(Press-News.org)
“[...] there has been limited research to date on the effect of cellular ‘ageing’, termed senescence, on amyloidosis.”
BUFFALO, NY- March 29, 2023 – A new editorial paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 5, entitled, “Senescence and extracellular vesicles: novel partners in vascular amyloidosis.”
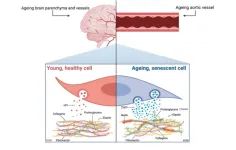
In their editorial, researchers Meredith Whitehead, Marco Antonazzi and Catherine M. Shanahan from King’s College London discussed amyloidosis—a prevalent age-associated pathology caused by the accumulation of fibrous, insoluble protein fibrils in tissues. The most common human amyloid is aortic medial amyloid (AMA), caused by aggregation of a 50-amino acid peptide called medin, which is cleaved by an unknown mechanism from its parent protein, milk fat globulin EGF-factor 8 (MFGE8). Medin is present in the vessel wall of 97% of Caucasians aged over 50- years, yet despite its prevalence in the ageing population there is a very limited understanding of the mechanisms driving AMA.
“Despite several forms of amyloidosis, including AMA and Alzheimer’s disease (AD), being frequently associated with ageing, there has been limited research to date on the effect of cellular ‘ageing’, termed senescence, on amyloidosis.”
The novel data presented in the paper by Whitehead et al. provides evidence that vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC)-derived small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) are key mediators of medin accumulation in the vessel wall. In addition, the authors identify, for the first time, a role for cellular senescence in triggering amyloidosis via changes in sEVs and extracellular matrix (ECM) composition. Thus, this study not only advances our understanding of how AMA is formed but uncovers potential therapeutic targets for mitigating the detrimental effects of amyloidosis on tissue function.
“Further work is now required to understand the relationships between cellular ageing pathways, different forms of amyloidosis and potentially other ageing pathologies with shared mechanisms, such as vascular calcification, that often occur concomitantly within the aged ECM.”
Continue Reading the Full Editorial: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.204571
Corresponding Author: Catherine M. Shanahan
Corresponding Email: cathy.shanahan@kcl.ac.uk
Keywords: amyloid, smooth muscle cells, senescence, extracellular vesicles, medin
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://aging.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Faging.204571
About Aging-US:
Launched in 2009, Aging publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research and age-related diseases, including cancer—and now, with a special focus on COVID-19 vulnerability as an age-dependent syndrome. Topics in Aging go beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR, among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
SoundCloud
Facebook
Twitter
Instagram
YouTube
LabTube
LinkedIn
Reddit
Pinterest
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
END
A new analysis shows that, compared to similarly high-income European countries, the US continues to have substantially higher death rates at all but the oldest ages, resulting in more “excess deaths,” and this gap widened during the Covid-19 pandemic. Patrick Heuveline, of the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), presents these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on March 29, 2023.
Calculating excess death rates can be useful for comparing mortality between different countries or sub-populations, as well as before and after the onset of a health crisis. Prior research has documented a substantial widening of ...
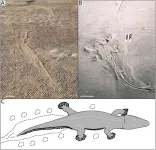
Ancient 2m-long amphibians swam like crocodiles long before true crocodiles existed, according to a study published March 29, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by David P. Groenewald of the University of the Witwatersrand, South Africa and colleagues.
During the Late Permian Period, just over 250 million years ago, South Africa was home to rhinesuchid temnospondyls, large predatory amphibians with bodies similar to crocodiles or big salamanders. These extinct animals are known mainly from skeletal remains, but in this study, researchers ...
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0283089
Article Title: The impact of BMI on psychological health in oldest old individuals–Are there differences between women and men?
Author Countries: Germany
Funding: This study was funded by the @ktivPLUS study (German Federal Ministry of Education and Research, grant number 01GY2108) awarded to M. Löbner. Publication was funded by the Open Access Publishing Fund of Leipzig University, which is supported by the German Research ...
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0282024
Article Title: Pedestrian street behavior mapping using unmanned aerial vehicles. A case study in Santiago de Chile
Author Countries: Spain
Funding: OM has received funding from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation of the Government of Spain (RyC RYC2020-029441-I). This research was also funded by the Ministry of Science and Innovation of the Government of Spain [grant number PID2019-104344RB-I00]. END ...
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0281752
Article Title: Mortality postponement and compression at older ages in human cohorts
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Unproductive, inflexible, and less motivated... these are some of the most common stereotypes about senior employees. Even though the stereotypes are usually unfounded, they nevertheless influence how senior employees perceive themselves and their status in the workplace. And they thus become a key factor in many senior employees’ retirement decisions, conclude University of Copenhagen researchers in a new study published in PLOS ONE.
“In our study, we refer to the uncertainty that senior employees feel about their status as ‘the worn-out syndrome’, which ...
Life comes in all shapes in sizes, but some sizes are more popular than others, new research from the University of British Columbia has found.
In the first study of its kind published today in PLOS ONE, Dr. Eden Tekwa, who conducted the study as a postdoctoral fellow at UBC’s department of zoology, surveyed the body sizes of all Earth’s living organisms, and uncovered an unexpected pattern. Contrary to what current theories can explain, our planet’s biomass—the material that makes up all living organisms—is ...
Life may come in all shapes and sizes, but in nature the most extreme size ranges predominate, according to Rutgers researchers.
A survey of body sizes of Earth organisms, published Wednesday, March 29, in the science journal PLoS ONE, shows that the planet’s biomass – the material that makes up all living organisms – is concentrated in organisms at either end of the size spectrum.
“This conclusion – that life on earth comes packaged predominantly in the largest and smallest sizes – was a discovery that surprised us,” said Malin Pinsky, an associate professor ...
Study Title: Aberrant cell state plasticity mediated by developmental reprogramming precedes colorectal cancer initiation
Publication: Science Advances: March 29, 2023, 2:00pm ET 10.1126/sciadv.adf0927
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute author: Pratyusha Bala, PhD, Jonathan P. Rennhack, PhD, Daulet Aitymbayev, MS, Matthew B. Yurgelun, MD, William C. Hahn, MD, PhD, Nilay S. Sethi, MD, PhD
Summary:
Normally the lining of the colon forms a series of steep hills and valleys. At the surface, where the hills peak, are functional colon cells that do the organ’s work of absorption and secretion. Deep in the valleys are stem cells that constantly ...
Traces of ancient empires that stretched across Africa remain in the DNA of people living on the continent, reveals a new genetics study led by UCL researchers.
Published in Science Advances, the collaboration between UCL geneticists working alongside anthropologists, archaeologists, historians and linguists in Africa and beyond found evidence for when different peoples intermixed across the continent. Their findings indicate migration linked to vast empires such as the Kanem-Bornu and the kingdoms of Aksum and Makuria, ...