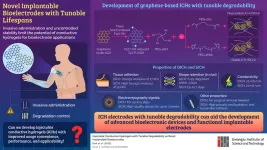
Is artificial intelligence better at assessing heart health?
Published in Nature, new research from the Smidt Heart Institute shows whether artificial intelligence or sonographers provide most accurate heart evaluations
2023-04-05
(Press-News.org)
Who can assess and diagnose cardiac function best after reading an echocardiogram: artificial intelligence (AI) or a sonographer?
According to Cedars-Sinai investigators and their research published today in the peer-reviewed journal Nature, AI proved superior in assessing and diagnosing cardiac function when compared with echocardiogram assessments made by sonographers.
The findings are based on a first-of-its-kind, blinded, randomized clinical trial of AI in cardiology led by investigators in the Smidt Heart Institute and the Division of Artificial Intelligence in Medicine at Cedars-Sinai.
“The results have immediate implications for patients undergoing cardiac function imaging as well as broader implications for the field of cardiac imaging,” said cardiologist David Ouyang, MD, principal investigator of the clinical trial and senior author of the study. “This trial offers rigorous evidence that utilizing AI in this novel way can improve the quality and effectiveness of echocardiogram imaging for many patients.”
Investigators are confident that this technology will be found beneficial when deployed across the clinical system at Cedars-Sinai and health systems nationwide.
“This successful clinical trial sets a superb precedent for how novel clinical AI algorithms can be discovered and tested within health systems, increasing the likelihood of seamless deployment for improved patient care,” said Sumeet Chugh, MD, director of the Division of Artificial Intelligence in Medicine and the Pauline and Harold Price Chair in Cardiac Electrophysiology Research.
In 2020, researchers at the Smidt Heart Institute and Stanford University developed one of the first AI technologies to assess cardiac function, specifically, left ventricular ejection fraction—the key heart measurement used in diagnosing cardiac function. Their research also was published in Nature.
Building on those findings, the new study assessed whether AI was more accurate in evaluating 3,495 transthoracic echocardiogram studies by comparing initial assessment by AI or by a sonographer—also known as an ultrasound technician.
Among the findings:
Cardiologists more frequently agreed with the AI initial assessment and made corrections to only 16.8% of the initial assessments made by AI.
Cardiologists made corrections to 27.2% of the initial assessments made by the sonographers.
The physicians were unable to tell which assessments were made by AI and which were made by sonographers.
The AI assistance saved cardiologists and sonographers time.
“We asked our cardiologists to guess if the preliminary interpretation was performed by AI or by a sonographer, and it turns out that they couldn’t tell the difference,” said Ouyang. “This speaks to the strong performance of the AI algorithm as well as the seamless integration into clinical software. We believe these are all good signs for future AI trial research in the field.”
The hope, Ouyang says, is to save clinicians time and minimize the more tedious parts of the cardiac imaging workflow. The cardiologist, however, remains the final expert adjudicator of the AI model output.
The clinical trial and subsequent published research also shed light on the opportunity for regulatory approvals.
“This work raises the bar for artificial intelligence technologies being considered for regulatory approval, as the Food and Drug Administration has previously approved artificial intelligence tools without data from prospective clinical trials,” said Susan Cheng, MD, MPH, director of the Institute for Research on Healthy Aging in the Department of Cardiology at the Smidt Heart Institute and co-senior author of the study. “We believe this level of evidence offers clinicians extra assurance as health systems work to adopt artificial intelligence more broadly as part of efforts to increase efficiency and quality overall.”
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-04-05
Pictures of melting glaciers and stranded polar bears on shrinking sea ice in the Arctic are perhaps the most striking images that have been used to highlights the effects of global warming. However, they do not convey the full extent of the consequences of warmer Arctic. In recent years, there has been growing recognition of the Arctic’s role in driving extreme weather events in other parts of the world. While the Arctic has been warming at a rate twice as fast as the global average, winters in the midlatitude regions have experienced colder and more severe weather events. For instance, the winter of 2022-2023 saw record-breaking cold temperatures and snowfall ...
2023-04-05
A new study has identified potential neurological biomarkers of long COVID-19 in nonhuman primates that may help physicians diagnose, monitor and treat this condition.
Over 65 million people worldwide have developed long COVID after being infected with SARS-CoV-2, and cases are only becoming more common. Long COVID symptoms can last weeks, months or years. Even more perplexing is the fact that symptoms can vary widely between individuals and consist of any combination of fatigue, fever, chest pain, trouble breathing, neurological symptoms such as ...
2023-04-05
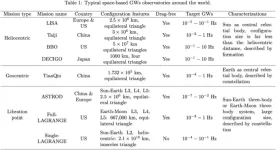
Gravitational waves (GWs) are “ripples in space-time”. The detection of gravitational waves (GWs) is critical to the understanding of the origin and evolution of stars, galaxies, and the Universe. At present, the laser interferometry is the most commonly use technology to detect GWs by measuring the phase change between two beams of coherent light. Due to the limitations of arm length, the ground-based GWs measurement is hard to detect the low-frequency GWs. While the space-based GWs observation is capable of longer arm length of the interferometer, the detection of GWs in space is expected to cover a greater number and variety of ...
2023-04-05
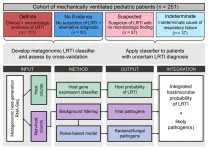
Lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI), which includes conditions such as pneumonia, has long been the leading cause of death from communicable agents and a leading cause of death in children worldwide. But despite its prevalence, LRTI is tricky for doctors to treat effectively because the current diagnostic approach often fails to conclusively determine whether an infection is present at all, and if so, what pathogen is causing it.
Now, in a study published April 3, 2023 in The Journal of Clinical Investigation, a team led by researchers at the Chan Zuckerberg Biohub San Francisco (CZ Biohub SF), UC San Francisco (UCSF), the University ...
2023-04-05
Being the most abundant and persistent greenhouse gas emitted, carbon dioxide (CO2) is the key driver of climate change. To address the pressing problems associated with climate change and fossil fuel depletion, scientists are looking for viable solutions that can minimize the amount of CO2 released into the atmosphere. One attractive solution to this problem is to convert atmospheric CO2 into more useful compounds. Towards this end, methanol - a raw material, fuel additive, and energy carrier, is widely being explored as a promising conversion option for CO2.
Now, while various catalysts ...
2023-04-05
SAN ANTONIO — April 5, 2023 —Southwest Research Institute and Tecnológico de Monterrey (Tec de Monterrey) will jointly fund three research and development initiatives to advance sustainable manufacturing and technology in the United States and Mexico. The trio of projects are the first selected to receive support through the Sustainable Manufacturing Program, a transnational research and development collaboration established between SwRI and Tec de Monterrey — a private, nonprofit, independent university based in Monterrey, Mexico — in August 2022. The program provides grant opportunities funded ...
2023-04-05
Our solar system formed from a molecular cloud, which was composed of gas and dust that was emitted into the interstellar medium (ISM), a vast space between stars. On collapse of the molecular cloud, the early sun was formed, with a large disk of gas and dust orbiting it. The dusty material collided to produce rocky material that would eventually grow in size to give large bodies called planetesimals.
The planetesimals that formed far enough from the sun, also contained large quantities of ice. The ice consisted of water and other volatile compounds, such as carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), methanol (CH3OH) and ammonia (NH3), as well as ...
2023-04-05
People exposed to higher levels of air pollution before the pandemic had lower antibody responses to COVID-19 vaccines, according to a study led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), an institution supported by “la Caixa” Foundation, in collaboration with the Germans Trias i Pujol Research Institute (IGTP). In particular, exposure to fine particulate matter (PM2.5), nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and blank carbon (BC) was associated with about a 10% decrease in IgM and IgG antibody responses in people without prior infection. The findings, published in Environmental Health Perspectives, ...
2023-04-05
WILMINGTON, Del. (April 5, 2023) – More than one in three children ages 9 to 13 (37%) worry at least once a week, primarily about school (64%) and friendships (41%), with their tendency to worry progressing with age. Older children (age 13) are more likely than their younger counterparts to report feeling as though they will never stop worrying (48% vs. 22% for 9-year-olds). This is according to the results of What’s Worrying America’s Kids, a national survey conducted by The Harris Poll on behalf of Nemours KidsHealth. The survey results ...
2023-04-05
ROCKVILLE, Md.—The Obesity Society (TOS) has joined several European, US and Canadian obesity organizations in an editorial statement published in the journal Pediatric Obesity championing the use of people-first language for pediatric overweight and obesity to address weight stigma and bias.
Professor David Thivel, president of the European Childhood Obesity Group and coordinator of the joint statement, said, "This paper emphasizes the importance of considering the use of people-first language when it comes to pediatric obesity, by all who work with, care for or support children and adolescents, in order to avoid stigmatization and to create an appropriate and optimal ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Is artificial intelligence better at assessing heart health?
Published in Nature, new research from the Smidt Heart Institute shows whether artificial intelligence or sonographers provide most accurate heart evaluations