(Press-News.org) Research Highlights:
Weight loss was associated with decreased risk factors for cardiovascular disease and Type 2 diabetes for at least five years — even if some weight was regained, according to a review of research on behavioral weight loss programs.
People who lost weight through an intensive behavioral weight loss program had lower systolic blood pressure levels, total cholesterol-to-good cholesterol ratio and HbA1c levels (a diabetes marker), when compared to people who did not participate in a program or participated in a lower-intensity behavioral program.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET, Tuesday, March 28, 2023
DALLAS, March 28, 2023 — Losing weight with lifestyle changes in an intensive behavioral weight loss program was associated with a decrease in risk factors for cardiovascular disease and Type 2 diabetes for at least five years — even if some weight was regained, according to a systematic review of research, published today in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes, a peer-reviewed American Heart Association journal.
People affected by obesity or who are overweight are at increased risk for high cholesterol and high blood pressure — factors that heighten risk of cardiovascular disease; as well as insulin resistance, a precursor to Type 2 diabetes. Globally, overweight and obesity contributed to 2.4 million deaths in 2020, according to the American Heart Association’s 2023 Statistical Update.
Behavioral weight loss programs can help people lose and maintain a healthy weight by encouraging lifestyle and behavior changes, such as eating healthy foods and increasing physical activity. Regaining some weight is common after behavioral weight loss programs. Some observational studies suggest this weight change pattern of weight loss followed by weight regain may increase cardiovascular risk. However, according to the authors of this analysis, data from randomized trials and long-term follow-up studies is lacking.
“Many doctors and patients recognize that weight loss is often followed by weight regain, and they fear that this renders an attempt to lose weight pointless,” said study co-senior author Susan A. Jebb, Ph.D., a professor of diet and population health at the University of Oxford in the United Kingdom. “This concept has become a barrier to offering support to people to lose weight. For people with overweight or obesity issues, losing weight is an effective way to reduce the risk of Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.”
In this review, researchers assessed international scientific studies available in 2018 to compare risk factors for cardiovascular disease and Type 2 diabetes among people who followed an intensive behavioral weight loss program to those who followed a less intensive or no weight loss program. The studies in the analysis included diet and/or exercise interventions, partial or total meal replacement, intermittent fasting, or financial incentives contingent on weight loss. The studies took place in a variety of settings and included varying modes of delivery (in person, app-based, telephone, etc.).
Researchers combined the results of 124 studies totaling more than 50,000 participants, with an average follow-up of 28 months. They used the combined results to estimate changes in risk factors for cardiovascular disease and Type 2 diabetes after weight loss. The average weight loss across the different studies ranged from 2-5 kilograms, or 5-10 pounds. Weight regain averaged 0.12 to 0.32 kg (0.26 pounds to 0.7 pounds) a year. Participants were an average age 51 years old, with a body mass index of 33, which is considered obese.
Compared to people in a less intensive program and those in no weight loss program, participants who lost weight through an intensive weight loss program had lower risk factors for cardiovascular disease and Type 2 diabetes. These lower risk factors lasted for at least five years after the weight loss program ended.
Based on pooled results of the studies reviewed, on average:
Systolic blood pressure, the top number in a blood pressure reading, was 1.5 mm Hg (millimeters of mercury) lower at one year, and 0.4 mm Hg lower at five years after participation in an intensive weight loss program.
In addition, the percentage of HbA1c, a protein in red blood cells used to test for diabetes, was reduced by 0.26 at both one and five years after participation in an intensive weight loss program.
The ratio of total cholesterol to good cholesterol – known as high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol – was 1.5 points lower one year and five years after participation in an intensive weight loss program.
These changes are important because they represent improvements at the population level, Jebb explained.
In a preliminary finding, the decreased risk of being diagnosed with cardiovascular disease or Type 2 diabetes also appeared to remain lower even after weight regain. However, few studies followed people for more than 5 years and “more information is needed to confirm whether this potential benefit persists,” Jebb said.
“Most trials look at whether new treatments are effective and focus on weight change in the short-term rather than the effect on later disease,” Jebb said. “Individual studies are often too small to detect differences between groups in the incidence of cardiovascular conditions because, fortunately, they affect only a small proportion of the whole group, and studies may not continue long enough to see the effects on ‘hard’ outcomes, such as a new diagnosis of Type 2 diabetes or a heart attack.
“Our findings should provide reassurance that weight loss programs are effective in controlling cardiovascular risk factors and very likely to reduce the incidence of cardiovascular disease,” she said.
Evidence suggests that cardiovascular health is improved by following the American Heart Association’s Life’s Essential 8 health metrics: eating healthy food, being physically active, not smoking, getting enough sleep, maintaining a healthy weight, and controlling cholesterol, blood sugar and blood pressure levels.
The analysis had several limitations: information included in the review was not updated after 2019 and the review focused on research papers published in English, so eligible studies written in other languages may have been missed.
An accompanying editorial notes that much remains to be understood about various weight loss interventions, their long-term impact and how this impact may be diminished by regaining weight. Behavioral weight loss programs constitute the backbone of weight management in clinical practice. However, they are often resource intensive, and emerging medication therapies are expensive, according to editorial authors Vishal N. Rao, M.D., M.P.H., and Neha J. Pagidipati, M.D., M.P.H., both from the division of cardiology at Duke University School of Medicine in Durham, North Carolina.
“The present study has interesting implications for the impact of weight regain that may occur after pharmacologic therapies,” they write. “What is still unknown is whether these temporary improvements in weight and cardiometabolic risk factors after weight loss intervention (behavioral or pharmacological) lead to long-term clinical benefit. In other words, is it better to have lost and regained than never to have lost at all?”
Co-authors are Jamie Hartmann-Boyce, D.Phil.; Annika Theodoulou, M.Clin.Sc.; Jason L. Oke, D.Phil.; Ailsa R. Butler, D.Phil.; Anastasios Bastounis, Ph.D.; Anna Dunnigan, M.Sc.; Rimu Byadya, M.Sc.; Linda J. Cobiac, Ph.D.; Peter Scarborough, D.Phil.; F. D. Richard Hobbs, F.Med.Sci.; Falko F. Sniehotta, Ph.D.; and Paul Aveyard, Ph.D. Authors’ disclosures are listed in the manuscript.
This research was funded by the British Heart Foundation and the National Institute for Health Research Oxford Biomedical Research Centre.
Studies published in the American Heart Association’s scientific journals are peer-reviewed. The statements and conclusions in each manuscript are solely those of the study authors and do not necessarily reflect the Association’s policy or position. The Association makes no representation or guarantee as to their accuracy or reliability. The Association receives funding primarily from individuals; foundations and corporations (including pharmaceutical, device manufacturers and other companies) also make donations and fund specific Association programs and events. The Association has strict policies to prevent these relationships from influencing the science content. Revenues from pharmaceutical and biotech companies, device manufacturers and health insurance providers and the Association’s overall financial information are available here.
Additional Resources:
Available multimedia is on right column of release link https://newsroom.heart.org/news/shedding-pounds-may-benefit-your-heart-even-if-some-weight-is-regained?preview=459ce7fa2d139a18a8da7f9582260c1d
After March 28, 2023, view the manuscript and editorial online.
AHA health information: Keeping a Healthy Body Weight
AHA health information: 5 Steps to Lose Weight and Keep It Off
AHA health information: Lifestyle Changes for Heart Attack Prevention
AHA news release: Reducing total calories may be more effective for weight loss than intermittent fasting (Jan. 2023)
AHA news release: Diet change may make biggest impact on reducing heart risk in people with hypertension (Sept. 2022)
Follow AHA/ASA news on Twitter @HeartNews
Follow news from the AHA’s Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes journal @CircOutcomes
About the American Heart Association
The American Heart Association is a relentless force for a world of longer, healthier lives. We are dedicated to ensuring equitable health in all communities. Through collaboration with numerous organizations, and powered by millions of volunteers, we fund innovative research, advocate for the public’s health and share lifesaving resources. The Dallas-based organization has been a leading source of health information for nearly a century. Connect with us on heart.org, Facebook, Twitter or by calling 1-800-AHA-USA1.
###
END
Shedding pounds may benefit your heart — even if some weight is regained
Heart health benefits lasted for at least five years after losing weight via a lifestyle change program, according to a research review in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes
2023-03-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Turtles and crocodiles with unique characteristics are more likely to go extinct
2023-03-28
New research led by the University of Oxford has revealed that the most endangered turtle and crocodile species are those that are most unique. Their loss could have widespread impacts on the ecosystems they live in, since they carry out critical processes important for many other species.
Turtles and crocodiles are two of the world's most endangered animal groups, with approximately half of species globally threatened (International Union for Conservation of Nature, IUCN). Greater understanding on which species are most threatened and why is urgently needed to inform conservation efforts to save them.
In a new study led by researchers at the Department of Biology, ...
A final present from birds killed in window collisions: poop that reveals their microbiomes
2023-03-28
Every year, millions of birds crash into windows in cities along their migratory path. For decades, scientists and volunteers have risen at dawn in spring and fall to collect the fallen birds, rehabilitating the injured and documenting the dead. The bodies of the birds killed in these collisions are a treasure trove of scientific information, especially when compared year after year. A new study in the journal Molecular Ecology makes use of these specimens to help understand the relationship between birds and the microbes living in their guts—which appears ...
ISTA welcomes first journalists in residence
2023-03-28
Understanding of and trust in science and scientists are dangerously low, and initial studies suggest that a general lack of interest in science is even more of a problem than skepticism in Austria. A key partner in alleviating this mistrust, clearing up misunderstandings, and building up enthusiasm for science must be the media in general and science journalists in particular. However, these journalists need access to the information as well as the resources to work independently and give full flight to their curiosity and creativity. To work towards these goals and promote excellent science journalism, ISTA initiated a program to host journalists for two-to-four-month ...
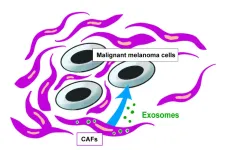
Candidate found to inhibit malignant melanoma growth
2023-03-28
Malignant melanoma is a relatively aggressive type of skin cancer. When detected early, it is usually treatable by surgical resection only, but metastases develop often spreading to distant areas. Currently, tumor thickness and the presence of ulceration are some of the known prognostic factors used as indicators of malignant melanoma. Therefore, the discovery of valuable markers to assess the malignant potential of melanoma more accurately may be necessary to develop appropriate treatments.
Cross talk between cancer cells and surrounding stromal cells is ...
New form of omega-3 could prevent visual decline with Alzheimer’s disease
2023-03-28
For the first time, researchers have developed a form of the omega-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) that is capable of crossing into the eye’s retina to ward off visual declines related to Alzheimer’s disease, diabetes and other disorders.
The DHA found in fish oil capsules and other supplements is typically in a form called triacylglycerol (TAG) DHA. Although TAG-DHA has benefits in other parts of the body, it does not reach the eyes because it cannot travel from the bloodstream into the retina. For the study, ...
Less ‘risky’ sex of early pandemic still evident year after first lockdown in Britain
2023-03-28
The lower prevalence of ‘risky’ sex—with multiple or new partners without using condoms—which occurred during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic, was still evident a year after Britain’s first lockdown, reveal the results of a major national survey, published online in the journal Sexually Transmitted Infections.
While there were fewer reported unplanned pregnancies and abortions than indicated by a comparable survey a decade earlier, there were significantly higher prevailing levels of sexual dissatisfaction and worries ...
Allergic (atopic) asthma/eczema linked to heightened risk of osteoarthritis
2023-03-28
People with atopic (allergic) diseases like asthma or eczema may be at heightened risk of the painful and often disabling joint condition, osteoarthritis, finds research published online in the Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
Drugs used to dampen down the physiological prompts for allergic reactions in the body may help lessen this risk, suggest the researchers.
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis. But despite the high prevalence, substantial costs, and debilitating impact of the disease, there is as yet no effective ...
SMART warnings could protect communities at risk from flooding
2023-03-28
Engaging communities in developing a real-time early warning system could help to reduce the often-devastating impact of flooding on people and property – particularly in mountainous regions where extreme water events are a ‘wicked’ problem, a new study reveals
Flash floods are becoming more frequent and damaging to the lives and property of vulnerable people, but researchers believe that using a SMART approach to engage with those living in such areas will help to better signal impending risk from flooding.
Scientists believe that combining meteorological data with information on how people live and work in such regions, will help disaster risk ...
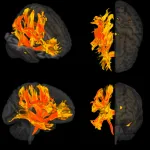
World first: Researchers identify specific regions of the brain that are damaged by high blood pressure and are involved in a decline in mental processes and dementia
2023-03-28
For the first time, researchers have identified specific regions of the brain that are damaged by high blood pressure and may contribute to a decline in mental processes and the development of dementia.
High blood pressure is known to be involved in causing dementia and damage to brain function. The study, which is published in the European Heart Journal [1] today (Tuesday), shows how this happens. It gathered information from a combination of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of brains, genetic analyses and observational data from thousands of patients to look at the effect of high blood pressure on cognitive function. The researchers then checked their findings ...
Phthalate alternative may harm brain development and health
2023-03-28
Growing concerns over the potential health effects of exposure to phthalates, a component of many plastics and also known as a plasticizer, have led to a search for safer alternatives. In a new study conducted in cell cultures, researchers found that the chemical acetyl tributyl citrate (ATBC) might not be the best replacement because it appears to interfere with the growth and maintenance of neurons.
“In the past, industries have promptly shifted away from the usage of toxic chemicals only to produce an equally toxic chemical, so this is something we are actively trying to avoid repeating,” said Kyle Sease, a graduate student at Central Washington ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Nanoplastics can interact with Salmonella to affect food safety, study shows
Eric Moore, M.D., elected to Mayo Clinic Board of Trustees
NYU named “research powerhouse” in new analysis
New polymer materials may offer breakthrough solution for hard-to-remove PFAS in water
Biochar can either curb or boost greenhouse gas emissions depending on soil conditions, new study finds
Nanobiochar emerges as a next generation solution for cleaner water, healthier soils, and resilient ecosystems
Study finds more parents saying ‘No’ to vitamin K, putting babies’ brains at risk
Scientists develop new gut health measure that tracks disease
Rice gene discovery could cut fertiliser use while protecting yields
Jumping ‘DNA parasites’ linked to early stages of tumour formation
Ultra-sensitive CAR T cells provide potential strategy to treat solid tumors
Early Neanderthal-Human interbreeding was strongly sex biased
North American bird declines are widespread and accelerating in agricultural hotspots
Researchers recommend strategies for improved genetic privacy legislation
How birds achieve sweet success
More sensitive cell therapy may be a HIT against solid cancers
Scientists map how aging reshapes cells across the entire mammalian body
Hotspots of accelerated bird decline linked to agricultural activity
How ancient attraction shaped the human genome
NJIT faculty named Senior Members of the National Academy of Inventors
App aids substance use recovery in vulnerable populations
College students nationwide received lifesaving education on sudden cardiac death
Oak Ridge National Laboratory launches the Next-Generation Data Centers Institute
Improved short-term sea level change predictions with better AI training
UAlbany researchers develop new laser technique to test mRNA-based therapeutics
New water-treatment system removes nitrogen, phosphorus from farm tile drainage
Major Canadian study finds strong link between cannabis, anxiety and depression
New discovery of younger Ediacaran biota
Lymphovenous bypass: Potential surgical treatment for Alzheimer's disease?
When safety starts with a text message
[Press-News.org] Shedding pounds may benefit your heart — even if some weight is regainedHeart health benefits lasted for at least five years after losing weight via a lifestyle change program, according to a research review in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes