(Press-News.org) “There’s no doubt we can produce enough food for the world’s population - humanity is strategic enough to achieve that. The question is whether - because of war and conflict and corruption and destabilization - we do,” said World Food Programme leader David Beasley in an interview with Time magazine earlier this year.
Indeed, projections show that we are not on track to achieve Sustainable Development Goal 2 of Zero Hunger by 2030. As climate and security crises continue to destabilise our food sources, researchers are taking a critical look not just at how we produce food - but at the entire systems behind our food supplies. In this case, the systems behind the seeds that produce our food crops.
“Whilst adapting crops to climate change and conserving their variation is essential for food security, these measures are meaningless if farmers do not have access to the seeds,” says crop scientist and food system expert Ola Westengen. Westengen leads the team of researchers from the Norwegian University of Life Sciences (NMBU) who recently reviewed the state of seed systems for small-holder farmers in low/middle income countries. Their findings are now published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
What are seed systems?
Seed systems are the provision, management and distribution of seeds. They cover the entire seed chain, from the conservation of their diversity and variety development, to their production and distribution, and the rules that govern these activities. In short, they are the structures that make seeds available to farmers so that crops can be sown, harvested and end up on our plates.
Whilst a well-functioning seed system will ensure seed security for all farmers, the researchers say that, in practice, it is rarely the case that seed systems function as well as they might. Seed systems can be disrupted by conflict and disasters, as well as by problems stemming from social inequality, lack of coordination or inappropriate policies.
What does this study tell us that we don’t already know?
“There are recent innovations and investments by governments and donors to improve farmers’ access to diverse crop varieties and quality seeds,” explains Teshome Hunduma, a seed governance researcher and co-author of the study. “For example, there are now more flexible policies and regulations that encourage diversity in the seed systems used by farmers, rather than pushing farmers to switch to commercial seed systems that focus on less diverse commodity crops - which is the norm.” Commodity crops are those grown in large volume and high intensity for the purpose of sale, as opposed to those grown by small-holder farmers for direct processing and consumption.
“The study highlights emerging initiatives that are helping farmers to secure food supplies, such as participatory plant breeding,” says Teshome. Participatory plant breeding is the development and selection of new crop varieties where the farmers are in control. Farmers, who know the needs of their farms best, work with researchers and others to improve crops and develop plant varieties that are in line with their household needs and culture, and that are resilient to environmental and climate challenges.
“Farmers prefer and need different types of seeds, based on diverse social, cultural and ecological conditions,” adds ethnobotanist and co-author Sarah Paule Dalle.
The study discusses various disruptions to farmer’s access to seeds. Social inequality is one such disruption. How so?
“A seed system that only serves a segment of a farming society contributes to seed insecurity,” replies Teshome. “For example, commercial seed systems deliver high-yielding varieties of quality hybrid seeds. Whilst wealthy farmers can afford such seeds, poor farmers can’t.”
“Similarly, whilst commercial seed systems that focus on commodity crops may benefit men who might primarily be interested in market value, such systems have little to offer women who want crops that provide household nutrition and meet their cultural preferences.”
“This means poor farmers and women do not have the same access to seeds that meet their needs. The result is seed, and thus food, insecurity due to social and economic inequality.”
Political-economic factors have driven the globalization of food systems over the last decades, which also includes seed systems. “Seeds have become big business”, say the researchers. According to studies quoted in the article, the four largest multinational companies in seed trade today control about 60% of the ~50 billion USD global commercial seed market. The large private actors have the power not only to shape markets, but also to influence science and innovation agendas and policy frameworks.
This can be problematic, say the researchers, when private sector research and development typically focuses on the most profitable crops, such as maize and soy. Crops grown and consumed by subsistence farmers are thus largely neglected, and the potential of crop diversity - the foundation of agriculture - remains largely untapped. Technology that could help develop more robust varieties remains hypothetical.
How does the ownership of crop diversity threaten food supplies and what can be done?
The term crop diversity refers both to different crops and different varieties of a crop. According to the Global Crop Diversity Trust (one of the world’s primary international organizations on crop diversity conservation), securing and making available the world’s crop diversity is essential for future food and nutrition security.
“Plant breeders and scientists use crop diversity to develop new, more resilient and productive varieties that consumers want to eat, that are nutritious and tasty, and that are adapted to local preferences, environments and challenges,” explains Benjamin Kilian, a plant genetics expert at the Global Crop Diversity Trust. The Crop Trust, together with the Norwegian University of Life Sciences, implements the major project from which this study emerged: Biodiversity for Opportunities, Livelihoods and Development (BOLD). Coordinated by Kilian, the project supports the conservation and use of crop diversity to strengthen food and nutrition security on a global scale. It builds on the Crop Wild Relatives project and is funded by the Norwegian government.
“In the BOLD project, researchers work with genebanks, plant breeders and others in the seed value chain to co-develop seed systems that are both resilient to climate stresses and inclusive of small-holder farmers on the frontline of adaptation,” adds Westengen.
Will access to seeds in the vulnerable areas that you are studying be improved in time to make a difference?
“We hope so, if we make the right moves to include small-holder farmers in seed system development,” says Dalle. “A well-functioning seed system should also be resilient. That is, it should withstand shocks such as drought or pandemics and breakdowns or disruptions such as war and conflict.”
“To do this, the system should promote a diversity of seeds, both local varieties and those improved to better adapt to stresses. It should also involve diverse groups of people such as farmer cooperatives/groups, and both public and private companies to increase the choice of seeds and seed sources. During lockdowns in the COVID-19 pandemic, for example, farmers’ own seed systems enabled access to seeds in developing countries when the activities of private companies and agro-dealers were restricted,” explains Dalle.
Westengen summarizes: “Our study highlights links between the crucial work of the Global Crop Diversity Trust and the farmers on the frontline of adapting our food systems to climate change. It is an argument for co-designing seed system development in full cooperation with farmers and other actors in the seed system. This way, efforts can meet the needs of various groups of farmers in different agroecological contexts. There is no one-size-fits-all; if there is one natural law in biology, it is that diversity is key to future evolution. That also goes for seed systems - and food system development.”
Navigating towards resilient and inclusive seed systems by Ola T. Westengen, Sarah Paule Dalle and Teshome Hunduma Mulesa was published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) this week. PNAS is widely considered one of the most prestigious and highly cited multidisciplinary research journals.
About the Norwegian University of Life Sciences (NMBU)
NMBU's research and education enables people all over the world to tackle the big, global challenges regarding the environment, sustainable development, how to improve human and animal health, renewable energy sources, food production, and land- and resource management.
About the Crop Trust
The Crop Trust is an international organization working to conserve crop diversity and thus protect global food and nutrition security. At the core of Crop Trust is an endowment fund dedicated to providing guaranteed long-term financial support to key genebanks worldwide. The Crop Trust supports the Svalbard Global Seed Vault and coordinates large-scale projects worldwide to secure crop diversity and make it available for use. The Crop Trust is recognized as an essential element of the funding strategy of the International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture.
About the BOLD Project
BOLD (Biodiversity for Opportunities, Livelihoods, and Development) is a major 10-year project to strengthen food and nutrition security worldwide by supporting the conservation and use of crop diversity. The project works with national genebanks, pre-breeding and seed system partners globally. Funded by the government of Norway, BOLD is led by the Crop Trust in partnership with the Norwegian University of Life Sciences and the International Plant Treaty.
END
New ways to protect food crops from climate change and other disruptions
2023-03-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Antitumor Response: Decoding Molecular Mechanisms
2023-03-29
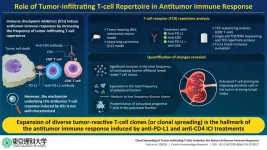
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are widely sought after for the treatment of different types of cancers. Unfortunately, only 20–30% patients with cancer respond to ICI treatment. Although the factors that influence the positive or negative response to ICI treatment are poorly understood, the strength of the ICIs’ antitumor response by TILs is thought to play a key role. Hence, investigating the antitumor response induced by ICIs might provide insights into their underlying mechanism.
It is known that CD8+ tumor-infiltrating T-lymphocytes (TILs) are the primary effector cells that lead ...
Olivier Delattre, MD, Ph.D., honored with 2023 AACR-St. Baldrick’s Foundation Award for Outstanding Achievement in Pediatric Cancer Research
2023-03-29
PHILADELPHIA – The American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) will award Olivier Delattre, MD, PhD, with the 2023 AACR-St. Baldrick’s Foundation Award for Outstanding Achievement in Pediatric Cancer Research during the AACR Annual Meeting 2023, April 14-19 at the Orange County Convention Center in Orlando, Florida.
Delattre is the director of the SIREDO Oncology Center and the research unit director of the Cancer, Heterogeneity, Instability and Plasticity (CHIP) unit at Inserm/Institut Curie. ...
SwRI’s NASGRO software selected for Space Technology Hall of Fame
2023-03-29
SAN ANTONIO — March 29, 2023 —The NASGRO® software suite will be inducted into the Space Technology Hall of Fame alongside the leaders of its development team, Southwest Research Institute’s Dr. Craig McClung and Joe Cardinal, as well as Joachim Beek of NASA’s Johnson Space Center (JSC). The award ceremony will occur during the annual Space Symposium in Colorado Springs. NASGRO, originally developed by NASA and currently managed by SwRI, analyzes fatigue crack growth and fracture in structures and mechanical components. It is a key tool used to substantiate the structural integrity of aircraft, spacecraft, rotorcraft, gas turbine engines, pressure ...
Study shows human brain can assist with computational ghost imaging
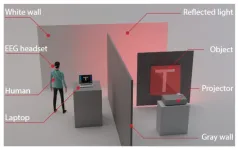
2023-03-29
Interacting with computers by brain activity seems less futuristic these days, thanks to researchers and entrepreneurs who have been attempting to tap the potential of brain-computer interfaces for augmented cognitive abilities. Recently, Gao Wang and Daniele Faccio at the University of Glasgow demonstrated that it is possible to connect a human brain and a computer to perform simple computational imaging tasks. Similar advances could someday extend the sensing range of human vision and provide new approaches to the neurophysics of human perception. This research was published Feb. 24 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner ...
COVID-19 during pregnancy may increase obesity risk in children
2023-03-29
WASHINGTON—Children born to mothers who had COVID-19 during pregnancy may be more likely to develop obesity, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society’s Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
More than 100 million COVID-19 cases have been reported in the United States since 2019, and there is limited information on the long-term health effects of the infection. Pregnant women make up 9% of reproductive-aged women with COVID-19, and millions of babies will be exposed to maternal infection during ...
Advanced pancreatic cancer model for developing personalized therapies
2023-03-29
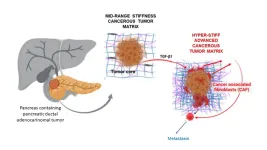
(LOS ANGELES) – March 28, 2023 - Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), is highly aggressive and lethal. It is the most prevalent type of pancreatic cancer, making up 90% of cases; it also has a high rate of metastasis, with an average five-year survival rate of less than 10%.
It is thought that the dense, stiff matrix immediately surrounding its tumor cells plays a major role in PDAC disease progression. In addition to influencing pancreatic tissue fibrosis, it also limits accessibility and effectiveness of anticancer drugs against the tumor and enhances the promotion of surface ...
Surgical sealing made better with robust thermosensitive bioadhesives
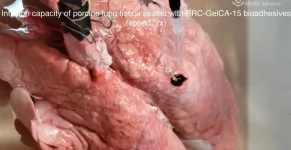
2023-03-29
(LOS ANGELES) – March 28, 2023 - As part of a collaborative effort, scientists from the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI) have employed inventive chemistry to produce an injectable biomaterial with significantly improved adhesive strength, stretchability, and toughness. This chemically modified, gelatin-based hydrogel had attractive features, including rapid gelation at room temperature and tunable levels of adhesion. This custom-engineered biomaterial is ideal as a surgical wound sealant, with its controllable adhesion and injectability and its superior ...
Personalized gut microbiome analysis for colorectal cancer classification with explainable AI
2023-03-29
The gut microbiome comprises a complex population of different bacterial species that are essential to human health. In recent years, scientists across several fields have found that changes in the gut microbiome can be linked to a wide variety of diseases, notably colorectal cancer (CRC). Multiple studies have revealed that a higher abundance of certain bacteria, such as Fusobacterium nucleatum and Parvimonas micra, is typically associated with CRC progression.
Based on these findings, researchers have ...
Three newly discovered sea worms that glow in the dark named after creatures from Japanese folklore and marine biologist
2023-03-29
A research group from Nagoya University in central Japan has discovered three new species of bioluminescent polycirrus worms from different parts of Japan. Usually found in shallow water, polycirrus are small worms, known for their bioluminescence. The researchers named one of their discoveries after a ghostly yokai, a creature in Japanese foklore; another after a lantern yokai; and the other after an influential Japanese marine biologist. They published their findings in the journal Royal Society Open Science.
Scientists have studied only a small fraction of the more than 7,000 species of luminescent organisms in the world. Research remains limited to certain species because ...
The element of surprise: How unexpected syntax makes marketing communications more effective
2023-03-29
Researchers from Frankfurt School of Finance and Management published a new Journal of Marketing article that examines the role of syntactic surprise in formulating effective written messages.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Creating Effective Marketing Messages Through Moderately Surprising Syntax” and is authored by A. Selin Atalay, Siham El Kihal, and Florian Ellsaesser.
Consider a manager advertising for a job, deciding whether to go with “Apply today to join a great ...