(Press-News.org) Insilico Medicine (“Insilico”), a clinical-stage generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven drug discovery company, today announced that it has successfully discovered a potent, selective, and orally bioavailable small molecule inhibitor of CDK8 for the treatment of cancer using a structure-based generative chemistry approach enabled by the Chemistry42 multi-modal generative reinforcement learning platform. The research was published in the American Chemical Society’s Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, a leading journal in medicinal chemistry.
As members of the CDK family, CDK8 and its paralog protein CDK19 play critical roles in regulating transcription of many different signaling pathways involved in oncogenic control. Deregulation of CDK8/19 has been implicated as a driving force in many human cancers, particularly in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and advanced solid tumors. Moreover, CDK8/19 is also involved in immune modulation. Targeting CDK8/19 could enhance NK cell cytotoxicity and stimulate NK cell-mediated tumor surveillance. Therefore, targeting CDK8/19 is regarded as a promising strategy with a two-in-one mechanism of action that not only inhibits tumor cell growth, but also increases immune cell activity.
The research published by Insilico was supported by its generative chemistry engine, Chemistry42, which is built on years of modeling and pre-training of large biological, chemical and textual datasets. Chemistry42 includes 42 generative engines and more than 500 predictive engines for scoring which allows researchers to generate molecules with desired properties from scratch using deep learning technologies through structure-based drug design (SBDD) and ligand-based drug design (LBDD).
In this study, scientists described the process of using the SBDD module of Chemistry42 to generate a key anchor linker and identify the hit compound targeting CDK8. Over several optimization cycles, R&D scientists further improved in vitro metabolic stability, kinase selectivity, and in vivo pharmacokinetic profile cross-species, leading to the discovery of one potent, selective, and orally bioavailable inhibitor of CDK8, which was evaluated in in vivo efficacy studies and demonstrated robust tumor growth inhibition in multiple in vivo efficacy models.
In addition to the published molecule, Insilico scientists are progressing with another AI-generated CDK8 inhibitor with a novel structure. Insilico is open to potential partnerships with pharmaceutical companies to co-develop the drug candidate.
“At Insilico, we encourage scientists to share their innovative insights in AI-driven drug discovery with the industry by publishing peer-reviewed papers,” said Feng Ren, PhD, Co-CEO and Chief Scientific Officer of Insilico Medicine. “In this case, we have not only discovered a novel compound for a promising target, but also provided innovative practices in early drug discovery supported by generative AI.”
Insilico has pioneered applying multiple generative approaches for drug design in both generative chemistry and generative biology and published the first paper in generative chemistry. The company then submitted the relevant patents on applying these generative approaches for chemistry and biology, and integrated these approaches into the commercially available Pharma.AI platform, which includes PandaOmics™ a system utilizing multiple predictive and generative biology models; a generative chemistry engine, Chemistry42™; and a clinical trial outcomes prediction engine InClinico™, which utilizes a combination of omics-based predictors and text-based transformers. Powered by generative AI, Insilico is delivering breakthroughs for healthcare in multiple disease areas. The lead program targeting fibrosis-driven diseases has completed Phase 0 and Phase I clinical trials and received positive Phase I topline data and Orphan Drug Designation.
“We described the concept of using generative AI for the design of novel molecules in a peer-reviewed journal in 2016 for the first time. Later, we developed multiple approaches and new features for our GAN-based AI platform for drug design. We also started patenting our findings so that ,in some areas, patents preceded publications. Some of my favorite patents combine generative chemistry and generative biology,” said Alex Zhavoronkov, PhD, Founder and CEO of Insilico Medicine. “I am excited to see that with the support of generative AI, we have achieved several industry milestones and advanced the drug candidates discovered by generative AI to the clinical stage. In 2022 alone, we nominated 9 preclinical candidates utilizing generative AI. We are committed to refining our approach and tools to reshape the future of healthcare by generative innovation.”
About Insilico Medicine
Insilico Medicine, a clinical-stage generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven drug discovery company, is connecting biology, chemistry, and clinical trials analysis using next-generation AI systems. The company has developed AI platforms that utilize deep generative models, reinforcement learning, transformers, and other modern machine learning techniques for novel target discovery and the generation of novel molecular structures with desired properties. Insilico Medicine is developing breakthrough solutions to discover and develop innovative drugs for cancer, fibrosis, immunity, central nervous system diseases, infectious diseases, autoimmune diseases, and aging-related diseases. www.insilico.com
END
Insilico Medicine successfully discovered potent, selective, and orally bioavailable small-molecule inhibitor of CDK8 using generative AI
2023-04-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
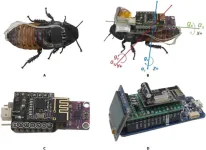
Movement optimization for a cyborg cockroach in a bounded space incorporating machine learning
2023-04-12
Have you ever wondered why some insects like cockroaches prefer to stay or decrease movement in darkness? Some may tell you it’s called photophobia, a habit deeply coded in their genes. A further question would be whether we can correct this habit of cockroaches, that is, moving in the darkness just as they move in bright backgrounds. Scientists from Osaka University may have answered this question with a positive answer. They solved this question by converting a cockroach into a cyborg. They published this research in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems. ...
SwRI joins new NASA institute to qualify, certify additive manufacturing methods
2023-04-12
SAN ANTONIO — April 12, 2023—Southwest Research Institute will contribute to a new NASA institute to improve understanding and enable rapid certification of metal parts created using advanced additive manufacturing (AM) techniques. The Institute for Model-based Qualification & Certification of Additive Manufacturing (IMQCAM) will work to improve computer models of additively manufactured metal parts and expand their utility in spaceflight applications.
Additive manufacturing uses 3D printing or rapid prototyping to build ...
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center experts to present noteworthy research at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) 2023 Annual Meeting
2023-04-12
Physicians and scientists from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK) will join oncology experts and members of the global cancer research community to present the latest advances in cancer during the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting on April 14-19 in Orlando, Florida.
MSK experts will present significant research and will be available to comment on topics including cancer disparities, analytical tools for precision medicine, genomic biomarkers, tumor biology, immunology and more.
Deb Schrag, MD, MPH, will offer insights ...
Noted MS neurologist Dr. Roland Martin wins 2023 John Dystel Prize for Multiple Sclerosis Research
2023-04-12
Roland Martin, MD, a world-class neurologist and investigator, is the winner of the 2023 John Dystel Prize for MS Research. He is being honored for advancing our understanding of immune mechanisms underlying multiple sclerosis and translating them to develop innovative strategies to treat the disease.
Martin uncovered how key MS susceptibility genes are involved in launching immune attacks on the nervous system and identified specific components of nerve-insulating myelin that are targeted by those attacks. His team has developed an experimental therapy designed to make ...
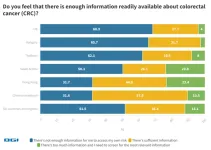
62 percent of Thais lack sufficient colorectal cancer awareness | BGI Insight
2023-04-12
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the fourth most common cancer and accounts for 11% of the cancer burden in Thailand in 2020, with over 21,000 new CRC cases annually, and stage III and IV CRC account for up to 70%–80% of overall CRC cases, according to the Society of Colorectal Surgeons of Thailand.
This report indicates Thailand has a high percentage of respondents (62.1%) who feel they lack CRC information to assess their risk, far higher than global average of 51.5%. In addition, 48.2% of Thais say that cost concerns are holding them back from CRC screening, way higher than global average of ...
Millions with opioid addiction don't receive residential treatment
2023-04-12
First study to do apples-to-apples comparison of residential treatment use among Medicaid enrollees across several states
Nine states represent 14.9 million people (20% of all Medicaid enrollees)
CHICAGO --- Approximately 7 million adults in the U.S. are living with opioid use disorder (OUD). Yet a new Northwestern Medicine study that measured residential treatment use among Medicaid enrollees across nine states found only 7% of enrollees with OUD received residential treatment, an integral part of the recovery process ...
Looking to boost revenue as an online retailer? Charge an upfront membership fee in exchange for unlimited free shipping
2023-04-12
Researchers from NC State University and Texas A&M University published a new Journal of Marketing article that examines membership fee shipping programs and the effect on consumers’ purchase behaviors and company net revenue.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “The Effectiveness of Membership-Based Free Shipping: An Empirical Investigation of Consumers’ Purchase Behaviors and Revenue Contribution” and is authored by Fangfei Guo and Yan Liu.
What is the top reason 50% of customers abandon items in online shopping carts? Why do e-commerce brands incur an annual revenue loss of about ...
Toward a safer ‘artificial muscle’ material
2023-04-12
Whether wriggling your toes or lifting groceries, muscles in your body smoothly expand and contract. Some polymers can do the same thing — acting like artificial muscles — but only when stimulated by dangerously high voltages. Now, researchers in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces report a series of thin, elastic films that respond to substantially lower electrical charges. The materials represent a step toward artificial muscles that could someday operate safely in medical devices.
Artificial muscles could become key components of movable soft robotic implants and functional artificial organs. Electroactive elastomers, such as bottlebrush polymers, are attractive ...
Testing vaccine candidates quickly with lab-grown mini-organs
2023-04-12
Developing and testing new treatments or vaccines for humans almost always requires animal trials, but these experiments can sometimes take years to complete and can raise ethical concerns about the animals’ treatment. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Central Science have developed a new testing platform that encapsulates B cells — some of the most important components of the immune system — into miniature “organoids” to make vaccine screening quicker and greatly reduce the number of animals needed.
Vaccines ...
Your fork could someday be made of sugar, wood powders and degrade on-demand (video)
2023-04-12
Single-use hard plastics are all around us: utensils, party decorations and food containers, to name a few examples. These items pile up in landfills, and many biodegradable versions stick around for months, requiring industrial composting systems to fully degrade. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering have created a sturdy, lightweight material that disintegrates on-demand — and they made it from sugar and wood-derived powders. Watch a video about the material here.
Sturdy, degradable materials made from plants and other non-petroleum sources have come ...