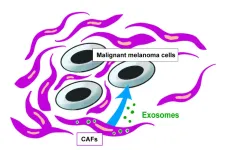
Candidate found to inhibit malignant melanoma growth
Possible early warning sign for skin cancer
2023-03-28
(Press-News.org)
Malignant melanoma is a relatively aggressive type of skin cancer. When detected early, it is usually treatable by surgical resection only, but metastases develop often spreading to distant areas. Currently, tumor thickness and the presence of ulceration are some of the known prognostic factors used as indicators of malignant melanoma. Therefore, the discovery of valuable markers to assess the malignant potential of melanoma more accurately may be necessary to develop appropriate treatments.
Cross talk between cancer cells and surrounding stromal cells is believed to orchestrate cancer progression through a variety of mechanisms. Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs)—key factors in the tumor microenvironment—in particular have been implicated in cancer cell progression. It has also been reported that the exosomes, a type of small vesicles, produced by CAFs play an important role in cancer progression.
A research group led by Naho Fujii, M.D., and Professor Hisashi Motomura from Osaka Metropolitan University Graduate School of Medicine investigated the effect of CAF-derived exosomes on the growth of malignant melanoma cells. The group found that the transmembrane proteins CD9 and CD63 were mainly present on CAF-derived exosomes, and that among the exosomes, the CD9-positive ones inhibited the growth of malignant melanoma cells.
“As a plastic surgeon, usually I provide surgical treatment for skin cancer, but I have wanted to study other treatment methods for a long time,” explained Fujii, M.D. “This study suggests that CD9-positive exosomes inhibit the growth of malignant melanoma, so CD9-positive exosomes may be a useful marker to evaluate the malignant grade of melanoma. We expect further research will lead to the development of new treatments in that line.”
###
About OMU
Osaka Metropolitan University is a new public university established in April 2022, formed by merger between Osaka City University and Osaka Prefecture University. For more research news visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ or follow @OsakaMetUniv_en and #OMUScience.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-03-28
For the first time, researchers have developed a form of the omega-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) that is capable of crossing into the eye’s retina to ward off visual declines related to Alzheimer’s disease, diabetes and other disorders.
The DHA found in fish oil capsules and other supplements is typically in a form called triacylglycerol (TAG) DHA. Although TAG-DHA has benefits in other parts of the body, it does not reach the eyes because it cannot travel from the bloodstream into the retina. For the study, ...
2023-03-28
The lower prevalence of ‘risky’ sex—with multiple or new partners without using condoms—which occurred during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic, was still evident a year after Britain’s first lockdown, reveal the results of a major national survey, published online in the journal Sexually Transmitted Infections.
While there were fewer reported unplanned pregnancies and abortions than indicated by a comparable survey a decade earlier, there were significantly higher prevailing levels of sexual dissatisfaction and worries ...
2023-03-28
People with atopic (allergic) diseases like asthma or eczema may be at heightened risk of the painful and often disabling joint condition, osteoarthritis, finds research published online in the Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
Drugs used to dampen down the physiological prompts for allergic reactions in the body may help lessen this risk, suggest the researchers.
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis. But despite the high prevalence, substantial costs, and debilitating impact of the disease, there is as yet no effective ...
2023-03-28
Engaging communities in developing a real-time early warning system could help to reduce the often-devastating impact of flooding on people and property – particularly in mountainous regions where extreme water events are a ‘wicked’ problem, a new study reveals
Flash floods are becoming more frequent and damaging to the lives and property of vulnerable people, but researchers believe that using a SMART approach to engage with those living in such areas will help to better signal impending risk from flooding.
Scientists believe that combining meteorological data with information on how people live and work in such regions, will help disaster risk ...
2023-03-28
For the first time, researchers have identified specific regions of the brain that are damaged by high blood pressure and may contribute to a decline in mental processes and the development of dementia.
High blood pressure is known to be involved in causing dementia and damage to brain function. The study, which is published in the European Heart Journal [1] today (Tuesday), shows how this happens. It gathered information from a combination of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of brains, genetic analyses and observational data from thousands of patients to look at the effect of high blood pressure on cognitive function. The researchers then checked their findings ...
2023-03-28
Growing concerns over the potential health effects of exposure to phthalates, a component of many plastics and also known as a plasticizer, have led to a search for safer alternatives. In a new study conducted in cell cultures, researchers found that the chemical acetyl tributyl citrate (ATBC) might not be the best replacement because it appears to interfere with the growth and maintenance of neurons.
“In the past, industries have promptly shifted away from the usage of toxic chemicals only to produce an equally toxic chemical, so this is something we are actively trying to avoid repeating,” said Kyle Sease, a graduate student at Central Washington ...
2023-03-28
A new study found that people who are currently suffering or face a high risk of post-traumatic stress disorder show particular patterns in four biomarkers measurable with a simple blood test. The findings suggest these biomarkers could be used to predict a person’s likelihood of developing PTSD, diagnose the disorder or monitor the response to treatment.
PTSD can occur after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. It is currently diagnosed based on symptoms such as flashbacks, difficulty sleeping or concentrating, ...
2023-03-28
M1 and M2 are activated macrophages that protect our immune system and maintain homeostasis. Interestingly, they are characterized by distinct and opposing phenotypes. M1 macrophages are known for their bactericidal and tumoricidal properties by secreting pro-inflammatory cytokines, while M2 macrophages facilitate immunosuppressive responses and help cancer progression. As such, reprogramming macrophages from M2 to M1 phenotype has been regarded as a significant interest in the view of potential cancer ...
2023-03-28
People reveal more personal information when you ask them the same questions a second time – according to new research from the University of East Anglia.
A new study published today reveals how simple repetition can make people over-disclose, and potentially put themselves at risk of identity theft and cyber crime.
The research team say that understanding why people disclose personal data could help inform measures to address the problem.
From subscribing to online newspapers to completing customer surveys, our personal data is being mined continuously; the world’s most valuable resource is no longer oil, but data.
But for consumers who provide their personal ...
2023-03-28
In February of this year, Graphene Flagship associated member Graphenest and manufacturing company Hubron International entered a new strategic partnership. Their shared aim is to explore the development and commercialization of graphene-based polymer masterbatch and compounds with unprecedented electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding performance for electronic enclosures manufacturing.
This new product line will start with a graphene-based thermoplastic suitable to be implemented as a remarkable EMI shielding solution in medium-high and high frequencies (for 5G and beyond).
The agreement brings together Graphenest’s knowledge around graphene ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Candidate found to inhibit malignant melanoma growth
Possible early warning sign for skin cancer