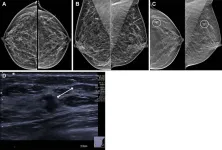
(Press-News.org) OAK BROOK, Ill. – Researchers who surveyed women attending breast cancer screening appointments found that one in five is likely to skip additional testing after an abnormal finding on their mammogram if there is a deductible or co-payment, according to an editorial published in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Health care costs and insurance premiums have increased in recent years. With the advent of the Affordable Care Act (ACA), high-deductible health plans (HDHPs) have grown in popularity, particularly among younger, healthy people.
It is believed that HDHPs lower overall health care costs by making individuals more cognizant of their medical expenses. The higher deductible also lowers monthly insurance premiums, making these plans an attractive option for healthy people who may typically need coverage only for preventative care or health emergencies.
But while HDHPs offer some advantages, the high out-of-pocket deductible cost—a minimum of $1,500 for individuals and $3,000 for families—may prevent people from seeking necessary care.
“Currently, there is no out-of-pocket payment or co-payment for screening mammography since it’s covered under the ACA,” said the study’s lead author, Michael Ngo, M.D., radiology resident at Boston Medical Center and Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine. “However, any follow-up diagnostic imaging for an abnormal finding seen on screening mammography may require the patient to pay a co-payment or deductible, depending on their healthcare plan.”
Dr. Ngo and colleagues wanted to assess the impact that these payments had on a patient’s willingness to return for important follow-up imaging.
The researchers surveyed 932 patients presenting for breast imaging at Boston Medical Center between September 2021 and February 2022. The survey was comprised of demographic questions on race, education level, annual household income and insurance payor, as well as scenarios about utilization of breast imaging. There was a variable response rate on questions.
When asked whether they would skip indicated imaging if they knew they had to pay a deductible, of 714 respondents, 151 (21.2%) said they would skip imaging, 424 (59.4%) said they would not skip imaging, and 139 (19.5%) were undecided.
“The patients who were more likely to say they would skip diagnostic imaging tended to be racial/ethnic minorities, have a lower educational level, have a lower-income household, are on Medicaid or have no insurance at all,” Dr. Ngo said.
The groups with the highest percentage of responses indicating they would skip additional imaging were Hispanic (33.0%), high school educated or less (31.0%), household income less than $35,000 (27.0%) and Medicaid/uninsured (31.5%).
“Prior research has shown that these groups tend to already have lower adherence to preventative services, including breast cancer screening, and tend to have worse breast cancer outcomes,” Dr. Ngo said. “Based on these results, these out-of-pocket payments may account for at least a part of the delay in seeking care. This, in turn, leads to delays in breast cancer diagnosis and treatment, increases overall breast cancer mortality and exacerbates existing gaps in breast cancer care in women who already have financial barriers in care.”
The survey also asked whether respondents would forgo the initial screening mammography exam if they knew they would have to pay a deductible for follow-up tests. Of 707 respondents, 129 (18.3%) said they would skip the screening mammography exam, 465 (65.8%) would not skip mammography, and 113 (16.0%) were undecided.
Identifying socioeconomic barriers to health care is critical in addressing existing disparities and ensuring better outcomes for vulnerable patient populations. The researchers hope that these findings will be useful in efforts to remove financial barriers to care.
“We hope these results can be used to advocate for legislation to eliminate out-of-pocket expenditure for screening diagnostic imaging follow-up to alleviate the existing healthcare disparities,” Dr. Ngo said.
###
“Effect of a High-Deductible Health Plan on Patients’ Willingness to Undergo Indicated Breast Imaging.” Collaborating with Dr. Ngo were Muhammad Qureshi, M.B.B.S., M.P.H., Geunwon Kim, M.D. Ph.D., Michael D. C. Fishman, M.D., and Priscilla J. Slanetz, M.D., M.P.H.
In 2023, Radiology is celebrating its 100th anniversary with 12 centennial issues, highlighting Radiology’s legacy of publishing exceptional and practical science to improve patient care.
Radiology is edited by Linda Moy, M.D., New York University, New York, N.Y., and owned and published by the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. (https://pubs.rsna.org/journal/radiology)
RSNA is an association of radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research, and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Illinois. (RSNA.org)
For patient-friendly information on screening mammography, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
END
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Ultrasound is an effective standalone diagnostic method in patients with focal breast complaints, according to a study published in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). Focal breast complaints can refer to pain, lumps, nipple discharge or other symptoms and conditions confined to a specific area of the breast.
In women, focal breast complaints are a frequent problem. In the Netherlands, approximately 70,000 women visit radiology departments annually with focal breast complaints. The most common being the presence of lumps or pain. Many women who have focal breast complaints are between the ages of 30 and 50 years.
Digital breast ...
BALTIMORE, April, 4, 2023-- As more consumers turn to the newly available ChatGPT for health advice, researchers are eager to see whether the information provided by the artificial intelligence chatbot is reliable and accurate. A new study conducted by researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) indicates that the answers generated provide correct information the vast majority of the time; sometimes, though, the information is inaccurate or even fictitious.
Findings were published today in the journal Radiology.
In February 2023, UMSOM researchers created a set of 25 questions related to advice on getting screened ...
A recent study in the Journal of Biological Chemistry revealed the key to a protein that commonly causes blindness. The biological process involves a protein that is essential for transporting toxic compounds out of the eye, similar to a garbage recycling service. The challenge is that, like food and the waste it generates, these compounds are essential for the eye to function properly — until they build up and cause blindness.
The scientists behind the study research a protein transporter, called ABCA4, that lines the edges of specialized photoreceptor cells in the retina and is normally poised to remove toxic, fatty retinal byproducts ...
In a study conducted in the lab as well as during the COVID-19 lockdowns, participants reported higher levels of tiredness after eight hours of social isolation. The results suggest that low energy may be a basic human response to a lack of social contact. The study conducted at the University of Vienna and published in Psychological Science also showed that this response was affected by social personality traits of the participants.
If we do not eat for an extended period, a series of biological processes ensue that create a craving sensation we recognize as hunger. As a social species, we also need other people to survive. Evidence shows that a lack of social contact induces ...
Insilico Medicine (“Insilico”), a clinical-stage generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven drug discovery company, today announced that four abstracts have been accepted as poster presentations at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2023.
Insilico will present four novel inhibitors for the treatment of cancer developed with its end-to-end Pharma.AI platform. Drawing from trillions of data points and millions of compounds and molecular fragments, the platform uses ...
Red tides, caused by Karenia brevis blooms, are a recurring problem in the coastal Gulf of Mexico. The organism, Karenia brevis, produces toxins that can cause fish kills, respiratory irritation in humans and cause death in sea turtles, dolphins, manatees and birds.
The ability to detect red tide blooms at all life stages and cell concentrations is critical to increasing predictive capabilities and developing potential mitigation strategies to protect public health and vital resources.
Current methods used to monitor red tide such as microscopic identification and enumeration, standard flow cytometry, as well as others have limitations. Some of these ...
April 4, 2023, TORONTO — Becoming the first genomics lab to be accredited by three of the leading North American accreditation organizations positions OICR Genomics to generate new discoveries about what drives diseases like cancer and new, personalized ways to diagnose and treat them.
The lab earned a Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) certificate of accreditation in January 2023 for its whole genome and whole transcriptome sequencing assay, a comprehensive genetic test that can find all changes in the DNA of a tumour. This comes after accreditation from the College of American Pathologists (CAP) in 2021 and from Accreditation Canada Diagnostics (ACD) — ...
SPOKANE, Wash.—Researchers have long known that many animals live longer in colder climates than in warmer climates. New research in C. elegans nematode worms suggests that this phenomenon is tied to a protein found in the nervous system that controls the expression of collagens, the primary building block of skin, bone and connective tissue in many animals.
Since the C. elegans’ protein is similar to nervous system receptor proteins found in other species including humans, the discovery potentially brings scientists closer to finding ways to harness collagen expression to slow down human aging and increase lifespan in the ...
In the United States alone, drug-resistant bacteria and fungi infect almost 3 million people per year and kill about 35,000. Antibiotics are essential and effective, but in recent years overuse has led to some bacteria developing resistance to them. The infections are so difficult to treat, the World Health Organization deemed antibiotic resistance a top 10 global public health threat.
Now, Professor John E. Moses at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) has created a new weapon against these drug-resistant ...
Sixty per cent of the world's fresh water is bound up in Antarctic ice sheets. Thirty million cubic kilometres of ice is perhaps a difficult number to grasp. But if absolutely all Antarctica’s ice melted, the seas would rise by 58 metres on average.
“The ice sheet in East Antarctica stores enormous amounts of water. This means that this is the biggest possible source of future sea level rise – up to 53 meters if all of the East Antarctic ice melts – and is seen as the largest source of uncertainties in the ...