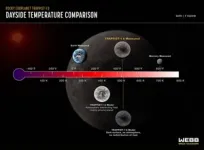
(Press-News.org) An international team of researchers has used NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope to measure the temperature of the rocky exoplanet TRAPPIST-1 b. The measurement is based on the planet’s thermal emission: heat energy given off in the form of infrared light detected by Webb’s Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI). The result indicates that the planet’s dayside has a temperature of about 500 kelvins (roughly 450 degrees Fahrenheit) and suggests that it has no significant atmosphere.
This is the first detection of any form of light emitted by an exoplanet as small and as cool as the rocky planets in our own solar system. The result marks an important step in determining whether planets orbiting small active stars like TRAPPIST-1 can sustain atmospheres needed to support life. It also bodes well for Webb’s ability to characterize temperate, Earth-sized exoplanets using MIRI.
“These observations really take advantage of Webb’s mid-infrared capability,” said Thomas Greene, an astrophysicist at NASA’s Ames Research Center and lead author on the study published today in the journal Nature. “No previous telescopes have had the sensitivity to measure such dim mid-infrared light.”
Rocky Planets Orbiting Ultracool Red Dwarfs
In early 2017, astronomers reported the discovery of seven rocky planets orbiting an ultracool red dwarf star (or M dwarf) 40 light-years from Earth. What is remarkable about the planets is their similarity in size and mass to the inner, rocky planets of our own solar system. Although they all orbit much closer to their star than any of our planets orbit the Sun – all could fit comfortably within the orbit of Mercury – they receive comparable amounts of energy from their tiny star.
TRAPPIST-1 b, the innermost planet, has an orbital distance about one hundredth that of Earth’s and receives about four times the amount of energy that Earth gets from the Sun. Although it is not within the system’s habitable zone, observations of the planet can provide important information about its sibling planets, as well as those of other M-dwarf systems.
“There are ten times as many of these stars in the Milky Way as there are stars like the Sun, and they are twice as likely to have rocky planets as stars like the Sun,” explained Greene. “But they are also very active – they are very bright when they’re young, and they give off flares and X-rays that can wipe out an atmosphere.”
Co-author Elsa Ducrot from the French Alternative Energies and Atomic Energy Commission (CEA) in France, who was on the team that conducted earlier studies of the TRAPPIST-1 system, added, “It's easier to characterize terrestrial planets around smaller, cooler stars. If we want to understand habitability around M stars, the TRAPPIST-1 system is a great laboratory. These are the best targets we have for looking at the atmospheres of rocky planets.”
Detecting an Atmosphere (or Not)
Previous observations of TRAPPIST-1 b with the Hubble and Spitzer space telescopes found no evidence for a puffy atmosphere, but were not able to rule out a dense one.
One way to reduce the uncertainty is to measure the planet’s temperature. “This planet is tidally locked, with one side facing the star at all times and the other in permanent darkness,” said Pierre-Olivier Lagage from CEA, a co-author on the paper. “If it has an atmosphere to circulate and redistribute the heat, the dayside will be cooler than if there is no atmosphere.”
The team used a technique called secondary eclipse photometry, in which MIRI measured the change in brightness from the system as the planet moved behind the star. Although TRAPPIST-1 b is not hot enough to give off its own visible light, it does have an infrared glow. By subtracting the brightness of the star on its own (during the secondary eclipse) from the brightness of the star and planet combined, they were able to successfully calculate how much infrared light is being given off by the planet.
Measuring Minuscule Changes in Brightness
Webb’s detection of a secondary eclipse is itself a major milestone. With the star more than 1,000 times brighter than the planet, the change in brightness is less than 0.1%.
“There was also some fear that we’d miss the eclipse. The planets all tug on each other, so the orbits are not perfect,” said Taylor Bell, the post-doctoral researcher at the Bay Area Environmental Research Institute who analyzed the data. “But it was just amazing: The time of the eclipse that we saw in the data matched the predicted time within a couple of minutes.”
The team analyzed data from five separate secondary eclipse observations. “We compared the results to computer models showing what the temperature should be in different scenarios,” explained Ducrot. “The results are almost perfectly consistent with a blackbody made of bare rock and no atmosphere to circulate the heat. We also didn’t see any signs of light being absorbed by carbon dioxide, which would be apparent in these measurements.”
This research was conducted as part of Webb Guaranteed Time Observation (GTO) program 1177, which is one of eight programs from Webb’s first year of science designed to help fully characterize the TRAPPIST-1 system. Additional secondary eclipse observations of TRAPPIST-1 b are currently in progress, and now that they know how good the data can be, the team hopes to eventually capture a full phase curve showing the change in brightness over the entire orbit. This will allow them to see how the temperature changes from the day to the nightside and confirm if the planet has an atmosphere or not.
“There was one target that I dreamed of having,” said Lagage, who worked on the development of the MIRI instrument for more than two decades. “And it was this one. This is the first time we can detect the emission from a rocky, temperate planet. It’s a really important step in the story of discovering exoplanets.”
The James Webb Space Telescope is the world's premier space science observatory. Webb will solve mysteries in our solar system, look beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probe the mysterious structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Webb is an international program led by NASA with its partners, ESA (European Space Agency), and CSA (Canadian Space Agency). MIRI was contributed by NASA and ESA, with the instrument designed and built by a consortium of nationally funded European Institutes (the MIRI European Consortium) and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, in partnership with the University of Arizona.
END
NASA’s Webb measures the temperature of a rocky exoplanet
2023-03-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Benefiting from orphan drug and rare pediatric disease designations for gene therapy
2023-03-27
Providing an overview of the submissions process and examples of U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) applications for Orphan Drug Designation (ODD) and Rare Pediatric Disease Designation (RPDD), a new article can help developers of gene therapies for rare genetic diseases. The article is published in the peer-reviewed journal Human Gene Therapy. Click here to read the article now.
Anne Pariser and Elizabeth Ottinger, from the National Center for Advances in Translational Sciences (NCATS), National Institutes of Health, and coauthors, describe the ODD and RPDD programs, which provide financial incentives for the development of ...
Study paves way to more efficient production of 2G ethanol using specially modified yeast strain
2023-03-27
A Brazilian study paves the way to increased efficiency of second-generation (2G) ethanol production based on the discovery of novel targets for metabolic engineering in a more robust strain of industrial yeast. An article on the study is published in the journal Scientific Reports.
The databases compiled by the authors are at the disposal of the scientific community in the repository of the State University of Campinas (UNICAMP), which is a member of the Dataverse Project, an international collaborative initiative supported by FAPESP.
First-generation (1G) ethanol is produced from sources rich in carbohydrates ...
UC Davis Health collaborates with Propeller Health to improve clinical outcomes of COPD patients
2023-03-27
UC Davis Health and Propeller Health have announced a new collaboration that will offer personalized treatment for high-risk patients with asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) aiming to improve their health outcomes.
As part of the collaboration, UC Davis Health will provide the Propeller program – including sensors, mobile app, web portal, and personalized support – to eligible patients, with eventual expansion to patients in other UC locations and UC affiliates. The sensors attach to a patient’s inhaler to capture unique signals that record events, such as ...
Largest study to date of minipuberty identifies two new patterns of the reproductive hormone, AMH, in infant girls
2023-03-27
Minipuberty is a stage of reproductive development during infancy in both sexes when reproductive hormones change and reproductive organs develop. The importance of minipuberty is not well understood but could represent an opportunity for the early identification of future reproductive conditions and enable prompt treatment. Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) is one of the hormones that changes during minipuberty, and it plays a key role in the development of reproductive organs in boys. However, the role of AMH in infant girls is less clear.
In ...
Bomb-sniffing rodents undergo ‘unusual’ reproductive transformations
2023-03-27
ITHACA, N.Y. – Female giant African pouched rats, used for sniffing out landmines and detecting tuberculosis, can undergo astounding reproductive organ transformations, according to a new study.
The paper, “Extreme plasticity of reproductive state in a female rodent,” which published March 27 in Current Biology, explores how traits once considered “fixed” in adult animals may become variable under specific pressures.
Though these rodents could have important military, biodetection and humanitarian uses, breeding them at high rates has been a challenge. ...
ENGOT-EN6-NSGO/GOG-3031/RUBY trial results: The new standard of care in advanced/recurrent endometrial cancer
2023-03-27
EMBARGO DATE: Monday, March 27, 2023, 12:30 pm ET
PRESS RELEASE
ENGOT-EN6-NSGO/GOG-3031/RUBY trial results:
The new standard of care in advanced/recurrent endometrial cancer
ENGOT, NSGO-CTU & GOG-Foundation proudly announce the ground-breaking results of ENGOT-EN6-NSGO/GOG-3031/RUBY trial.
The results reveal improvement in overall survival at 24 months in whole study population from 56% (CP+placebo) to 71.3% (CP+dostarlimab). “although these are interim data, we believe they are robust and will be confirmed with longer follow-up.”, said Mansoor R Mirza.
The trial is presented on 27th of March 2023 through ESMO’s ...
Human body a breeding ground for antimicrobial resistance genes
2023-03-27
The community of microbes living in and on our bodies may be acting as a reservoir for antibiotic resistance, according to new research from the Earlham Institute and Quadram Institute in Norwich.
The use of antibiotics leads to ‘collateral damage’ to the microbiome, ramping0 up the number of resistance genes being passed back and forth between strains in the microbiome.
The findings also suggest these genes spread so easily through a population that, regardless of your own health and habits, the number of resistance genes in your gut is heavily influenced by national trends in antibiotic consumption.
The rise of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) among human pathogens is widely seen ...
U of I study gives a thumbs up to carefully formulated vegan diets for dogs
2023-03-27
URBANA, Ill. – In today’s pet food market, there are products to match nearly every lifestyle, value system, and price point pet owners demand, including vegan formulations. New University of Illinois research shows at least two human-grade, lightly cooked vegan diets provide adequate nutrition for dogs.
“The trends of vegan foods and human grade foods are increasing for dogs. Because people are feeding these diets to their pets, it’s important they be tested like all other foods to make sure they're safe and ‘complete and balanced,’” ...
Epstein-Barr virus associated tumors and drug repurposing
2023-03-27
A new study published in the peer-reviewed OMICS: A Journal of Integrative Biology identified differentially expressed host and viral microRNAs (miRNAs) in six Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) associated tumors. The study reports several drug candidates for repurposing and targeting EBV latent infection: Glyburide, Levodopa, Nateglinide, and Stiripentol, among others. Click here to read the article now.
The authors, Anamika Thakur and Manoj Kumar, PhD, from the Institute of Microbial Technology, Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), Chandigarh, India, note: “This is the first integrative analysis, to the best of our knowledge, in regard to the potential ...
Researchers identify 6 challenges humans face with artificial intelligence
2023-03-27
ORLANDO, March 27, 2023 - A University of Central Florida professor and 26 other researchers have published a study identifying the challenges humans must overcome to ensure that artificial intelligence is reliable, safe, trustworthy and compatible with human values.
The study, “Six Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence Grand Challenges,” was published in the International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction.
Ozlem Garibay ’01MS ’08PhD, an assistant professor in UCF’s Department ...