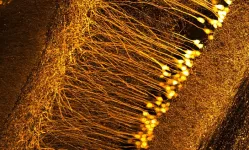
(Press-News.org) The human body contains more than 30 trillion cells. Until recently, the sheer number of cells in the organism meant that approaches to understanding human diseases and developmental processes based on the analysis of single cells were a futuristic vision. The development of new sequencing methods is currently revolutionising our understanding of cellular heterogeneity. These technologies can detect rare or even new cell types by extracting and sequencing the genetic information from the cells based on ribonucleic acid chains.
In cooperation with Helmholtz Munich, Professor Matthias Meier from the Centre for Biotechnology and Biomedicine at Leipzig University and his research group have developed a new, effective and comparatively inexpensive method to make rare cell types, cell communication types and disease patterns visible in tissue. The researchers have now published their findings in the prestigious journal “Nature Communications”.
All methods of single-cell analysis require cells to be detached from the tissue composite, losing spatial information about cell types and thus information about the cellular environment, cellular communication pathways or function. To obtain spatially resolved information about individual cells, imaging and sequencing techniques must be used in combination. In recent years, several approaches have been developed to unify the merging of imaging and sequencing data. Depending on the research question, different parameters such as spatial resolution, detection limit, accessibility of the ribonucleic acids and cost were weighed against each other. An earlier analysis method was based on the idea of attaching local information to the ribonucleic acids using a barcode based on the sequence of DNA bases. After extraction of all the ribonucleic acids and subsequent mass sequencing, the barcodes can be used to create an artificial image.
This is where Johannes Wirth’s work came in. As a doctoral researcher in Matthias Meier’s lab, the researcher at Helmholtz Munich has developed an advanced workflow that makes it possible to acquire locally resolved genomic data paired with high-quality microscopy images. This enables the visualisation of rare cell types, cell communication types and disease patterns in tissue. The focus was on the development of a new microfluidic chip that makes it possible to analyse ribonucleic acid chains in large tissue sections at low cost. “Compared to the original method, the new approach has increased the amount of image information per pixel by a factor of six or twelve. This means that we can resolve about 5000 genes per pixel, which allows us to visualise rare cell types in the kidney or liver,” explains Wirth. By comparison, a standard HD screen can only display the three primary colours with 256 different brightness levels per pixel.
In addition to the technical advances, the team also provided an open source analysis pipeline to make the method easily accessible. As the method is suitable for a wide range of tissues, it will facilitate studies of complex diseases and multi-organ functions and dysfunctions. “The method we have developed, which combines imaging and sequencing techniques, was a vision until recently. It has revolutionised our understanding of cellular heterogeneity and allowed us to find new cell types in all organisms,” says Professor Meier. With the development of single-cell sequencing methods, it is now possible to better understand cellular developmental pathways and how diseases progress.
END
Making rare cell types visible: Researchers are developing a new method
Microfluidic chip makes new cell types visible in all organisms
2023-03-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
More than 1,200 LOINC® registrants represent 78 countries for version 2.74 webinar
2023-03-31
INDIANAPOLIS -- LOINC®, an international data standard maintained at Regenstrief Institute, hosted an educational release webinar for version 2.74. More than 1,200 participants signed up, representing 78 countries.
The hour and a half webinar served as an opportunity for the LOINC team to introduce and explain the new concepts from the 2.74 release update. Participants were presented with opportunities to learn more about each new concept and ask questions.
LOINC, short for Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes, is a global standard for health terminology. Created and maintained at Regenstrief, LOINC enables the identification, exchange and collection of data across ...
NRG Oncology combined trial long-term results indicate that pathologic complete response is prognostic of outcomes for soft tissue sarcoma patients
2023-03-31
Combined long-term survival results from nonrandomized phase II trial NRG Oncology RTOG 0630 and the ancillary analysis of the combined NRG-RTOG 0630/9514 trials indicate that pathologic complete response (pCR) is associated with improved survival outcomes for patients with localized soft tissue sarcoma (STS) who receive preoperative chemoradiotherapy or radiotherapy. This data suggests that pCR can be used as a prognostic factor for clinical outcomes in future STS research. These results were recently published in the JAMA Oncology.
NRG-RTOG 0630 and 9514 both evaluated STS patients who were receiving either preoperative image-guided radiotherapy (IGRT; 0630) or neoadjuvant ...
Pensoft joins Advisory Panel to further develop the Journal Comparison Service by cOAlition S
2023-03-31
Back in December, we announced that Pensoft joined 27 other publishers in sharing prices and services via the Journal Comparison Service developed by cOAlition S, in order to boost transparency in scholarly publishing.
Now, we are up to another challenge: we have joined the Advisory Panel appointed by cOAlition S to help further the improvement and development of this important service. The Advisory Panel consists of twelve members (six publishers and six end-users) representing different stakeholders in the scholarly communication ecosystem.
Journal Comparison Service (JSC) is an initiative by cOAlition S aimed to improve ...
Scallop eyes as inspiration for new microscope objectives
2023-03-31
Some species of mussels can see. Scallops, for example, have up to 200 eyes that help them detect predators such as an approaching starfish. However, the eyes of scallops differ significantly from the human eye. While in our eyes the combination of cornea and lens creates an image on the retina, in scallop eyes light is focused by a hemispherical mirror.
Optical imaging with lenses or mirrors
Creating images with mirrors instead of lenses is especially common in astronomical telescopes, in order to capture as much light as possible from planets, stars and galaxies. In the Schmidt telescope developed in the 1930s by Bernhard Schmidt (1879-1935) and still in use in many observatories today, ...
Path to net-zero carbon capture and storage may lead to ocean
2023-03-31
Lehigh Engineering researcher Arup SenGupta has developed a novel way to capture carbon dioxide from the air and store it in the “infinite sink” of the ocean.
The approach uses an innovative copper-containing polymeric filter and essentially converts CO2 into sodium bicarbonate (aka baking soda) that can be released harmlessly into the ocean. This new hybrid material, or filter, is called DeCarbonHIX (i.e., decarbonization through hybrid ion exchange material), and is described in a paper recently published in the journal Science Advances.
The research, which demonstrated a 300 percent increase in the amount of carbon captured ...
Association between daily alcohol intake and risk of all-cause mortality
2023-03-31
About The Study: In this updated systematic review and meta-analysis of 107 studies involving more than 4.8 million participants, daily low or moderate alcohol intake was not significantly associated with all-cause mortality risk, while increased risk was evident at higher consumption levels, starting at lower levels for women than men.
Authors: Jinhui Zhao, Ph.D., of the University of Victoria in Victoria, British Columbia, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.6185)
Editor’s ...
Racial, ethnic differences in insurance after job loss during COVID-19
2023-03-31
About The Study: While the decline in employer-sponsored insurance in 2020 was offset by an increase in Medicaid coverage among newly unemployed white working-age adults, there was no such rise among newly unemployed Black and Hispanic workers.
Authors: Peter J. Huckfeldt, Ph.D., of the University of Minnesota School of Public Health in Minneapolis, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2023.0168)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including ...
Pictures inside a cell: USC researchers develop new tool to provide greater insight into biological processes
2023-03-31
A groundbreaking technique developed by researchers affiliated with the USC Michelson Center for Convergent Bioscience presents a new way of gathering and organizing highly detailed information about organic tissues in record time.
The methods could someday be used to rapidly process tissue biopsies in cancer care or detecting bacteria in food processing plants.
Tissues emit signals, or intrinsic fields, that while detectable are very weak and hard to differentiate. The technique, detailed in a pair of papers published in Nature Methods ...
Vaginal microbiome does not influence babies’ gut microbiome
2023-03-31
New University of British Columbia research is challenging a longstanding assumption that a baby’s gut microbiome is primarily shaped by their mother’s vaginal microbiome, while shedding new light on the factors that do influence its development.
When babies are born, their gut is a nearly sterile environment. But that quickly changes as the infant’s digestive tract becomes home to trillions of microbial cells throughout their early development. This gut microbiome is an important part of overall health and alterations early in life have been associated with negative health outcomes later on, including asthma and obesity.
It has ...
Green technologies for a greener environment
2023-03-31
About Book:
Green tech refers to materials and technology that are used to reduce adverse human impact on Earth. It encompasses a wide area of scientific research, including energy, atmospheric science, agriculture, material science, and hydrology.
Using sustainable resources to produce energy for a better greener tomorrow has been at the epicentre of man’s thought since 1987, in the United Nations Brundtland Report was published, which defined sustainable development as “needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs”.
It has real-world examples some ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
[Press-News.org] Making rare cell types visible: Researchers are developing a new methodMicrofluidic chip makes new cell types visible in all organisms