(Press-News.org) A new study has identified potential neurological biomarkers of long COVID-19 in nonhuman primates that may help physicians diagnose, monitor and treat this condition.
Over 65 million people worldwide have developed long COVID after being infected with SARS-CoV-2, and cases are only becoming more common. Long COVID symptoms can last weeks, months or years. Even more perplexing is the fact that symptoms can vary widely between individuals and consist of any combination of fatigue, fever, chest pain, trouble breathing, neurological symptoms such as “brain fog,” and many more. Long COVID puts a gigantic burden on the U.S. healthcare system, and some doctors doubt the condition exists, leaving some patients unable to find care.
A team of researchers at Tulane University is trying to shed light on this condition and find tools to manage it. They published their work in the journal Molecular & Cellular Proteomics.
“Our primary goal was to better understand the inside of the brain after COVID infection,” said Jia Fan, an assistant professor of biochemistry and molecular biology who oversaw the study. “This understanding could provide a potential target to use in the clinic for long COVID evaluation and monitoring. We also thought this study may give us some clues to find a potential treatment strategy for long COVID in patients.”
However, because long COVID can vary drastically between individuals, studying this disorder has been difficult for scientists and clinicians alike.
“There's a very limited understanding of the neuropathogenesis of long COVID,” Fan said. “It is almost impossible to get any brain tissue or samples of any kind from patients that have mild symptoms or no long COVID symptoms because there is no reason for invasive procedures.”
Therefore, the group turned to a nonhuman primate model of long COVID.
The team found that certain proteins associated with neurodegenerative disorders, such as Parkinson's disease, were elevated in the brain, cerebrospinal fluid and blood after SARS-CoV-2 infection even in nonhuman primates that showed mild or no symptoms. Maity explained that these elevated proteins indicate that the immune systems of the monkeys remained activated even after infection.
“Our findings suggest that the major neurological complications are arising due to the body's natural immune defenses,” Maity said. “The immune system has a very important and significant impact on the neurological complications of COVID.”
The next steps of the project involve validating the biomarkers the team identified in human samples such as blood, said Fan.
“It is currently hard to score the severity of (long COVID) patient symptoms because they are based on self-reports,” Fan said. “If we can find a group of proteins in the blood associated with long COVID, this is a less invasive way to easily evaluate the severity of the long COVID patients. We hope what we started can provide a clue to find a potential treatment to better the long COVID patient experience.”
About the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (ASBMB): The ASBMB is a nonprofit scientific and educational organization with more than 12,000 members worldwide. Founded in 1906 to advance the science of biochemistry and molecular biology, the society publishes three peer-reviewed journals, advocates for funding of basic research and education, supports science education at all levels, and promotes the diversity of individuals entering the scientific workforce. For more information about the ASBMB, visit www.asbmb.org.
END
Finding a way to combat long COVID
Recent study reveals neurodegenerative biomarkers after COVID-19, gives clues for monitoring and potential treatment
2023-04-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
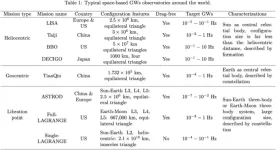
Overview of orbital mechanics for space-based gravitational wave observatories
2023-04-05
Gravitational waves (GWs) are “ripples in space-time”. The detection of gravitational waves (GWs) is critical to the understanding of the origin and evolution of stars, galaxies, and the Universe. At present, the laser interferometry is the most commonly use technology to detect GWs by measuring the phase change between two beams of coherent light. Due to the limitations of arm length, the ground-based GWs measurement is hard to detect the low-frequency GWs. While the space-based GWs observation is capable of longer arm length of the interferometer, the detection of GWs in space is expected to cover a greater number and variety of ...
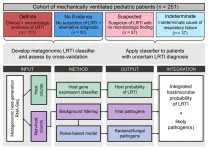
Cracking the puzzle of lower respiratory tract infections in children
2023-04-05
Lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI), which includes conditions such as pneumonia, has long been the leading cause of death from communicable agents and a leading cause of death in children worldwide. But despite its prevalence, LRTI is tricky for doctors to treat effectively because the current diagnostic approach often fails to conclusively determine whether an infection is present at all, and if so, what pathogen is causing it.
Now, in a study published April 3, 2023 in The Journal of Clinical Investigation, a team led by researchers at the Chan Zuckerberg Biohub San Francisco (CZ Biohub SF), UC San Francisco (UCSF), the University ...
Opening a new frontier: PdMo intermetallic catalyst for promoting CO2 utilization
2023-04-05
Being the most abundant and persistent greenhouse gas emitted, carbon dioxide (CO2) is the key driver of climate change. To address the pressing problems associated with climate change and fossil fuel depletion, scientists are looking for viable solutions that can minimize the amount of CO2 released into the atmosphere. One attractive solution to this problem is to convert atmospheric CO2 into more useful compounds. Towards this end, methanol - a raw material, fuel additive, and energy carrier, is widely being explored as a promising conversion option for CO2.
Now, while various catalysts ...
SwRI, Tec de Monterrey award funding for sustainable manufacturing research
2023-04-05
SAN ANTONIO — April 5, 2023 —Southwest Research Institute and Tecnológico de Monterrey (Tec de Monterrey) will jointly fund three research and development initiatives to advance sustainable manufacturing and technology in the United States and Mexico. The trio of projects are the first selected to receive support through the Sustainable Manufacturing Program, a transnational research and development collaboration established between SwRI and Tec de Monterrey — a private, nonprofit, independent university based in Monterrey, Mexico — in August 2022. The program provides grant opportunities funded ...
How were amino acids, one of the key building blocks of life, formed before the origin of life on Earth? Tiny particles from the near Earth asteroid Ryugu can help answer this profound question
2023-04-05
Our solar system formed from a molecular cloud, which was composed of gas and dust that was emitted into the interstellar medium (ISM), a vast space between stars. On collapse of the molecular cloud, the early sun was formed, with a large disk of gas and dust orbiting it. The dusty material collided to produce rocky material that would eventually grow in size to give large bodies called planetesimals.
The planetesimals that formed far enough from the sun, also contained large quantities of ice. The ice consisted of water and other volatile compounds, such as carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), methanol (CH3OH) and ammonia (NH3), as well as ...
Air pollution is linked to lower COVID-19 vaccine responses
2023-04-05
People exposed to higher levels of air pollution before the pandemic had lower antibody responses to COVID-19 vaccines, according to a study led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), an institution supported by “la Caixa” Foundation, in collaboration with the Germans Trias i Pujol Research Institute (IGTP). In particular, exposure to fine particulate matter (PM2.5), nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and blank carbon (BC) was associated with about a 10% decrease in IgM and IgG antibody responses in people without prior infection. The findings, published in Environmental Health Perspectives, ...
More than a third of children worry at least once a week, with their tendency to worry progressing with age, according to national survey by Nemours KidsHealth(R)
2023-04-05
WILMINGTON, Del. (April 5, 2023) – More than one in three children ages 9 to 13 (37%) worry at least once a week, primarily about school (64%) and friendships (41%), with their tendency to worry progressing with age. Older children (age 13) are more likely than their younger counterparts to report feeling as though they will never stop worrying (48% vs. 22% for 9-year-olds). This is according to the results of What’s Worrying America’s Kids, a national survey conducted by The Harris Poll on behalf of Nemours KidsHealth. The survey results ...
TOS endorses global editorial on people-first language and pediatric obesity
2023-04-05
ROCKVILLE, Md.—The Obesity Society (TOS) has joined several European, US and Canadian obesity organizations in an editorial statement published in the journal Pediatric Obesity championing the use of people-first language for pediatric overweight and obesity to address weight stigma and bias.
Professor David Thivel, president of the European Childhood Obesity Group and coordinator of the joint statement, said, "This paper emphasizes the importance of considering the use of people-first language when it comes to pediatric obesity, by all who work with, care for or support children and adolescents, in order to avoid stigmatization and to create an appropriate and optimal ...
Complications for procedure to open clogged pulmonary arteries decrease significantly
2023-04-05
For patients with high blood pressure in their pulmonary arteries caused by chronic blood clots, complications after a minimally invasive balloon angioplasty have decreased substantially over the last decade, a Michigan Medicine-led study finds.
Researchers examined over 7,500 cases of balloon pulmonary angioplasty for patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension, an elevated blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries due to persistent blockages known as CTEPH, between 2013 and 2022. The procedure, which is offered ...
New tool shows progress in fighting spread of invasive grass carp in Great Lakes
2023-04-05
New research reveals the progress scientists at The University of Toledo are making in their ongoing efforts to capture and remove invasive grass carp from the Great Lakes.
Researchers based at the UToledo Lake Erie Center created a new way to estimate the abundance of invasive “sleeper” species in freshwater ecosystems and help guide management strategies.
Using data collected during their efforts to remove invasive grass carp from Lake Erie and its tributaries, the aquatic ecologists and environmental ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Putting some ‘muscle’ into material design
House fires release harmful compounds into the air
Novel structural insights into Phytophthora effectors challenge long-held assumptions in plant pathology
Q&A: Researchers discuss potential solutions for the feedback loop affecting scientific publishing
A new ecological model highlights how fluctuating environments push microbes to work together
Chapman University researcher warns of structural risks at Grand Renaissance Dam putting property and lives in danger
Courtship is complicated, even in fruit flies
Columbia announces ARPA-H contract to advance science of healthy aging
New NYUAD study reveals hidden stress facing coral reef fish in the Arabian Gulf
36 months later: Distance learning in the wake of COVID-19
Blaming beavers for flood damage is bad policy and bad science, Concordia research shows
The new ‘forever’ contaminant? SFU study raises alarm on marine fiberglass pollution
Shorter early-life telomere length as a predictor of survival
Why do female caribou have antlers?
How studying yeast in the gut could lead to new, better drugs
Chemists thought phosphorus had shown all its cards. It surprised them with a new move
A feedback loop of rising submissions and overburdened peer reviewers threatens the peer review system of the scientific literature
Rediscovered music may never sound the same twice, according to new Surrey study
Ochsner Baton Rouge expands specialty physicians and providers at area clinics and O’Neal hospital
New strategies aim at HIV’s last strongholds
Ambitious climate policy ensures reduction of CO2 emissions
Frontiers in Science Deep Dive webinar series: How bacteria can reclaim lost energy, nutrients, and clean water from wastewater
UMaine researcher develops model to protect freshwater fish worldwide from extinction
Illinois and UChicago physicists develop a new method to measure the expansion rate of the universe
Pathway to residency program helps kids and the pediatrician shortage
How the color of a theater affects sound perception
Ensuring smartphones have not been tampered with
Overdiagnosis of papillary thyroid cancer
Association of dual eligibility and medicare type with quality of postacute care after stroke
Shine a light, build a crystal
[Press-News.org] Finding a way to combat long COVIDRecent study reveals neurodegenerative biomarkers after COVID-19, gives clues for monitoring and potential treatment