(Press-News.org) Whether wriggling your toes or lifting groceries, muscles in your body smoothly expand and contract. Some polymers can do the same thing — acting like artificial muscles — but only when stimulated by dangerously high voltages. Now, researchers in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces report a series of thin, elastic films that respond to substantially lower electrical charges. The materials represent a step toward artificial muscles that could someday operate safely in medical devices.
Artificial muscles could become key components of movable soft robotic implants and functional artificial organs. Electroactive elastomers, such as bottlebrush polymers, are attractive materials for this purpose because they start soft but stiffen when stretched. And they can change shape when electrically charged. However, currently available bottlebrush polymer films only move at voltages over 4,000 V, which exceeds the 50 V maximum that the U.S. Occupational Safety & Health Administration states is safe. Reducing the thickness of these films to less than 100 µm could lower the required voltages, but this hasn’t been done successfully yet for bottlebrush polymers. So, Dorina Opris and colleagues wanted to find a simple way to produce thinner films.
The researchers synthesized a suite of bottlebrush polymers by reacting norbornene-grafted polydimethylsiloxane macromonomers and cross-linking the products by ultraviolet light. A 60-µm-thick material was the most electroactive, expanding more than previously reported elastomers, with an operating voltage of 1,000 V. And a circular actuator made out of that material expanded and contracted more than 10,000 times before degrading. In another set of experiments, the researchers introduced polar side chains to the polymers and produced materials that responded to voltages as low as 800 V. However, they didn’t expand as much as the team’s most electroactive film. Based on the results, the researchers say that, with some tweaks, the material could someday be used to develop durable implants and other medical devices that work at safer voltages.
The authors acknowledge funding from the European Research Council under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program, the Swiss National Science Foundation, the Swiss Federal Laboratories for Materials Science and Technology and the China Scholarship Council.
The paper’s abstract will be available on April 12 at 8 a.m. Eastern time here: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsami.2c23026
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
END
Toward a safer ‘artificial muscle’ material
2023-04-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Testing vaccine candidates quickly with lab-grown mini-organs
2023-04-12
Developing and testing new treatments or vaccines for humans almost always requires animal trials, but these experiments can sometimes take years to complete and can raise ethical concerns about the animals’ treatment. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Central Science have developed a new testing platform that encapsulates B cells — some of the most important components of the immune system — into miniature “organoids” to make vaccine screening quicker and greatly reduce the number of animals needed.
Vaccines ...
Your fork could someday be made of sugar, wood powders and degrade on-demand (video)
2023-04-12
Single-use hard plastics are all around us: utensils, party decorations and food containers, to name a few examples. These items pile up in landfills, and many biodegradable versions stick around for months, requiring industrial composting systems to fully degrade. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering have created a sturdy, lightweight material that disintegrates on-demand — and they made it from sugar and wood-derived powders. Watch a video about the material here.
Sturdy, degradable materials made from plants and other non-petroleum sources have come ...
Sugar molecule in blood can predict Alzheimer’s disease
2023-04-12
Early diagnosis and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease requires reliable and cost-effective screening methods. Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have now discovered that a type of sugar molecule in blood is associated with the level of tau, a protein that plays a critical role in the development of severe dementia. The study, which is published in Alzheimer's & Dementia, can pave the way for a simple screening procedure able to predict onset ten years in advance.
“The role of glycans, ...
Starting small and simple - key to success for evolution of mammals
2023-04-12
The ancestors of modern mammals managed to evolve into one of the most successful animal lineages – the key was to start out small and simple, a new study reveals.
In many vertebrate groups, such as fishes and reptiles, the skull and lower jaw of animals with a backbone are composed of numerous bones. This was also the case in the earliest ancestors of modern mammals over 300 million years ago.
However, during evolution the number of skull bones was successively reduced in early mammals around 150 to 100 million years ago.
Publishing their findings today ...
New “AI scientist” combines theory and data to discover scientific equations
2023-04-12
In 1918, the American chemist Irving Langmuir published a paper examining the behavior of gas molecules sticking to a solid surface. Guided by the results of careful experiments, as well as his theory that solids offer discrete sites for the gas molecules to fill, he worked out a series of equations that describe how much gas will stick, given the pressure.
Now, about a hundred years later, an “AI scientist” developed by researchers at IBM Research, Samsung AI, and the University of Maryland, Baltimore County (UMBC) has reproduced a key part of Langmuir’s Nobel Prize-winning work. The system—artificial intelligence ...
When cells sense the cue for growth
2023-04-12
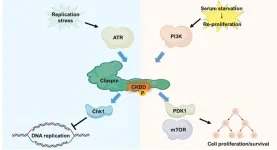
Researchers of the Genome Dynamics Project team at Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Medical Science ·revealed new mechanism controlling cellular proliferation in response to serum, which triggers growth of resting cells.
One of the key pathways for cellular growth is the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) –mTOR (mechanistic/mammalian target of rapamycin) pathway. mTOR regulates the cellular response to nutrient availability. Dysregulation of the mTOR signaling pathway is intimately involved in many human diseases, especially the multitude of different human cancers. This ...
Most plastic eaten by city vultures comes straight from food outlets
2023-04-12
Since the 1950s, humanity has produced an estimated 8.3bn tons of plastic, adding a further 380m tons to this amount each year. Only 9% of this gets recycled. The inevitable result is that plastic is everywhere, from the depths of the oceans to the summit of Everest – and notoriously, inside the tissues of humans and other organisms.
The long-term effects of ingested plastic on people aren’t yet known. But in rodents, ingested microplastics can impair the function of the liver, intestines, and exocrine and reproductive organs.
Especially ...
To more effectively sequester biomass and carbon, just add salt
2023-04-12
Reducing global greenhouse gas emissions is critical to avoiding a climate disaster, but current carbon removal methods are proving to be inadequate and costly. Now researchers from the University of California, Berkeley, have proposed a scalable solution that uses simple, inexpensive technologies to remove carbon from our atmosphere and safely store it for thousands of years.
As reported today in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, researchers propose growing biomass crops to capture carbon from the air, then burying the harvested vegetation in engineered dry biolandfills. This ...
How to cool your brain? These warm-blooded animals use their nose
2023-04-12
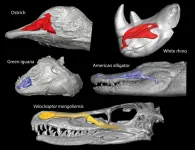
A research team led by Seishiro Tada and Takanobu Tsuihiji of the University of Tokyo shows that the living warm-blooded descendants of theropod dinosaurs evolved a better nasal cooling system aided by larger nasal cavities than cold-blooded animals. The study provides clues to the evolution of nasal cooling in warm-blooded animals from their theropod dinosaur ancestors.
Endotherms, or warm-blooded animals, maintain their high body temperature through internal heat sources. Birds, humans, and other mammals are endotherms. But ectotherms, or cold-blooded animals such as reptiles, use external heat sources to keep ...
It’s all in the wrist: energy-efficient robot hand learns how not to drop the ball
2023-04-12
Researchers have designed a low-cost, energy-efficient robotic hand that can grasp a range of objects – and not drop them – using just the movement of its wrist and the feeling in its ‘skin’.
Grasping objects of different sizes, shapes and textures is a problem that is easy for a human, but challenging for a robot. Researchers from the University of Cambridge designed a soft, 3D printed robotic hand that cannot independently move its fingers but can still carry out a range of complex movements.
The robot hand was trained to ...