Since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, researchers have been working on mucosal vaccines that can be administered through the nose. Now, scientists in Berlin have developed a live attenuated vaccine for the nose. In “Nature Microbiology”, they describe the special immune protection it induces.
Joint press release by Freie Universität Berlin, Max Delbrück Center and Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin
Coronaviruses spread primarily through the air. When infected people speak, cough, sneeze or laugh, they expel droplets of saliva containing the virus. Other people then breathe in these airborne pathogens and become infected themselves. A research team in Berlin decided to try to fight the virus that causes COVID-19 where it first takes hold: the mucous membranes of the nose, mouth, throat, and lungs. To do so, the scientists developed a live attenuated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine that is administered through the nose. In the latest issue of the journal “Nature Microbiology”, the interdisciplinary team describes how this live attenuated vaccine confers better immunity than vaccines injected into muscle.
Already in the fall of last year, two nasal vaccination formulations were approved for use in India and China. These contain modified adenoviruses – which typically cause respiratory or gastrointestinal illnesses – that are self-attenuating, meaning they either replicate poorly or stop replicating altogether, and therefore never trigger disease. Other live nasal vaccines are currently undergoing development and testing around the world.
Protection at the site of infection
The benefits of a nasal vaccine go far beyond just providing an alternative for people afraid of needles. When a vaccine is injected, it infers immunity primarily in the blood and throughout the entire body. However, this means that the immune system only detects and combats coronaviruses relatively late on in an infection, as they enter the body via the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract. “It is here, therefore, that we need local immunity if we want to intercept a respiratory virus early on,” explains the study’s co-last author Dr. Jakob Trimpert, a veterinarian and research group leader at the Institute of Virology at Freie Universität Berlin.
“Nasal vaccines are far more effective in this regard than injected vaccines, which fail or struggle to reach the mucous membranes,” emphasizes Dr. Emanuel Wyler, another co-last author. He has been researching COVID-19 since the start of the pandemic as part of the RNA Biology and Posttranscriptional Regulation Lab, which is led by Professor Markus Landthaler at the Berlin Institute for Medical Systems Biology of the Max Delbrück Center (MDC-BIMSB).
In an ideal scenario, a live intranasal vaccine stimulates the formation of the antibody immunoglobulin A (IgA) directly on site, thus preventing infection from occurring in the first place. IgA is the most common immunoglobin in the mucous membranes of the airways. It is able to neutralize pathogens by binding to them and preventing them from infecting respiratory tract cells. At the same time, the vaccine stimulates systemic immune responses that help provide effective overall protection from infection.
“Memory T cells that reside in lung tissue play a similarly useful role to antibodies in the mucosa,” explains Dr. Geraldine Nouailles, an immunologist and research group leader at the Department of Pneumology, Respiratory Medicine, and Intensive Care Medicine at Charité. “These white blood cells remain in affected tissue long after an infection has passed and remember pathogens they have encountered before. Thanks to their location in the lungs, they can respond quickly to viruses that enter through the airways.” The co-first author draws attention to one of the observations the team made during their study: “We were able to show that prior intranasal vaccination results in the increased reactivation of these local memory cells in the event of a subsequent SARS-CoV-2 infection. Needless to say, we were particularly pleased with this result.”
Local immunity impedes viral infection
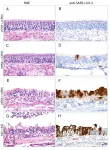
The scientists tested the efficacy of the newly developed intranasal COVID-19 vaccine on hamster models that had been established by Trimpert and his team at Freie Universität Berlin at the beginning of the pandemic. These rodents are currently the most important non-transgenic model organisms for research into the novel coronavirus, as they can be infected with the same virus variants as humans and develop similar symptoms. They found that after two doses of the vaccine, the virus could no longer replicate in the model organism. “We witnessed strong activation of the immunological memory, and the mucous membranes were very well protected by the high concentration of antibodies,” Trimpert explains. The vaccine could therefore also significantly reduce the transmissibility of the virus.
In addition, the scientists compared the efficacy of the live attenuated vaccine with that of vaccines injected into the muscle. To do so, they vaccinated the hamsters either twice with the live vaccine, once with the mRNA and once with the live vaccine, or twice with an mRNA or adenovirus-based vaccine. Then, after the hamsters were infected with SARS-CoV-2, they used tissue samples from the nasal mucosa and lungs to see how strongly the virus was still able to attack the mucosal cells. They also determined the extent of the inflammatory response using single-cell sequencing. “The live attenuated vaccine performed better than the other vaccines in all parameters,” Wyler summarizes. This is probably due to the fact that the nasally administered vaccine builds up immunity directly at the viral entry site. In addition, the live vaccine contains all components of the virus – not just the spike protein, as is the case with the mRNA vaccines. While spike is indeed the virus’s most important antigen, the immune system can also recognize the virus from about 20 other proteins.
Better than conventional vaccines
The best protection against the SARS-CoV-2 was provided by double nasal vaccination, followed by the combination of a muscular injection of the mRNA vaccine and the subsequent nasal administration of the live attenuated vaccine. “This means the live vaccine could be particularly interesting as a booster,” says the study’s co-first author Julia Adler, a veterinarian and doctoral student at the Institute of Virology at Freie Universität Berlin.
The principle of live attenuated vaccines is old and is already used in measles and rubella vaccinations, for example. But in the past, scientists generated the attenuation by chance – sometimes waiting years for mutations to evolve that produced an attenuated virus. The Berlin researchers, on the other hand, were able to specifically alter the genetic code of the coronaviruses. “We wanted to prevent the attenuated viruses from mutating back into a more aggressive variant,” explains Dr. Dusan Kunec, a scientist at the Institute of Virology at Freie Universität Berlin and another co-last author of the study. “This makes our live vaccine entirely safe and means it can be tailored to new virus variants,” stresses Kunec, who was instrumental in developing the vaccine.
The next step is safety testing: The researchers are collaborating with RocketVax AG, a Swiss start-up based in Basel. The biotech company is developing the live attenuated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine and preparing a phase 1 clinical trial in humans. “We are thrilled to be at the forefront of developing and manufacturing the live attenuated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine as a nasal spray at RocketVax. Our goal is to rapidly scale-up production and advance clinical development towards market access to provide protection against post-COVID symptoms for all. We see great potential in the market for seasonal nasal vaccines”, says Dr. Vladimir Cmiljanovic, CEO of RocketVax.
The future will show which nasal vaccine will ultimately provide better protection. The manufacturers of the nasal adenovirus vaccines developed in India and China have not yet applied for approval in Europe. But one thing is clear to the scientists: since they are administered as nasal sprays or drops, nasal vaccines are a good option for use in places with limited access to trained medical staff. They are also inexpensive to produce and easy to store and transport. Last but not least, live attenuated vaccines such as this one have been proven to provide cross-protection against related viral strains, and thus presumably also against future SARS-CoV-2 variants.
About the study
The study was financially supported, among others, by the German Research Foundation (DFG) under Grant Nos. OS 143/16-1 and SFB-TR84/Z01b The Berlin researchers are collaborating with the Swiss company RocketVax AG on the further development of the vaccine.
Max Delbrück Center
The Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine in the Helmholtz Association (Max Delbrück Center) is one of the world’s leading biomedical research institutions. Max Delbrück, a Berlin native, was a Nobel laureate and one of the founders of molecular biology. At the Center’s locations in Berlin-Buch and Mitte, researchers from some 70 countries analyze the human system – investigating the biological foundations of life from its most elementary building blocks to systems-wide mechanisms. By understanding what regulates or disrupts the dynamic equilibrium in a cell, an organ, or the entire body, we can prevent diseases, diagnose them earlier, and stop their progression with tailored therapies. Patients should benefit as soon as possible from basic research discoveries. The Max Delbrück Center therefore supports spin-off creation and participates in collaborative networks. It works in close partnership with Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin in the jointly run Experimental and Clinical Research Center (ECRC), as well as with the Berlin Institute of Health (BIH) at Charité and the German Center for Cardiovascular Research (DZHK). Founded in 1992, the Max Delbrück Center today employs 1,800 people and is funded 90 percent by the German federal government and 10 percent by the State of Berlin. www.mdc-berlin.de
Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin
Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin is one of the largest university hospitals in Europe, boasting 3,099 beds and approximately 100 departments and institutes spread across 4 separate campuses. At Charité, the areas of research, teaching and medical care are closely interlinked. With a total of 20,921 members of staff employed across its group of companies (17,615 of which at Charité), the organization is one of the largest employers in Berlin. 5,047 of its employees work in the field of nursing, with a further 4,988 in research and medical care. Last year, Charité treated 123,793 in- and day case patients, in addition to 682,731 outpatients. In 2021, Charité recorded a turnover of approximately € 2.3 billion (including external funding and investment grants) and set a new record by securing more than € 215.8 million in external funding. Charité’s Medical Faculty is one of the largest in Germany, educating and training more than 9,000 students across the subjects of medicine, dentistry, health sciences and nursing. Charité also offers 730 training positions across 11 different health care professions, in addition to 111 training positions in a further 8 professions. Within the field of academic medicine, Charité’s priorities are highlighted by its main areas of research focus: infection; inflammation and immunity including COVID-19 research; cardiovascular research and metabolism; neuroscience; oncology; regenerative therapies; and rare diseases and genetics. Examples of the work conducted by Charité researchers include involvement in 28 DFG Collaborative Research Centers (of which seven are led by Charité), three Clusters of Excellence (of which one is led by Charité), 10 Emmy Noether Independent Junior Research Groups, 14 European Research Council grants and 8 European collaborative projects (coordinated by Charité).
END