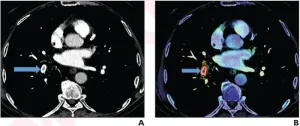
(Press-News.org) Leesburg, VA, April 5, 2023—According to an accepted manuscript published in ARRS’ own American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), a worklist reprioritization tool with artificial intelligence reduced both report turnaround time and wait time for pulmonary embolus-positive CT pulmonary angiography examinations.
“By assisting radiologists in providing rapid diagnoses, the artificial intelligence (AI) tool could potentially enable earlier interventions for acute pulmonary embolus (PE),” concluded lead researcher Kiran Batra, MD, from the department of radiology at University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas.
Batra et al.’s AJR accepted manuscript included patients who underwent CT pulmonary angiography (CTPA) before (October 1, 2018–March 31, 2019) and after (October 1, 2019–March 31, 2020) implementing an FDA-approved AI tool that reprioritized CTPA examinations atop radiologists’ reading list, if acute PE was detected. Timestamps from EMR and dictation systems were then utilized to determine three times: wait (examination completion to report initiation), read (report initiation to availability), as well as report turnaround (sum of wait and read). Times for PE positive reports, using final imaging for reference, were compared between periods.
Ultimately, the authors’ AI-driven worklist reprioritization tool was associated with significantly shorter report turnaround (47.6 vs. 59.9 mins) and wait (21.4 vs. 33.4 mins) times—though no significant difference in reading time (26.3 vs. 26.5 mins)—for CTPA reports positive for acute PE, compared to reports from before AI implementation.
“During regular hours,” the authors of this AJR accepted manuscript added, “the reduction in wait time was observed for examinations with routine, but not urgent or stat, priority.”
North America’s first radiological society, the American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS) remains dedicated to the advancement of medicine through the profession of medical imaging and its allied sciences. An international forum for progress in radiology since the discovery of the x-ray, ARRS maintains its mission of improving health through a community committed to advancing knowledge and skills with the world’s longest continuously published radiology journal—American Journal of Roentgenology—the ARRS Annual Meeting, InPractice magazine, topical symposia, myriad multimedia educational materials, as well as awarding scholarships via The Roentgen Fund®.
MEDIA CONTACT:
Logan K. Young, PIO
44211 Slatestone Court
Leesburg, VA 20176
lyoung@arrs.org
END
AI cuts CT turnaround, wait times for positive pulmonary embolus
A worklist reprioritization tool with artificial intelligence reduced both report turnaround time and wait time for pulmonary embolus-positive CT pulmonary angiography examinations
2023-04-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Gone for good? California’s beetle-killed, carbon-storing pine forests may not come back
2023-04-05
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., April 4, 2023—Ponderosa pine forests in the Sierra Nevada that were wiped out by western pine beetles during the 2012-2015 megadrought won’t recover to pre-drought densities, reducing an important storehouse for atmospheric carbon.
“Forests store huge amounts of atmospheric carbon, so when western pine beetle infestations kill off millions of trees, that carbon dioxide goes back into the atmosphere,“ said Zachary Robbins, a postdoctoral at Los Alamos National Laboratory.
Robbins is corresponding author of a new paper published in the journal Frontiers in Environmental Science about carbon stored in living ponderosa pines in the ...
Dual quasars blaze bright at the center of merging galaxies
2023-04-05
Galaxies grow and evolve by merging with other galaxies, blending their billions of stars, triggering bursts of vigorous star formation, and often fueling their central supermassive black holes to produce luminous quasars that outshine the entire galaxy. Some of these mergers eventually go on to become massive elliptical galaxies that contain black holes that are many billions of times the mass of our Sun. Although astronomers have observed a veritable menagerie of merging galaxies with more than one quasar in our own cosmic neighborhood, more distant examples, seen when the Universe was only a quarter of its current age, are quite rare and ...
SFU research aids fight against treatment-resistant superbugs
2023-04-05
Researchers at Simon Fraser University are studying the genes of superbugs to aid the development of new and effective treatments for drug-resistant bacterial infections. Superbugs are characterized as infection-causing bacteria resistant to treatment with antibiotics.
“Antimicrobial resistance occurs when the disease-causing bacteria has ways to overcome the antibiotics that we use in treatment for infections,” says assistant professor Amy Lee, of SFU's Department of Molecular Biology and Biochemistry. The initiative is a collaboration between the Lee Lab and Brinkman Lab, which are working together as ...
Underground water could be the solution to green heating and cooling
2023-04-05
About 12% of the total global energy demand comes from heating and cooling homes and businesses. A new study suggests that using underground water to maintain comfortable temperatures could reduce consumption of natural gas and electricity in this sector by 40% in the U.S. The approach, called aquifer thermal energy storage (ATES), could also help prevent blackouts caused by high power demand during extreme weather events.
“We need storage to absorb the fluctuating energy from solar and wind, and most people are interested in batteries ...
WVU researchers earn $8M for rare earth extraction facility, an economic and environmental game changer
2023-04-05
West Virginia University researchers will continue to develop and advance their pioneering method to extract and separate rare earth elements and critical minerals from acid mine drainage and coal waste, courtesy of $8 million in new funding from the U.S. Department of Energy.
The grant, part of President Joe Biden’s Investing in America agenda, will lead to the design, construction and operation of a pre-commercial demonstration facility for separating and refining rare earth elements and critical minerals, according to Paul Ziemkiewicz, project lead and director of the West Virginia Water ...
Danger or pleasure? How we learn to tell the difference
2023-04-05
Deep within our brain’s temporal lobes, two almond-shaped cell masses help keep us alive. This tiny region, called the amygdala, assists with a variety of brain activities. It helps us learn and remember. It triggers our fight-or-flight response. It even promotes the release of a feel-good chemical called dopamine. Scientists have learned all this by studying the amygdala over hundreds of years. But we still haven’t reached a full understanding of how these processes work.
Now, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory neuroscientist Bo Li has brought us several important steps closer. His lab recently made a series of discoveries ...
Ice sheets can collapse faster than previously thought possible
2023-04-05
Ice sheets can retreat up to 600 metres a day during periods of climate warming, 20 times faster than the highest rate of retreat previously measured.
An international team of researchers, led by Dr Christine Batchelor of Newcastle University, UK, used high-resolution imagery of the seafloor to reveal just how quickly a former ice sheet that extended from Norway retreated at the end of the last Ice Age, about 20,000 years ago.
The team, which also included researchers from the universities of Cambridge and Loughborough in the UK and the Geological Survey of Norway, mapped more than 7,600 small-scale landforms called ‘corrugation ridges’ across the seafloor. The ridges ...
Chinese researchers achieve superionic hydride ion conduction at ambient temperatures
2023-04-05
Materials that can conduct negatively charged hydrogen atoms in ambient conditions would pave the way for advanced clean energy storage and electrochemical conversion technologies. A research team from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) demonstrated a technique that enables a room-temperature all-solid-state hydride cell by introducing and exploiting defects in the lattice structure of rare earth hydrides.
Their study was published in Nature on April 5.
Solid materials ...
Therapy for babies with signs of autism cuts long-term disability costs
2023-04-05
New research evaluating the potential cost savings of a therapy for babies displaying early autism signs has predicted a three dollar return to Australia’s National Disability Insurance Scheme (NDIS) for every dollar invested in therapy.
Published in the prestigious JAMA Network Open, the health economic study drew on the results of a landmark multi-centre randomised clinical trial which reported the world’s first evidence that a therapy commenced in infancy (iBASIS-VIPP)* could reduce early developmental disability to the point where a childhood clinical autism diagnosis was two-thirds ...
CHOP researchers reveal complex assembly process involved in DNA virus replication
2023-04-05
Philadelphia, April 5, 2023—In a twist on the question, “Which came first, the chicken or the egg?”, scientists have long faced a similar question about how human adenovirus replicates: “Which comes first, assembly of the viral particle, or packaging of the viral genome?” Now, in a new study published today in Nature, researchers at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have answered that question, showing that viral proteins use a process called phase separation to coordinate production ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Novel structural insights into Phytophthora effectors challenge long-held assumptions in plant pathology
Q&A: Researchers discuss potential solutions for the feedback loop affecting scientific publishing
A new ecological model highlights how fluctuating environments push microbes to work together
Chapman University researcher warns of structural risks at Grand Renaissance Dam putting property and lives in danger
Courtship is complicated, even in fruit flies
Columbia announces ARPA-H contract to advance science of healthy aging
New NYUAD study reveals hidden stress facing coral reef fish in the Arabian Gulf
36 months later: Distance learning in the wake of COVID-19
Blaming beavers for flood damage is bad policy and bad science, Concordia research shows
The new ‘forever’ contaminant? SFU study raises alarm on marine fiberglass pollution
Shorter early-life telomere length as a predictor of survival
Why do female caribou have antlers?
How studying yeast in the gut could lead to new, better drugs
Chemists thought phosphorus had shown all its cards. It surprised them with a new move
A feedback loop of rising submissions and overburdened peer reviewers threatens the peer review system of the scientific literature
Rediscovered music may never sound the same twice, according to new Surrey study
Ochsner Baton Rouge expands specialty physicians and providers at area clinics and O’Neal hospital
New strategies aim at HIV’s last strongholds
Ambitious climate policy ensures reduction of CO2 emissions
Frontiers in Science Deep Dive webinar series: How bacteria can reclaim lost energy, nutrients, and clean water from wastewater
UMaine researcher develops model to protect freshwater fish worldwide from extinction
Illinois and UChicago physicists develop a new method to measure the expansion rate of the universe
Pathway to residency program helps kids and the pediatrician shortage
How the color of a theater affects sound perception
Ensuring smartphones have not been tampered with
Overdiagnosis of papillary thyroid cancer
Association of dual eligibility and medicare type with quality of postacute care after stroke
Shine a light, build a crystal
AI-powered platform accelerates discovery of new mRNA delivery materials
Quantum effect could power the next generation of battery-free devices
[Press-News.org] AI cuts CT turnaround, wait times for positive pulmonary embolusA worklist reprioritization tool with artificial intelligence reduced both report turnaround time and wait time for pulmonary embolus-positive CT pulmonary angiography examinations