(Press-News.org) AMHERST, Mass. – Three engineers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst have invented a fabric that concludes the 80-year quest to make a synthetic textile modeled on Polar bear fur. The results, published recently in the journal ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, are already being developed into commercially available products.
Polar bears live in some of the harshest conditions on earth, shrugging off Arctic temperatures as low as -50 Fahrenheit. While the bears have many adaptations that allow them to thrive when the temperature plummets, since the 1940s scientists have focused on one in particular: their fur. How, the scientific community has asked, does a polar bear’s fur keep them warm?
Typically, we think that the way to stay warm is to insulate ourselves from the weather. But there’s another way: One of the major discoveries of the last few decades is that many polar animals actively use the sunlight to maintain their temperature, and polar bear fur is a well-known case in point.
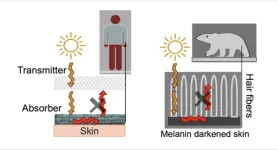
Scientists have known for decades that part of the bears’ secret is their white fur. One might think that black fur would be better at absorbing heat, but it turns out that the polar bears’ fur is extremely effective at transmitting solar radiation toward the bears’ skin.
“But the fur is only half the equation,” says the paper’s senior author, Trisha L. Andrew, associate professor of chemistry and adjunct in chemical engineering at UMass Amherst. “The other half is the polar bears’ black skin.”
As Andrew explains it, polar bear fur is essentially a natural fiberoptic, conducting sunlight down to the bears’ skin, which absorbs the light, heating the bear. But the fur is also exceptionally good at preventing the now-warmed skin from radiating out all that hard-won warmth. When the sun shines, it’s like having a thick blanket that warms itself up, and then traps that warmth next to your skin.
What Andrew and her team have done is to engineer a bilayer fabric whose top layer is composed of threads that, like polar bear fur, conduct visible light down to the lower layer, which is made of nylon and coated with a dark material called PEDOT. PEDOT, like the polar bears’ skin, warms efficiently.
So efficiently, in fact, that a jacket made of such material is 30% lighter than the same jacket made of cotton yet will keep you comfortable at temperatures 10 degrees Celsius colder than the cotton jacket could handle, as long as the sun is shining or a room is well lit.
“Space heating consumes huge amounts of energy that is mostly fossil fuel-derived,” says Wesley Viola, the paper’s lead author, who completed his Ph.D. in chemical engineering at UMass and is now at Andrew’s startup, Soliyarn, LLC. “While our textile really shines as outerwear on sunny days, the light-heat trapping structure works efficiently enough to imagine using existing indoor lighting to directly heat the body. By focusing energy resources on the ‘personal climate’ around the body, this approach could be far more sustainable than the status quo.”
The research, which was supported by the National Science Foundation, is already being applied, and Soliyarn has begun production of the PEDOT-coated cloth.
Contacts: Trisha Andrew, tandrew@umass.edu
Daegan Miller, drmiller@umass.edu
END
New textile unravels warmth-trapping secrets of polar bear fur
Team of UMass Amherst engineers invents bilayered fabric, 30% lighter than cotton and far warmer
2023-04-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Navigating the cosmos with Georgia State’s CHARA Array
2023-04-10
ATLANTA—Plans are underway to add a seventh movable telescope to Georgia State University’s Center for High Angular Resolution Astronomy— known as the CHARA Array—that would increase the resolution, or the ability to see small objects, by a factor of three.
Located at Mount Wilson Observatory in Southern California and operated by Georgia State, the new telescope will be connected using fiber optics to transport the starlight, a technique that will serve as a pathfinder ...
BU doc honored by the Association of University Radiologists
2023-04-10
(Boston)— Priscilla J. Slanetz, MD, MPH, professor of radiology at Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine, was awarded the 2023 Association of Program Directors in Radiology (APDR) Achievement Award at the Association of University Radiologists’ annual meeting. The honor is given for outstanding service to APDR or to someone who has made significant contributions to the advancement of education in radiology.
Slanetz is a practicing breast radiologist at Boston Medical Center specializing in all aspects of breast imaging including screening, diagnostic evaluation and image-guided intervention, providing breast care to Boston’s most vulnerable ...
BU researcher awarded $1.5 million NIH grant
2023-04-10
Boston—Esther Bullitt, PhD, associate professor of pharmacology, physiology & biophysics at Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine, was awarded $1.5 million from the National Institutes of Health that will go toward the purchase of a cryogenic electron microscope. Additional funds have been pledged by University President Robert A. Brown and Professor and Chair of Pharmacology, Physiology & Biophysics Venetia Zachariou, PhD.
The FEI ThermoFisher Glacios-2 cryo-EM is capable of determining structures at near-atomic resolution. Researchers will use this new instrumentation to study cellular function and dysfunction, and to guide ...
New UK data system will help predict and prevent opioid overdoses in Kentucky
2023-04-10
LEXINGTON, Ky. (April 10, 2023) — University of Kentucky researchers are creating an innovative statewide surveillance system to inform prevention and response efforts aimed at reducing the burden of opioid use disorder in Kentucky.
The Rapid Actionable Data for Opioid Response in Kentucky (RADOR-KY) will use data from federal, state, and local sources to guide evidence-based practices aimed at preventing opioid overdoses in the Commonwealth. Phase one of the project is supported by a three-year $3.1 million grant from the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA).
Driven by the COVID-19 pandemic and illegally manufactured fentanyl, drug overdose ...
AACR announces recipients of the 2023 AACR June L. Biedler Prize for Cancer Journalism
2023-04-10
PHILADELPHIA – The American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) is pleased to announce the recipients of the 2023 AACR June L. Biedler Prize for Cancer Journalism in the following categories:
Auditory Journalism
“‘No Mercy’ Chapter 5: With Rural Hospital Gone, Cancer Care Means a Daylong Trek”
Sarah Jane Tribble (Photo), Taunya English (Photo), Kaiser Health News
Greg Munteanu (Photo), Saint Louis Public Radio
Magazine
“One Man’s Search for the DNA Data That Could Save His Life”
By ...
Identifying cancer genes’ multiple personalities
2023-04-10
Mutations in our genes can lead to severe problems, like colon or liver cancer. But cancer is very complex. Mutations in the same genes can lead to different subtypes of tumors in different people. Currently, scientists don’t have a good way to produce such tumor subtypes for study in the lab.
Now, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Assistant Professor Semir Beyaz has created a new method to model certain liver cancer tumor subtypes using the gene-editing tool CRISPR-Cas9.
Genes contain the information our bodies need to create proteins. Highly similar proteins produced from the same gene are called isoforms. Different isoforms generate ...
Recent advances in mushroom research
2023-04-10
So, mushroom-zombies recently took over a fictional world, but in real life, they’re really not so scary. These fungi range in shape from broad, plate-like portobellos and gangly enokis to a version resembling a giant, shaggy lion’s mane. And now scientists are finding ways to grow mushrooms on new materials, as well as incorporate them in more sustainable products. Below are some recent papers published in ACS journals that report insights into additional applications for mushrooms. Reporters can request free access to these ...
Giant, swimming mouths: Oral dimensions of extant sharks do not accurately predict body size in Dunkleosteus terrelli (Placodermi: Arthrodira)
2023-04-10
A new study by Case Western Reserve University PhD student Russell Engelman published in PeerJ Life & Environment attempts to address a persistent problem in paleontology – what were the size of Dunkleosteus and other late Devonian arthrodire placoderms. Arthrodire placoderms are extinct fishes with had armor covering their head and part of their torso, but like sharks the rest of their skeleton was made of cartilage, meaning most of their body did not preserve when they became fossilized.
Previous size estimates for Dunkleosteus were ...
Scheduled childbirth may greatly reduce preeclampsia, a leading cause of maternal death
2023-04-10
Research Highlights:
Analysis found that more than half of preeclampsia cases that occur during weeks 37-42 of pregnancy (called at-term preeclampsia) may be prevented with timed birth, such as a scheduled induction or Cesarean delivery.
Planned labor inductions and Cesarean deliveries are already widely practiced for a range of reasons, however, they are seldom considered as an intervention to prevent at-term preeclampsia, which may be life-threatening.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Monday, April 10, 2023
DALLAS, April ...
Non-biological factors and social determinants of health important in women’s CVD risk assessment
2023-04-10
Statement Highlights:
A new American Heart Association scientific statement reviews research about racial and ethnic differences in cardiovascular risk factors among women in the U.S.
In addition to traditional risk factors, women of underrepresented races or ethnicities experience challenges in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular conditions due to language barriers, discrimination, difficulties in acculturation or assimilation, lack of financial resources or health insurance, or lack of access to health care.
Women of racial and ethnic backgrounds other than white have been underrepresented ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] New textile unravels warmth-trapping secrets of polar bear furTeam of UMass Amherst engineers invents bilayered fabric, 30% lighter than cotton and far warmer