(Press-News.org) ITHACA, N.Y. – Female giant African pouched rats, used for sniffing out landmines and detecting tuberculosis, can undergo astounding reproductive organ transformations, according to a new study.
The paper, “Extreme plasticity of reproductive state in a female rodent,” which published March 27 in Current Biology, explores how traits once considered “fixed” in adult animals may become variable under specific pressures.
Though these rodents could have important military, biodetection and humanitarian uses, breeding them at high rates has been a challenge. The study’s findings are a step toward understanding their reproductive biology, and possibly breeding them more effectively – and may even have broader implications for other mammals struggling to reproduce.
“The more we start to understand the full scope of the reproductive process, the more we can start to get insight into those sorts of questions,” said Alex Ophir, associate professor of psychology at Cornell University and the study’s senior author. “The more examples of other mammals we get, the better, and these unusual examples can sometimes reveal a lot about women’s health and reproductive health.”
While other species are known to undergo reproductive suppression – such as animals who only mate in certain seasons – most do this hormonally rather than closing off their genitals as giant African pouched rats do. More study is needed to understand why these rodents possess this unusual trait.
One hypothesis is that “dominant” female pouched rats might be sending suppression signals to other females through pheromones, or scents in their urine, that cause them to close up.
“You could interpret it as manipulation by one female to get other females to stop reproducing, and in effect, they’ll often in these cases, start to contribute to the care of the dominant reproducing female,” Ophir said.
Another theory could be tied to resource competition, where too many offspring in a population limits available food resources, and reducing the number of babies born to others could mean more resources for one’s own babies, Ophir said.
In future work, Ophir plans to continue investigating how the animals’ extraordinary olfactory systems work and hopes to learn more about their unusual behaviors and anatomies.
“The fact that there is this naturally occurring ability to sort of change reproductive morphology and physiology suggests that things are probably a whole lot more plastic than we realize,” Ophir said. “If nothing else, it just provides another example that things aren't as dogmatically simple as people think.”
This study was funded by the Army Research Office.
For additional information, see this Cornell Chronicle story.
Cornell University has dedicated television and audio studios available for media interviews.
-30-
END
Bomb-sniffing rodents undergo ‘unusual’ reproductive transformations
2023-03-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
ENGOT-EN6-NSGO/GOG-3031/RUBY trial results: The new standard of care in advanced/recurrent endometrial cancer
2023-03-27
EMBARGO DATE: Monday, March 27, 2023, 12:30 pm ET
PRESS RELEASE
ENGOT-EN6-NSGO/GOG-3031/RUBY trial results:
The new standard of care in advanced/recurrent endometrial cancer
ENGOT, NSGO-CTU & GOG-Foundation proudly announce the ground-breaking results of ENGOT-EN6-NSGO/GOG-3031/RUBY trial.
The results reveal improvement in overall survival at 24 months in whole study population from 56% (CP+placebo) to 71.3% (CP+dostarlimab). “although these are interim data, we believe they are robust and will be confirmed with longer follow-up.”, said Mansoor R Mirza.
The trial is presented on 27th of March 2023 through ESMO’s ...
Human body a breeding ground for antimicrobial resistance genes
2023-03-27
The community of microbes living in and on our bodies may be acting as a reservoir for antibiotic resistance, according to new research from the Earlham Institute and Quadram Institute in Norwich.
The use of antibiotics leads to ‘collateral damage’ to the microbiome, ramping0 up the number of resistance genes being passed back and forth between strains in the microbiome.
The findings also suggest these genes spread so easily through a population that, regardless of your own health and habits, the number of resistance genes in your gut is heavily influenced by national trends in antibiotic consumption.
The rise of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) among human pathogens is widely seen ...
U of I study gives a thumbs up to carefully formulated vegan diets for dogs
2023-03-27
URBANA, Ill. – In today’s pet food market, there are products to match nearly every lifestyle, value system, and price point pet owners demand, including vegan formulations. New University of Illinois research shows at least two human-grade, lightly cooked vegan diets provide adequate nutrition for dogs.
“The trends of vegan foods and human grade foods are increasing for dogs. Because people are feeding these diets to their pets, it’s important they be tested like all other foods to make sure they're safe and ‘complete and balanced,’” ...
Epstein-Barr virus associated tumors and drug repurposing
2023-03-27
A new study published in the peer-reviewed OMICS: A Journal of Integrative Biology identified differentially expressed host and viral microRNAs (miRNAs) in six Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) associated tumors. The study reports several drug candidates for repurposing and targeting EBV latent infection: Glyburide, Levodopa, Nateglinide, and Stiripentol, among others. Click here to read the article now.
The authors, Anamika Thakur and Manoj Kumar, PhD, from the Institute of Microbial Technology, Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), Chandigarh, India, note: “This is the first integrative analysis, to the best of our knowledge, in regard to the potential ...
Researchers identify 6 challenges humans face with artificial intelligence
2023-03-27
ORLANDO, March 27, 2023 - A University of Central Florida professor and 26 other researchers have published a study identifying the challenges humans must overcome to ensure that artificial intelligence is reliable, safe, trustworthy and compatible with human values.
The study, “Six Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence Grand Challenges,” was published in the International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction.
Ozlem Garibay ’01MS ’08PhD, an assistant professor in UCF’s Department ...
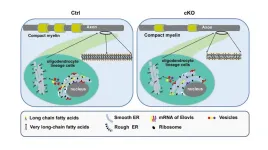
Mea6 deficiency in oligodendrocytes affects white matter formation in the brain
2023-03-27
More than half amount in adult human brain is made up of white matter. Lipid-rich myelin is a special structure formed by oligodendrocytes wrapping neuronal axons to form the major components of white matter. Abnormal myelin sheath is associated with many neurological diseases. Mea6/ cTAGE5C is essential for vesicle trafficking from ER to Golgi. However, its biological function in oligodendrocyte and white matter development remains unclear.
Scientists from Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology of Chinese Academy of Sciences generated mice with conditional knockout (cKO) of Mea6 in oligodendrocytes. Using ...
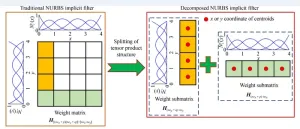
Massively effective filter for topology optimization based on the splitting of tensor product structure
2023-03-27
Recently, a research group lead by Prof. Shuting Wang from topology optimization of Huazhong University of Science and Technology has put forward a massively efficient filter utilizing the splitting of the tensor product structure. This study can be found in the journal Frontiers of Mechanical Engineering on 10 January, 2023.
With the aid of spitting technique, the traditional weight matrices of both B-splines and non-uniform rational B-splines implicit filters are equivalently decomposed into two or three submatrices, by which the sensitivity analysis is reformulated for the nodal design variables without altering ...
Routine preoperative medical consultations don’t improve surgery outcomes
2023-03-27
A large observational study published in JAMA Internal Medicine suggests that most patients do not medically benefit from consultation with a medical specialist before their surgery.
In Canada, surgeons refer more than 40,000 patients each year for consultation with a medical specialist (such as a general internist, cardiologist, endocrinologist, geriatrician, or nephrologist) before surgery. Between 10 and 40% of elective surgery patients will have a preoperative medical consultation.
These preoperative medical consultations are meant to address health issues that could lead to complications during surgery, but the evidence to support them has been limited ...
CU Anschutz experts call attention to unsupervised youth gun access in Colorado
2023-03-27
Public health experts at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus released a new research letter today in JAMA Pediatrics that examines how quickly Colorado’s children and teenagers can access a loaded gun and call attention to the critical importance of reducing access to guns when an adolescent is in crisis.
“There’s a high rate of firearm suicides in our youth and we know that for a large portion of those who attempt suicide, that ideation to action can happen under 10 minutes,” said principal investigator Ashley Brooks-Russell, ...
Study: Average privately insured family spends $1,300 for child’s hospitalization
2023-03-27
After a child’s hospital stay, many families covered by private insurance may experience sticker shock – on average spending $1,300 out of pocket – a new study in JAMA Pediatrics suggests.
For one in seven families, the price tag is even higher, exceeding $3,000.
“Bills for a child’s hospitalization can be astonishingly high for some families depending on how their insurance plan is structured,” said lead author Erin Carlton, M.D., a pediatric intensivist at University of Michigan Health C.S. Mott Children's ...