(Press-News.org) About The Study: The largest increase in children’s recreational screen time during the pandemic was on weekdays, especially at the outset of the pandemic when schools were closed; this increase was greater than expected for age-related growth. Change in weekend screen time during the pandemic was not significant compared with weekday screen time. Once in-person school resumed, weekday screen time decreased versus that during the COVID-1 wave (spring 2020), although it remained consistently higher than pre-pandemic estimates and age-related expectations.
Authors: Sheri Madigan, Ph.D., of the University of Calgary in Calgary, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.0393)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapediatrics/fullarticle/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.0393?guestAccessKey=d7164bc1-af26-4db7-afcc-fb8683699e44&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=041023
END
Changes in children’s screen time during pandemic
JAMA Pediatrics
2023-04-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study: Shutting down nuclear power could increase air pollution
2023-04-10
Nearly 20 percent of today’s electricity in the United States comes from nuclear power. The U.S. has the largest nuclear fleet in the world, with 92 reactors scattered around the country. Many of these power plants have run for more than half a century and are approaching the end of their expected lifetimes.
Policymakers are debating whether to retire the aging reactors or reinforce their structures to continue producing nuclear energy, which many consider a low-carbon alternative to climate-warming coal, oil, and natural gas.
Now, MIT researchers say there’s another factor to consider in weighing the future of nuclear power: ...
Study shows involuntary displacement of people experiencing homelessness may cause significant spikes in mortality, overdoses and hospitalizations
2023-04-10
AURORA, Colo. (April 10, 2023) – Involuntary displacement of people experiencing homelessness will likely lead to a substantial increase in morbidity and mortality over a 10-year period.
In a study, published today in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), researchers say practices such as encampment sweeps, bans, move-along-orders and cleanups that forcibly relocate individuals away from essential services will lead to substantial increases in overdose deaths, life threatening infections and hospitalizations.
In coordination with the National Healthcare for Homeless Council, the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the National Foundation ...
Protein Beclin-1 is a major player in uterine remodeling and the establishment of pregnancy
2023-04-10
Throughout a woman's reproductive life, the endometrium, the mucous membrane lining the uterus, goes through cyclical remodeling. It thickens during the menstrual cycle in preparation for embryo implantation, and it is shed during menstruation when there is no fertilization.
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and collaborating institutions are investigating little-known factors directing uterine remodeling to advance the understanding of this process and provide new insights into fertility-associated gynecological conditions. They report today in the journal Developmental ...
Scientists map gusty winds in a far-off neutron star system
2023-04-10
An accretion disk is a colossal whirlpool of gas and dust that gathers around a black hole or a neutron star like cotton candy as it pulls in material from a nearby star. As the disk spins, it whips up powerful winds that push and pull on the sprawling, rotating plasma. These massive outflows can affect the surroundings of black holes by heating and blowing away the gas and dust around them.
At immense scales, “disk winds” can offer clues to how supermassive black holes shape entire galaxies. Astronomers have observed signs of disk winds in many systems, ...
Health effects of involuntary displacement of homeless individuals who inject drugs
2023-04-10
About The Study: This simulation modeling study of 23 U.S. cities projects that involuntary displacement of people experiencing homelessness who inject drugs may yield substantial increases in morbidity and mortality over a 10-year period. Involuntary displacement is estimated to worsen overdose and hospitalizations, decrease initiations of medications for opioid use disorder, and contribute to deaths. These findings have implications for the practice of involuntary displacement, as well as policies such as access to housing and supportive services, that could mitigate these harms.
Authors: Joshua A. Barocas, M.D., ...
Bariatric surgery may reverse diabetes complications for people with obesity
2023-04-10
For more than 100 million Americans who are obese, bariatric surgery may reverse complications related to diabetes, including regenerating damaged nerves, a Michigan Medicine study shows.
A research team led by the University of Michigan Health Department of Neurology followed more than 120 patients who underwent bariatric surgery for obesity over two years after the procedure. They found that all metabolic risk factors for developing diabetes, such as high glucose and lipid levels, improved outside of blood pressure and total cholesterol, according to results published in Diabetologia.
Investigators ...
What is it good for? Absolutely one thing. Luna moths use their tails solely for bat evasion
2023-04-10
In a pair of complementary studies, researchers took a close look at Luna moth (Actias luna) tails through the eyes of birds and female moths to test the tails’ role in predation and sexual selection. Scientists have known for about a decade that Luna moths — and other related silkmoths — use their long, trailing tails to misdirect bat attacks.
“They have projections off the back of the hindwing that end in twisted, cupped paddles,” said Juliette Rubin, a doctoral student at the Florida Museum ...
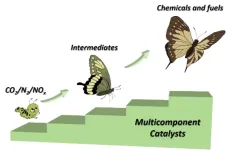
Breaking inert bonds: Multicomponent catalysts pave the way for green chemistry and green carbon science
2023-04-10
The chemical industry has played a significant role in the development of society, but its impact on the environment has become a growing concern. Green chemistry and chemical engineering have opened up possibilities for sustainability through the transformation of renewable feedstocks into environmentally friendly chemicals. However, the inert bonds in molecules such as CO2 and N2 present challenges to their activation and conversion.
Electrochemical conversion provides a promising carbon-neutral route to upgrading green chemical sources with inert bonds to chemicals and fuels under ambient conditions. Multicomponent electrocatalysts have advantages over monocomponent catalysts, ...
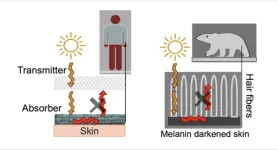
New textile unravels warmth-trapping secrets of polar bear fur
2023-04-10
AMHERST, Mass. – Three engineers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst have invented a fabric that concludes the 80-year quest to make a synthetic textile modeled on Polar bear fur. The results, published recently in the journal ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, are already being developed into commercially available products.
Polar bears live in some of the harshest conditions on earth, shrugging off Arctic temperatures as low as -50 Fahrenheit. While the bears have many adaptations that allow them to thrive when the temperature plummets, since the 1940s scientists have focused on one in particular: their fur. How, the scientific community ...
Navigating the cosmos with Georgia State’s CHARA Array
2023-04-10
ATLANTA—Plans are underway to add a seventh movable telescope to Georgia State University’s Center for High Angular Resolution Astronomy— known as the CHARA Array—that would increase the resolution, or the ability to see small objects, by a factor of three.
Located at Mount Wilson Observatory in Southern California and operated by Georgia State, the new telescope will be connected using fiber optics to transport the starlight, a technique that will serve as a pathfinder ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
[Press-News.org] Changes in children’s screen time during pandemicJAMA Pediatrics