucial for the development of prevention and tailored treatments to address the growing difficulty of an integrated management of these disorders”.
Dr Poletti was not involved in this work, this is an independent comment.
The European Congress of Psychiatry takes place from 25-28 March 2023, in Paris. It is Europe’s largest congress dedicated to psychiatry, with around 4500 attendees
https://epa-congress.org/
Notes
1This indication is part of a project from the Academy of Medical Sciences to improve press release communication. See https://tinyurl.com/37pp49xu
2 UK Biobank is a large-scale biomedical database and research resource containing anonymised genetic, lifestyle and health information from half a million UK participants. UK Biobank’s database, which includes blood samples, heart and brain scans and genetic data of the volunteer participants, is globally accessible to approved researchers who are undertaking health-related research that’s in the public interest. UK Biobank’s resource was opened for research use in April 2012. Since then 30,000 researchers from 100 countries have been approved to use it and more than 5,000 peer-reviewed papers that used the resource have now been published. You can find out more about UK Biobank at http://www.ukbiobank.ac.uk
3 https://bmcmedicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12916-022-02474-2.
4 https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(19)32316-5/fulltext
This research is funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) Maudsley Biomedical Research Centre at South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust and King’s College London. There are no relevant conflicts of interest.
ENDS
END
Bodies of people with mental illness are biologically older than their actual age
2023-03-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study identifies two promising molecular targets for drug development in recurrent and metastatic cervical cancer
2023-03-27
NRG Oncology GOG-0240 is the phase 3 randomized trial which demonstrated that the incorporation of bevacizumab with chemotherapy resulted in a statistically significant and clinically meaningful survival benefit for women with recurrent and metastatic cervical carcinoma (NCT00803062). GOG-0240 was a proof of concept in anti-angiogenesis therapy and a proof of principle in supportive care and led directly to an indication for bevacizumab in this disease in over 60 countries. Whole genome sequencing and whole exome sequencing of tumor samples obtained in GOG-0240 suggest that ARID1A and PIK3CA could represent potential targets ...
'Nano inks' could passively control temperature in buildings, cars
2023-03-27
World-first ‘phase change inks’ that could transform how we heat and cool buildings, homes and cars – to achieve sophisticated ‘passive climate’ control – have been developed, with enormous potential to help reduce energy use and global greenhouse gas emissions.
New research published in The Royal Society of Chemistry’s Journal of Materials Chemistry A led by Dr Mohammad Taha, documents proof-of-concept ‘phase change inks’ that use nanotechnology to control temperature in everyday environments. They achieve this by adjusting the amount of radiation that can pass through ...
Project helps thousands of people in England and France into employment and entrepreneurship
2023-03-27
New research led by the University of East Anglia (UEA) shows that large infrastructure projects which are the focus of the UK government’s levelling up agenda and include support for business start-ups, must also offer sustainable, local investment in deprived communities.
Through place-based micro-enterprise training and employment support over a longer time frame, lasting local impact can be demonstrated, according to the study’s policy recommendations.
Supporting people to return to their communities, increasing social cohesion within them, boosting digital literacy and enabling net zero jobs are also likely to play a role.
These goals can be easily ...
Embryos’ development is delayed in pregnancies that end in miscarriage
2023-03-27
Embryos in pregnancies that end in miscarriage take longer to develop in the womb than those in pregnancies that result in live births, according to new research published today (Monday) in Human Reproduction [1], one of the world’s leading reproductive medicine journals.
For the first time, researchers in The Netherlands have been able to look at the way embryos develop while pregnancies are ongoing. They used state-of-the-art imaging technology, including 3D ultrasound with high resolution transvaginal probes and ...
Global analysis of coronavirus protein research reveals how countries respond to disease
2023-03-27
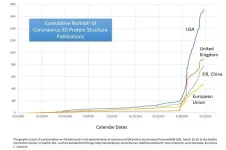
In a new study, researchers examined how a country’s number of published 3D protein structures for coronaviruses, including the one responsible for COVID-19, correlated with its economic output and population. The findings reveal important insights into how different countries' research establishments respond to disease outbreaks and could be useful for planning responses to future pandemics.
The study showed that countries with larger economies generated more 3D structure determinations for the protein components ...
Shh! Intensive care incubators resonate sounds and risk damage to premature babies’ hearing, scientists say
2023-03-27
For vulnerable premature babies, an incubator in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) is a lifesaver, but the consequences can last a lifetime. Many studies have shown that the NICU is a noisy environment and that babies who spend time there have higher rates of hearing impairment, which can lead to delays in language acquisition. Scientists from Vienna, Hamburg, Munich, and Osnabruck set out to investigate the role of the incubator, an underestimated element in the soundscape that surrounds babies during their time in the NICU.
“The ...
Securing new metal 3D printing technology that drives the renaissance of the manufacturing industry!
2023-03-27
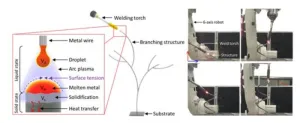
□ A research team led by Dr. Sang-woo Song, Dr. Chan-kyu Kim, Dr. Kang-myung Seo at the Department of Joining Technology of the Korea Institute of Materials Science(KIMS), a government-funded research institute under the Ministry of Science and ICT, has developed a foundational technology for controlling the volume of molten metal in the process of 3D printing metal using welding techniques. They achieved this through collaborative research with a research team led by Professor Young-tae Cho and Professor ...
Advanced technologies for longer-lasting electric vehicles
2023-03-27
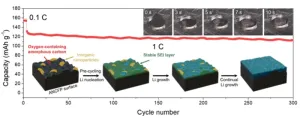
Owing to the worldwide trend of utilizing electric vehicles, there has been a rise in demand for next-generation secondary batteries with higher capacity and faster charging than the lithium-ion batteries currently in use. Lithium metal batteries have been recognized as promising rechargeable batteries because lithium metal anode exhibits theoretical capacity 10 times higher than commercial graphite anode. During charging-discharging processes, however, lithium dendrites grow on the anode, leading to poor battery performance and short-circuit.
Dr. Sungho Lee, Head of the ...
The genetics of temperature adaptation: how does life thrive in extreme conditions?
2023-03-27
The history of the Earth has been one of physical extremes—extreme atmospheric conditions, extreme chemical environments, and extreme temperatures. There was a time when the Earth was so hot all the water was vapor, and the first rain only fell once the planet cooled enough. Soon after, life emerged and through it all, life has found a way. Today life is found almost everywhere on Earth we have looked; it is difficult to find places where life does not exist. The remarkable ability of life to adapt to variable conditions is one of its defining characteristics. Of its many adaptations, the ability of life to adapt to varying temperatures ...
Opening up a different conversation about violence
2023-03-27
20 years on from the invasion of Iraq, nearly 25 years since the Good Friday Agreement in Northern Ireland, and in the midst of war in Ukraine and contested questions about migration and the legacies of war, a brand new Centre for the Study of Violence will launch this week at the University of Bath.
Led by academics across the University’s Faculty of Humanities & Social Sciences, including political theorists, development and humanitarian scholars, plus crime, defence and security experts, the new Centre will be the first of its kind in the UK. It aims to help society rethink how violence operates and to find ways to imagine a more peaceful world.
The Centre ...